
The Great Rift Valley is a series of contiguous geographic depressions, approximately 6000 or 7,000 kilometres (4,300 mi) in total length, the definition varying between sources, that runs from the southern Turkish Hatay Province in Asia, through the Red Sea, to Mozambique in Southeast Africa. While the name continues in some usages, it is rarely used in geology as it is considered an imprecise merging of separate though related rift and fault systems.
A massif is a principal mountain mass, such as a compact portion of a mountain range, containing one or more summits. In mountaineering literature, a massif is frequently used to denote the main mass of an individual mountain.

Mount Kenya is an extinct volcano in Kenya and the second-highest peak in Africa, after Kilimanjaro. The highest peaks of the mountain are Batian, Nelion and Point Lenana. Mount Kenya is located in the former Eastern and Central provinces of Kenya; its peak is now the intersection of Meru, Embu, Kirinyaga, Nyeri and Tharaka Nithi counties, about 16.5 kilometres south of the equator, around 150 km (90 mi) north-northeast of the capital Nairobi. Mount Kenya is the source of the name of the Republic of Kenya.

The Blue Ridge Mountains are a physiographic province of the larger Appalachian Highlands range. The mountain range is located in the Eastern United States and extends 550 miles southwest from southern Pennsylvania through Maryland, West Virginia, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee, and Georgia. The province consists of northern and southern physiographic regions, which divide near the Roanoke River gap. To the west of the Blue Ridge, between it and the bulk of the Appalachians, lies the Great Appalachian Valley, bordered on the west by the Ridge and Valley province of the Appalachian range.

Mount Longonot is a stratovolcano located southeast of Lake Naivasha in the Great Rift Valley of Kenya, Africa. It is thought to have last erupted in the 1860s. Its name is derived from the Maasai word Oloonong'ot, meaning "mountains of many spurs" or "steep ridges".

Seneca Rocks is a large crag and local landmark in Pendleton County in the Eastern Panhandle of West Virginia, United States. The south peak is the only peak inaccessible except by technical rock climbing techniques on the East Coast of the United States. One of the best-known scenic attractions in West Virginia, the sheer rock faces are a popular challenge for rock climbers.

Koobi Fora refers primarily to a region around Koobi Fora Ridge, located on the eastern shore of Lake Turkana in the territory of the nomadic Gabbra people. According to the National Museums of Kenya, the name comes from the Gabbra language:
In the language of the Gabbra people who live near the site, the term Koobi Fora means a place of the commiphora and the source of myrrh...

Bugaboo Spire is a peak in Bugaboo mountain range in Canada, located between the Vowell and Crescent glaciers, just under 2 km West of the ACC's Conrad Kain hut. It is known for its alpine climbing. The Spire was first climbed by Conrad Kain in 1916.

Walden Ridge is a mountain ridge and escarpment located in Tennessee in the United States. It marks the eastern edge of the Cumberland Plateau and is generally considered part of it. Walden Ridge is about 74 miles (119 km) long, running generally north-south. Its highest point is at Hinch Mountain, which reaches 3,048 feet (929 m) above sea level. Sometimes Walden Ridge is called the Cumberland Escarpment.

The Weisshorn is a major peak of Switzerland and the Alps, culminating at 4,505 metres above sea level. It is part of the Pennine Alps and is located between the valleys of Anniviers and Zermatt in the canton of Valais. In the latter valley, the Weisshorn is one of the many 4000ers surrounding Zermatt, with Monte Rosa and the Matterhorn.

Huo Hsing Vallis is an ancient river valley in the Syrtis Major quadrangle of Mars at 30.5° north latitude and 293.4° west longitude. It is about 318 km long and was named after the word for "Mars" in Chinese.

The Fern Ridge Wildlife Area is a wildlife management area located west of Eugene, Oregon, in the United States. It is named for the Fern Ridge Reservoir which it partially surrounds.

