 | |
CIS | Georgia |
|---|---|
Relations between Georgia and the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) is a multilateral international relationship between a third country and a supranational organization.
 | |
CIS | Georgia |
|---|---|
Relations between Georgia and the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) is a multilateral international relationship between a third country and a supranational organization.
On December 3, 1993, by decision of the Council of Heads of State, Georgia was accepted into the Commonwealth, [1] and on December 9, 1993, Georgia joined the CIS Charter. [2]
Georgia withdrew from the CIS Defense Ministers on 3 February 2006, as membership in that group was not compatible with participation in NATO. [3]
On August 12, 2008, the President of Georgia, Mikheil Saakashvili, announced his desire to withdraw from the CIS due Russo-Georgian War. [4] On August 14, 2008, the Georgian Parliament unanimously (117 votes) decided on Georgia's withdrawal from the organization. [5] [6] According to the CIS Charter [7] (Article 9 of Chapter I), a member state has the right to withdraw from the Commonwealth. The state shall notify the depositary of this Charter in writing of such intention 12 months before the exit. At the same time, the obligations that arose during the period of participation in this Charter bind the respective states to their full implementation. [8] On October 9, 2008, the Minister of Foreign Affairs of the Russian Federation, Sergey Lavrov, announced that the Council of Foreign Ministers of the CIS countries made a formal decision to terminate Georgia's membership in the Commonwealth in August 2009. On August 18, 2009, Georgia officially left the CIS. [9] [10] [11]

The Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) is a regional intergovernmental organization in Eastern Europe and Asia. It was formed following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. It covers an area of 20,368,759 km2 (7,864,422 sq mi) and has an estimated population of 239,796,010. The CIS encourages cooperation in economic, political and military affairs and has certain powers relating to the coordination of trade, finance, lawmaking, and security. It has also promoted cooperation on cross-border crime prevention.

The Belovezh Accords are accords forming the agreement declaring that the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) had effectively ceased to exist and established the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) in its place as a successor entity. The documentation was signed at the state dacha near Viskuli in Belovezhskaya Pushcha (Belarus) on 8 December 1991, by leaders of three of the four republics which had signed the 1922 Treaty on the Creation of the USSR:

The Economic Court of the Commonwealth of Independent States is a judicial organ which was formed in order to provide exercising of its economic commitments by the participating states. The Court is empowered to consider the disputes in the fulfillment of economic commitments in accordance with international treaties within the framework of the Commonwealth of Independent States. The Court considers other disputes under the agreement of the participating states. It is also empowered to interpret international treaties and the acts of the CIS bodies. The location of the Economic Court is the city of Minsk, Republic of Belarus.

The Commonwealth of Independent States Cup is a defunct annual regional association football tournament, recognized by FIFA.

Yevgeny Ivanovich Shaposhnikov was a Soviet and Russian military leader and business figure. He was awarded the rank of Marshal of Aviation in 1991. He was the final Minister of Defense of the Soviet Union.

The Community for Democracy and Rights of Nations, also commonly and colloquially known as the Commonwealth of Unrecognized States, rarely as CIS-2, is an international organization in Eastern Europe uniting several states in the former Soviet Union, all of which have limited to no recognition from the international community.
The Belarusian national bandy team has been competing in the annual Bandy World Championship since 2001, but not in 2010, 2018 and 2019. The plan was to participate also in 2018, but Federation of International Bandy seemingly was not interested in letting Belarus play. In 2004, Belarus defeated Canada to win the Group B championship. Belarus played in Group A in 2006, 2007 and again in 2008 after winning 9-1 against USA team, best team of Group B.

The Interstate Aviation Committee is an executive body of the Civil Aviation and Airspace Use Council of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) and was formed in 1991 according to the Civil Aviation and Airspace Use Multilateral Agreement, signed on 25 December 1991.

The Federal Agency for the Commonwealth of Independent States Affairs, Compatriots Living Abroad, and International Humanitarian Cooperation, commonly known as Rossotrudnichestvo, is an autonomous Russian federal government agency under the jurisdiction of the Russian Ministry of Foreign Affairs. It is primarily responsible for administering civilian foreign aid and cultural exchange. Rossotrudnichestvo operates in Central Asia, Latin America and Eastern Europe.
Joint CIS Air Defense System is a unified system that comprises air defense units and elements of the former Soviet republics under control of the Coordination Committee on Air Defense of the Council of Ministers of Defense of the CIS. Currently there are 6 de facto members of JADS: Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia and Tajikistan. 70% of all expenditures of the military budget of the Commonwealth of Independent States are directed to the improvement and development of this system.

There are 9 member states of the Commonwealth of Independent States.

The emblem of the Commonwealth of Independent States depicts a yellow sun on a dark blue field, with eight bending poles holding the sun.

The Council of Ministers of Defense of the CIS is a working body in the Commonwealth of Independent States responsible for military policy of the CIS. It coordinates military cooperation of the CIS member states, and develops military and defense policy of the CIS.

The Interparliamentary Assembly of Member Nations of the Commonwealth of Independent States is a parliamentary assembly for delegations from the national parliaments of the member countries of the CIS. The IPA CIS was established on 27 March 1992 in Almaty (Kazakhstan) under the terms of the Agreement signed by Heads of founding parliaments. On 26 May 1995, CIS leaders signed the Convention on the Interparliamentary Assembly of Member Nations of the Commonwealth of Independent States eventually ratified by nine CIS parliaments. The overarching mission is law-making and alignment of national laws in the CIS. The IPA is housed in the Tauride Palace in a historical landmark of Saint Petersburg.
The Charter of the Commonwealth of Independent States, also known as the Statutes of the Commonwealth of Independent States, is an international agreement between the states forming the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS).

The Supreme Court of Tajikistan is the most senior body of civil, criminal, and administrative law in the Republic of Tajikistan.
The Council of Heads of State of the CIS, abbreviated in the Russian language as the SGG (СГГ), is a working body in the Commonwealth of Independent States. It serves as the supreme body of the CIS, and includes all the chief of state of CIS member states. Regular meetings of the council are held annually. It was created following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, directly replacing the State Council of the Soviet Union. As of 2020 there are 9 members of the CIS: Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Moldova, Russia, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan. Turkmenistan is an associate state of the CIS.
The United Armed Forces of the Commonwealth of Independent States was a short-lived military entity associated with the Commonwealth of Independent States. It was created in 1992 after the demise of the Soviet Union, and was intended to be the continuation of the Armed Forces of the Soviet Union and to hold control over the Soviet Union's nuclear weapons.
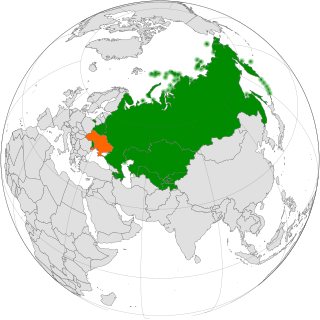
Relations between Ukraine and the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) are multilateral international relations between a third state and a supranational organization.