In distributed computing, a remote procedure call (RPC) is when a computer program causes a procedure (subroutine) to execute in a different address space, which is coded as if it were a normal (local) procedure call, without the programmer explicitly coding the details for the remote interaction. That is, the programmer writes essentially the same code whether the subroutine is local to the executing program, or remote. This is a form of client–server interaction, typically implemented via a request–response message-passing system. In the object-oriented programming paradigm, RPC calls are represented by remote method invocation (RMI). The RPC model implies a level of location transparency, namely that calling procedures is largely the same whether it is local or remote, but usually they are not identical, so local calls can be distinguished from remote calls. Remote calls are usually orders of magnitude slower and less reliable than local calls, so distinguishing them is important.
An instruction set architecture (ISA) is an abstract model of a computer. It is also referred to as architecture or computer architecture. A realization of an ISA is called an implementation. An ISA permits multiple implementations that may vary in performance, physical size, and monetary cost ; because the ISA serves as the interface between software and hardware. Software that has been written for an ISA can run on different implementations of the same ISA. This has enabled binary compatibility between different generations of computers to be easily achieved, and the development of computer families. Both of these developments have helped to lower the cost of computers and to increase their applicability. For these reasons, the ISA is one of the most important abstractions in computing today.
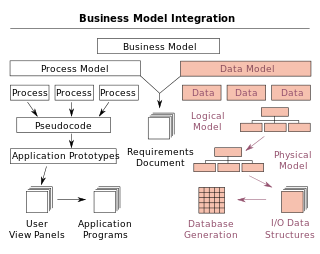
A data model is an abstract model that organizes elements of data and standardizes how they relate to one another and to properties of the real world entities. For instance, a data model may specify that the data element representing a car be composed of a number of other elements which, in turn, represent the color and size of the car and define its owner.

The spiral model is a risk-driven software development process model. Based on the unique risk patterns of a given project, the spiral model guides a team to adopt elements of one or more process models, such as incremental, waterfall, or evolutionary prototyping.
The Java Community Process (JCP), established in 1998, is a formalized mechanism that allows interested parties to develop standard technical specifications for Java technology. Anyone can become a JCP Member by filling a form available at the JCP website. JCP membership for organizations and commercial entities requires annual fees – but is free for individuals.

Audio editing software is software which allows editing and generating of audio data. Audio editing software can be implemented completely or partly as library, as computer application, as Web application or as a loadable kernel module. Wave Editors are digital audio editors and there are many sources of software available to perform this function. Most can edit music, apply effects and filters, adjust stereo channels etc.

PROFIBUS is a standard for fieldbus communication in automation technology and was first promoted in 1989 by BMBF and then used by Siemens. It should not be confused with the PROFINET standard for Industrial Ethernet.
PROFIBUS is openly published as part of IEC 61158.

Engineering tolerance is the permissible limit or limits of variation in:
- a physical dimension;
- a measured value or physical property of a material, manufactured object, system, or service;
- other measured values ;
- in engineering and safety, a physical distance or space (tolerance), as in a truck (lorry), train or boat under a bridge as well as a train in a tunnel ;
- in mechanical engineering the space between a bolt and a nut or a hole, etc.
CONFIG.SYS is the primary configuration file for the DOS and OS/2 operating systems. It is a special ASCII text file that contains user-accessible setup or configuration directives evaluated by the operating system during boot. CONFIG.SYS was introduced with DOS 2.0.
A memory barrier, also known as a membar, memory fence or fence instruction, is a type of barrier instruction that causes a central processing unit (CPU) or compiler to enforce an ordering constraint on memory operations issued before and after the barrier instruction. This typically means that operations issued prior to the barrier are guaranteed to be performed before operations issued after the barrier.
Apache Cocoon, usually just called Cocoon, is a web application framework built around the concepts of pipeline, separation of concerns and component-based web development. The framework focuses on XML and XSLT publishing and is built using the Java programming language. The flexibility afforded by relying heavily on XML allows rapid content publishing in a variety of formats including HTML, PDF, and WML. The content management systems Apache Lenya and Daisy have been created on top of the framework. Cocoon is also commonly used as a data warehousing ETL tool or as middleware for transporting data between systems.
ISO/IEC 15504 Information technology – Process assessment, also termed Software Process Improvement and Capability Determination (SPICE), is a set of technical standards documents for the computer software development process and related business management functions. It is one of the joint International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standards, which was developed by the ISO and IEC joint subcommittee, ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 7.
Signals are a limited form of inter-process communication (IPC), typically used in Unix, Unix-like, and other POSIX-compliant operating systems. A signal is an asynchronous notification sent to a process or to a specific thread within the same process in order to notify it of an event that occurred. Signals originated in 1970s Bell Labs Unix and have been more recently specified in the POSIX standard.
The thermal design power (TDP), sometimes called thermal design point, is the maximum amount of heat generated by a computer chip or component that the cooling system in a computer is designed to dissipate under any workload.
The standard Unix command who displays a list of users who are currently logged into the computer.

Object Process Methodology (OPM) is a conceptual modeling language and methodology for capturing knowledge and designing systems, specified as ISO/PAS 19450. Based on a minimal universal ontology of stateful objects and processes that transform them, OPM can be used to formally specify the function, structure, and behavior of artificial and natural systems in a large variety of domains.
The Process Specification Language (PSL) is a set of logic terms used to describe processes. The logic terms are specified in an ontology that provides a formal description of the components and their relationships that make up a process. The ontology was developed at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), and has been approved as an international standard in the document ISO 18629.
Surface finish, also known as surface texture or surface topography, is the nature of a surface as defined by the three characteristics of lay, surface roughness, and waviness. It comprises the small, local deviations of a surface from the perfectly flat ideal.
A specification often refers to a set of documented requirements to be satisfied by a material, design, product, or service. A specification is often a type of technical standard.
ISO 860 Terminology work – Harmonization of concepts and terms is an ISO standard that deals with the principles which are the basis upon which concept systems can be harmonized and with the development of harmonized terminologies, in order to improve the efficiency in interlinguistic communication.

![]()