The Fossil Ridge Wilderness is a U.S. Wilderness Area located approximately 16 miles (26 km) northeast of Gunnison, Colorado in the Gunnison National Forest. The 13,992-acre (56.62 km2) wilderness includes Fossil Ridge, a high, exposed ridge of Paleozoic carbonates that contain epeiric sea fossils. Elevations in the wilderness range from 8,880 feet (2,710 m) at Summerville Creek to 13,254 feet (4,040 m) at the summit of Henry Mountain. Elk, deer, mountain goats, and bighorn sheep can be found in the wilderness.

Pine Ridge is an unincorporated community in Fayette Township, Vigo County, in the U.S. state of Indiana. It is part of the Terre Haute metropolitan area.

Ambergris Glacier is a glacier flowing south-southeast from Mount Sara Teodora between Chintulov Ridge and Valkosel Ridge to join Flask Glacier just west of Fluke Ridge in Aristotle Mountains on the east coast of Graham Land, Antarctica. One of several names in the area that reflect a whaling theme, it was named in 1987 by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee from the substance secreted by the sperm whale and used in perfumery.

The Gruber Mountains are a small group of mountains consisting of a main massif and several rocky outliers, forming the northeast portion of the Wohlthat Mountains in Queen Maud Land, Antarctica. They were discovered and plotted from air photos by the Third German Antarctic Expedition (GerAE), 1938–39, under Alfred Ritscher. The mountains were remapped by the Sixth Norwegian Antarctic Expedition, 1956–60, who named them for Otto von Gruber, the German cartographer who compiled maps of this area from air photos taken by the GerAE. This feature is not to be confused with "Gruber-Berge," an unidentified toponym applied by the GerAE in northern the Mühlig-Hofmann Mountains.
Tramway Ridge is a ridge that rises to about 3450 m above sea level in the north-west part of the summit caldera of Mount Erebus on Ross Island, Antarctica. The ridge is formed by the levees (banks) on the side of a young lava flow. The appearance of the feature is suggestive of a set of railway or tram lines.

The Great Rift Valley is part of an intra-continental ridge system that runs through Kenya from north to south. It is part of the Gregory Rift, the eastern branch of the East African Rift, which starts in Tanzania to the south and continues northward into Ethiopia. It was formed on the "Kenyan Dome" a geographical upwelling created by the interactions of three major tectonics: the Arabian, Nubian, and Somalian plates. In the past, it was seen as part of a "Great Rift Valley" that ran from Madagascar to Syria. Most of the valley falls within the former Rift Valley Province.
Sheep Ridge Wilderness was designated in 1984, and it covers 9,315 acres (38 km2) in the Croatan National Forest in eastern North Carolina. The Wilderness Area is a vast wetland, and it lacks trails and campsites. Travel through this wilderness is difficult.
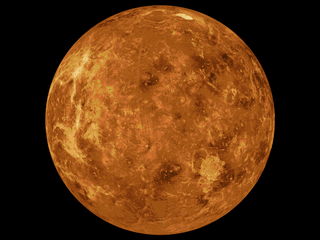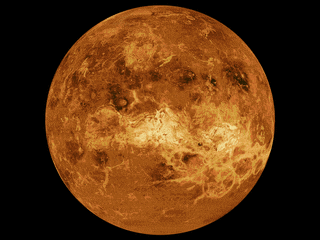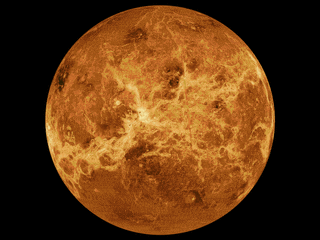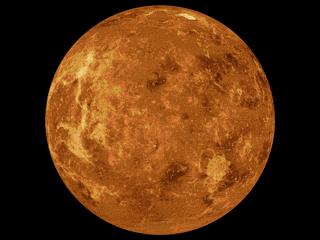
The mapping of Venus refers to the process and results of human description of the geological features of the planet Venus. It involves surface radar images of Venus, construction of geological maps, and the identification of stratigraphic units, volumes of rock with a similar age.

















