
An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The swelling may feel fluid-filled when pressed. The area of redness often extends beyond the swelling. Carbuncles and boils are types of abscess that often involve hair follicles, with carbuncles being larger.

A first aid kit is a collection of supplies and equipment that is used to give medical treatment. There is a wide variation in the contents of first aid kits based on the knowledge and experience of those putting it together, the differing first aid requirements of the area where it may be used, and variations in legislation or regulation in a given area.
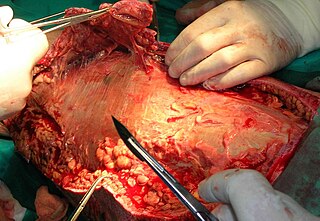
Debridement is the medical removal of dead, damaged, or infected tissue to improve the healing potential of the remaining healthy tissue. Removal may be surgical, mechanical, chemical, autolytic (self-digestion), and by maggot therapy.

Skin grafting, a type of graft surgery, involves the transplantation of skin. The transplanted tissue is called a skin graft.

A surgical instrument is a specialized tool or device, typically made of surgical steel, used during surgery to clamp, cut, dissect, retract, or otherwise manipulate and/or modify biological tissue.

A peripherally inserted central catheter, less commonly called a percutaneous indwelling central catheter, is a form of intravenous access that can be used for a prolonged period of time or for administration of substances that should not be done peripherally. It is a catheter that enters the body through the skin (percutaneously) at a peripheral site, extends to the superior vena cava, and stays in place for days or weeks.
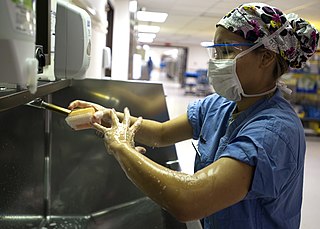
Asepsis is the state of being free from disease-causing micro-organisms. There are two categories of asepsis: medical and surgical. The modern day notion of asepsis is derived from the older antiseptic techniques, a shift initiated by different individuals in the 19th century who introduced practices such as the sterilizing of surgical tools and the wearing of surgical gloves during operations. The goal of asepsis is to eliminate infection, not to achieve sterility. Ideally, a surgical field is sterile, meaning it is free of all biological contaminants, not just those that can cause disease, putrefaction, or fermentation. Even in an aseptic state, a condition of sterile inflammation may develop. The term often refers to those practices used to promote or induce asepsis in an operative field of surgery or medicine to prevent infection.

A dental extraction is the removal of teeth from the dental alveolus (socket) in the alveolar bone. Extractions are performed for a wide variety of reasons, but most commonly to remove teeth which have become unrestorable through tooth decay, periodontal disease, or dental trauma, especially when they are associated with toothache. Sometimes impacted wisdom teeth cause recurrent infections of the gum (pericoronitis), and may be removed when other conservative treatments have failed. In orthodontics, if the teeth are crowded, healthy teeth may be extracted to create space so the rest of the teeth can be straightened.
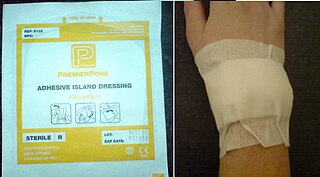
A dressing is a sterile pad or compress applied to a wound to promote healing and protect the wound from further harm. A dressing is designed to be in direct contact with the wound, as distinguished from a bandage, which is most often used to hold a dressing in place. Many modern dressings are self-adhesive.

Gossypiboma, textiloma or more broadly Retained Foreign Object (RFO) is the technical term for surgical complications resulting from foreign materials, such as a surgical sponge, accidentally left inside a patient's body.
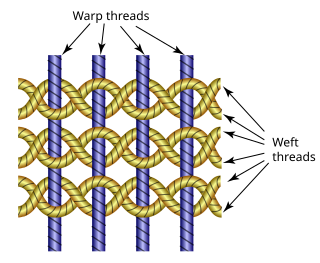
Gauze is a thin, translucent fabric with a loose open weave. In technical terms "gauze" is a weave structure in which the weft yarns are arranged in pairs and are crossed before and after each warp yarn keeping the weft firmly in place. This weave structure is used to add stability to fabric, which is important when using fine yarns loosely spaced. However, this weave structure can be used with any weight of yarn, and can be seen in some rustic textiles made from coarse hand-spun plant fiber yarns. Gauze is widely used for medical dressings.
The history of wound care spans from prehistory to modern medicine. Wounds naturally heal by themselves, but hunter-gatherers would have noticed several factors and certain herbal remedies would speed up or assist the process, especially if it was grievous. In ancient history, this was followed by the realisation of the necessity of hygiene and the halting of bleeding, where wound dressing techniques and surgery developed. Eventually the germ theory of disease also assisted in improving wound care.

