Related Research Articles

The Great Artesian Basin (GAB) of Australia is the largest and deepest artesian basin in the world, extending over 1,700,000 square kilometres (660,000 sq mi). Measured water temperatures range from 30 to 100 °C. The basin provides the only source of fresh water through much of inland Australia.

The Geological Survey of Canada is a Canadian federal government agency responsible for performing geological surveys of the country developing Canada's natural resources and protecting the environment. A branch of the Earth Sciences Sector of Natural Resources Canada, the GSC is the country's oldest scientific agency and was one of its first government organizations.

Coalbed methane, coalbed gas, or coal seam gas (CSG) is a form of natural gas extracted from coal beds. In recent decades it has become an important source of energy in United States, Canada, Australia, and other countries.
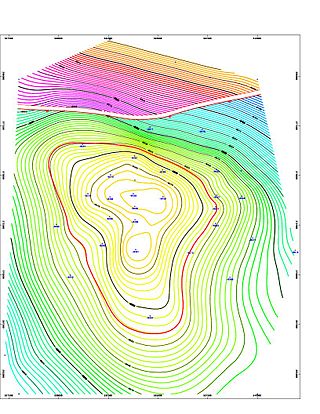
Geologic modelling,geological modelling or geomodelling is the applied science of creating computerized representations of portions of the Earth's crust based on geophysical and geological observations made on and below the Earth surface. A geomodel is the numerical equivalent of a three-dimensional geological map complemented by a description of physical quantities in the domain of interest. Geomodelling is related to the concept of Shared Earth Model; which is a multidisciplinary, interoperable and updatable knowledge base about the subsurface.

Rum Jungle or Unrungkoolpum is a locality in the Northern Territory of Australia, about 105 kilometres south of Darwin on the East Branch of the Finniss River. It is 10 kilometres west of Batchelor and shares a boundary with Litchfield National Park.

Geoscience Australia is a statutory agency of the Government of Australia that carries out geoscientific research. The agency is the government's technical adviser on aspects of geoscience, and serves as the repository of geographic and geological data collated by the Commonwealth.

The China Geological Survey (CGS) (Chinese: 中国地质调查局) is a government-owned, not-for-profit, Chinese organization researching China's mineral resources. It is a public institution managed by the State Council's ministries and commissions responsible for geological and mineral exploration under the State Council of the People's Republic of China. According to the national land and resources survey plan, it is now managed by the Ministry of Natural Resources. It is the largest Geoscience agency in China since being reinstated in 1999, and the headquarter is in Beijing, the capital of China.
The California Department of Conservation is a department within the government of California, belonging to the California Natural Resources Agency. With a team of scientists, engineers, environmental experts, and other specialists, the Department of Conservation administers a variety of programs vital to California's public safety, environment and economy. The department's mission is to manage California's working lands. It regulates oil, natural gas and geothermal wells; studies and maps earthquakes and other geologic phenomena; maps and classifies areas containing mineral deposits; ensures reclamation of land used for mining; and administers agricultural and open-space land conservation programs. A division within the department dedicated to encouraging beverage container recycling has been moved into the newly created Department of Resources Recovery and Recycling (CalRecycle). Despite the similar name, the Department of Conservation should not be confused with the California Conservation Corps, another department within the Natural Resources Agency, which provides work experience for young adults. The Department of Conservation often collaborates with its federal equivalents, such as the U.S. Geological Survey.
The Jackson School of Geosciences at The University of Texas at Austin unites the Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences with two research units, the Institute for Geophysics and the Bureau of Economic Geology.
Viridien (VIRI), formerly CGG, is a multinational technology, digital and Earth data company, specializing in solving complex natural resource, energy transition and infrastructure challenges.

Coal is mined in every state of Australia. The largest black coal resources occur in Queensland and New South Wales. About 70% of coal mined in Australia is exported, mostly to eastern Asia, and of the balance most is used in electricity generation. In 2019-20 Australia exported 390 Mt of coal and was the world's largest exporter of metallurgical coal and second largest exporter of thermal coal. While only employing 50,000 mining jobs nationally coal provides a rich revenue stream for governments.

