In genetics, an expressed sequence tag (EST) is a short sub-sequence of a cDNA sequence. ESTs may be used to identify gene transcripts, and were instrumental in gene discovery and in gene-sequence determination. The identification of ESTs has proceeded rapidly, with approximately 74.2 million ESTs now available in public databases. EST approaches have largely been superseded by whole genome and transcriptome sequencing and metagenome sequencing.

In genetics and bioinformatics, a single-nucleotide polymorphism is a germline substitution of a single nucleotide at a specific position in the genome that is present in a sufficiently large fraction of considered population.
Fungicides are pesticides used to kill parasitic fungi or their spores. They are most commonly chemical compounds, but may include biocontrols and fungistatics. Fungi can cause serious damage in agriculture, resulting in critical losses of yield, quality, and profit. Fungicides are used both in agriculture and to fight fungal infections in animals. Fungicides are also used to control oomycetes, which are not taxonomically/genetically fungi, although sharing similar methods of infecting plants. Fungicides can either be contact, translaminar or systemic. Contact fungicides are not taken up into the plant tissue and protect only the plant where the spray is deposited. Translaminar fungicides redistribute the fungicide from the upper, sprayed leaf surface to the lower, unsprayed surface. Systemic fungicides are taken up and redistributed through the xylem vessels. Few fungicides move to all parts of a plant. Some are locally systemic, and some move upward.

The SIB Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics is an academic not-for-profit foundation which federates bioinformatics activities throughout Switzerland.
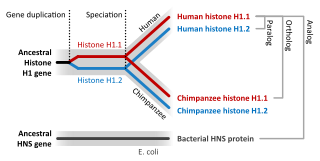
Sequence homology is the biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences, defined in terms of shared ancestry in the evolutionary history of life. Two segments of DNA can have shared ancestry because of three phenomena: either a speciation event (orthologs), or a duplication event (paralogs), or else a horizontal gene transfer event (xenologs).

Aspergillus is a genus consisting of several hundred mould species found in various climates worldwide.

A fusion gene is a hybrid gene formed from two previously independent genes. It can occur as a result of translocation, interstitial deletion, or chromosomal inversion. Fusion genes have been found to be prevalent in all main types of human neoplasia. The identification of these fusion genes play a prominent role in being a diagnostic and prognostic marker.

The Wellcome Sanger Institute, previously known as The Sanger Centre and Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute, is a non-profit British genomics and genetics research institute, primarily funded by the Wellcome Trust.
In academia, computational immunology is a field of science that encompasses high-throughput genomic and bioinformatics approaches to immunology. The field's main aim is to convert immunological data into computational problems, solve these problems using mathematical and computational approaches and then convert these results into immunologically meaningful interpretations.

Fiona Brinkman is a Professor in Bioinformatics and Genomics in the Department of Molecular Biology and Biochemistry at Simon Fraser University in British Columbia, Canada, and is a leader in the area of microbial bioinformatics. She is interested in developing "more sustainable, holistic approaches for infectious disease control and conservation of microbiomes".

https://canto.phi-base.org/PHI-baseFile:PHI-base+01.jpgContentDescriptionPathogen-Host+Interactions+databaseData+typescapturedphenotypes+of+microbial+mutantsOrganisms~280+fungal,+bacterial+and+protist+pathogens+of+agronomic+and+medical+importance+tested+on+~230+hostsContactResearch+centerRothamsted+ResearchPrimary+citationPMID 31733065Release+dateMay+2005AccessData+formatXML,+FASTAWebsitePHI-baseToolsWebPHI-base+SearchPHIB-BLASTPHI-Canto+(Author+curation)MiscellaneousLicenseCreative+Commons+Attribution-NoDerivatives+4.0+International+LicenseVersioningYesData+releasefrequency6+monthlyVersion4.15+(May+2023)Curation+policyManual+Curation

16S ribosomal RNA is the RNA component of the 30S subunit of a prokaryotic ribosome. It binds to the Shine-Dalgarno sequence and provides most of the SSU structure.

Plant disease resistance protects plants from pathogens in two ways: by pre-formed structures and chemicals, and by infection-induced responses of the immune system. Relative to a susceptible plant, disease resistance is the reduction of pathogen growth on or in the plant, while the term disease tolerance describes plants that exhibit little disease damage despite substantial pathogen levels. Disease outcome is determined by the three-way interaction of the pathogen, the plant and the environmental conditions.

OrthoDB presents a catalog of orthologous protein-coding genes across vertebrates, arthropods, fungi, plants, and bacteria. Orthology refers to the last common ancestor of the species under consideration, and thus OrthoDB explicitly delineates orthologs at each major radiation along the species phylogeny. The database of orthologs presents available protein descriptors, together with Gene Ontology and InterPro attributes, which serve to provide general descriptive annotations of the orthologous groups, and facilitate comprehensive orthology database querying. OrthoDB also provides computed evolutionary traits of orthologs, such as gene duplicability and loss profiles, divergence rates, sibling groups, and gene intron-exon architectures.

The Eukaryotic Pathgen Database, or EuPathDB, is a database of bioinformatic and experimental data related to a variety of eukaryotic pathogens. It was established in 2006 under a National Institutes of Health program to create Bioinformatics Resource Centers to facilitate research on pathogens that may pose biodefense threats. EuPathDB stores data related to its organisms of interest and provides tools for searching through and analyzing the data. It currently consists of 14 component databases, each dedicated to a certain research topic. EuPathDB includes:

Canto is a web-based tool to support the curation of gene-specific scientific data, by both professional biocurators and publication authors. Canto was developed as part of the PomBase project, and is funded by the Wellcome Trust.
Jessica Kissinger is a Distinguished Research Professor at the Franklin College of Arts and Sciences, University of Georgia and director of the Institute of Bioinformatics. Her research focus is on the evolution, assembly and data curation of protozoan parasite genomes, particularly Cryptosporidium, Toxoplasma gondii and Plasmodium.

Kim Dixon Pruitt is an American bioinformatician. She is chief of the information engineering branch at the National Center for Biotechnology Information. Pruitt led the development of the RefSeq gene database.
IMGT or the international ImMunoGeneTics information system is a collection of databases and resources for immunoinformatics, particularly the V, D, J, and C gene sequences, as well as a providing other tools and data related to the adaptive immune system. IMGT/LIGM-DB, the first and still largest database hosted as part of IMGT contains reference nucleotide sequences for 360 species' T-cell receptor and immunoglobulin molecules, as of 2023. These genes encode the proteins which are the foundation of adaptive immunity, which allows highly specific recognition and memory of pathogens.