Veterinary surgery is surgery performed on animals by veterinarians, whereby the procedures fall into three broad categories: orthopaedics, soft tissue surgery, and neurosurgery. Advanced surgical procedures such as joint replacement, fracture repair, stabilization of cranial cruciate ligament deficiency, oncologic (cancer) surgery, herniated disc treatment, complicated gastrointestinal or urogenital procedures, kidney transplant, skin grafts, complicated wound management, and minimally invasive procedures are performed by veterinary surgeons. Most general practice veterinarians perform routine surgeries such as neuters and minor mass excisions; some also perform additional procedures.

Negative-pressure wound therapy (NPWT), also known as a vacuum assisted closure (VAC), is a therapeutic technique using a suction pump, tubing and a dressing to remove excess exudate and promote healing in acute or chronic wounds and second- and third-degree burns. The therapy involves the controlled application of subatmospheric pressure to the local wound environment, using a sealed wound dressing connected to a vacuum pump. The use of this technique in wound management increased dramatically over the 1990s and 2000s and a large number of studies have been published examining NPWT. NPWT has many indications for use including:
Incision and drainage and clinical lancing are minor surgical procedures to release pus or pressure built up under the skin, such as from an abscess, boil, or infected paranasal sinus. It is performed by treating the area with an antiseptic, such as iodine-based solution, and then making a small incision to puncture the skin using a sterile instrument such as a sharp needle, a pointed scalpel or a lancet. This allows the pus fluid to escape by draining out through the incision.

Surgical suture is a medical device used to hold body tissues together after an injury or surgery. Application generally involves using a needle with an attached length of thread. A number of different shapes, sizes, and thread materials have been developed over its millennia of history. Surgeons, physicians, dentists, podiatrists, eye doctors, registered nurses and other trained nursing personnel, medics, clinical pharmacists and veterinarians typically engage in suturing. Surgical knots are used to secure the sutures.

Scrubs are the sanitary clothing worn by physicians, nurses, and other workers involved in patient care in hospitals. Originally designed for use by surgeons and other operating room personnel, who would put them on when sterilizing themselves, or "scrubbing in", before surgery, they are now worn by many hospital personnel.

Wound closure strips are porous surgical tape strips which can be used to close small wounds. They are applied across the laceration in a manner which pulls the skin on either side of the wound together. Wound closure strips may be used instead of sutures (stitches) in some injuries, because they lessen scarring and are easier to care for.
A retained surgical instrument is any item inadvertently left behind in a patient’s body in the course of surgery. There are few books about it and it is thought to be underreported. As a preventable medical error, it occurs more frequently than "wrong site" surgery. The consequences of retained surgical tools include injury, repeated surgery, excess monetary cost, loss of hospital credibility and in some cases the death of the patient.
A cyst is a pathological epithelial lined cavity that fills with fluid or soft material and usually grows from internal pressure generated by fluid being drawn into the cavity from osmosis. The bones of the jaws, the mandible and maxilla, are the bones with the highest prevalence of cysts in the human body. This is due to the abundant amount of epithelial remnants that can be left in the bones of the jaws. The enamel of teeth is formed from ectoderm, and so remnants of epithelium can be left in the bone during odontogenesis. The bones of the jaws develop from embryologic processes which fuse together, and ectodermal tissue may be trapped along the lines of this fusion. This "resting" epithelium is usually dormant or undergoes atrophy, but, when stimulated, may form a cyst. The reasons why resting epithelium may proliferate and undergo cystic transformation are generally unknown, but inflammation is thought to be a major factor. The high prevalence of tooth impactions and dental infections that occur in the bones of the jaws is also significant to explain why cysts are more common at these sites.
