Mining in Afghanistan was controlled by the Ministry of Mines and Petroleum, prior to the August 15th 2021 takeover by the Taliban. It is headquartered in Kabul with regional offices in other parts of the country. Afghanistan has over 1,400 mineral fields, containing barite, chromite, coal, copper, gold, iron ore, lead, natural gas, petroleum, precious and semi-precious stones, salt, sulfur, lithium, talc, and zinc, among many other minerals. Gemstones include high-quality emeralds, lapis lazuli, red garnet and ruby. According to a joint study by The Pentagon and the United States Geological Survey, Afghanistan has an estimated US$1 trillion of untapped minerals.
Semantic matching is a technique used in computer science to identify information which is semantically related.

Radioactive ores were first extracted in South Australia at Radium Hill in 1906 and Mount Painter in 1911. 2,000 tons of ore were treated to recover radium for medical use. Several hundred kilograms of uranium were also produced for use in ceramic glazes.

The Mines and Geosciences Bureau (MGB) is a government agency of the Philippines under the Department of Environment and Natural Resources (DENR). The MGB is responsible for the conservation, management, development, and use of the country's mineral resources, including those in reservations and public lands.
Knowledge extraction is the creation of knowledge from structured and unstructured sources. The resulting knowledge needs to be in a machine-readable and machine-interpretable format and must represent knowledge in a manner that facilitates inferencing. Although it is methodically similar to information extraction (NLP) and ETL, the main criterion is that the extraction result goes beyond the creation of structured information or the transformation into a relational schema. It requires either the reuse of existing formal knowledge or the generation of a schema based on the source data.

A McKelvey diagram or McKelvey box is a visual representation used to describe a natural resource such as a mineral or fossil fuel, based on the geologic certainty of its presence and its economic potential for recovery. The diagram is used to estimate the uncertainty and risk associated with availability of a natural resource. As geological assurance of a resource's occurrence decreases, risk increases. As economic recoverability of a resource decreases, risk also increases.
The Prairie Research Institute is a multidisciplinary research institute charged with providing objective research, expertise, and data on the natural and cultural resources of Illinois. It was established as a unit of the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign by a Public Act of the Illinois State Legislature in 2008. The institute comprises four state scientific surveys: the Illinois Natural History Survey (INHS), the Illinois State Archaeological Survey (ISAS), the Illinois State Geological Survey (ISGS), and the Illinois State Water Survey (ISWS), and the institute also houses the Illinois Sustainable Technology Center (ISTC). The institute has a combined total staff of more than 700 employees, with facilities located on the Urbana-Champaign campus of the University of Illinois, and field offices and research stations throughout the state.

The China University of Geosciences (Beijing) is a public university located in Beijing, China. It is affiliated with the Ministry of Education, and co-funded by the Ministry of Education and the Ministry of Natural Resources. The university is part of the Double First-Class Construction and Project 211.
The Australian Government Linked Data Working Group is an informal, advisory working group within Australia government, self-tasked "to meet the Linked Data challenges facing the Australian government". The Group was established in August 2012 and operates with monthly or more regular meetings.
References
- ↑ Natural Resources, Mines and Energy (23 September 2014). "Geological Survey of Queensland". www.business.qld.gov.au. Retrieved 18 December 2019.
- ↑ "Geological survey of Queensland". Queensland Historical Atlas. Archived from the original on 26 February 2020. Retrieved 18 December 2019.
- ↑ "About - GSQ Open Data Portal".[ permanent dead link ]
- ↑ "GSQ's New Discovery Program: Enabling data-driven exploration in the North-West Minerals Province" (PDF). Queensland Government. February 2019. Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 February 2020. Retrieved 7 January 2025.
- ↑ "Data for Discovery" (PDF). Queensland Government . Retrieved 7 January 2025.
- ↑ "The Geological Survey of Queensland". Eventbrite. Retrieved 18 December 2019.