
Kiel is the capital and most populous city in the northern German state of Schleswig-Holstein, with a population of 246,243 (2021).

Flensburg is an independent town in the north of the German state of Schleswig-Holstein. Flensburg is the north of the region of Schleswig. After Kiel and Lübeck, it is the third-largest town in Schleswig-Holstein.

Plön is the district seat of the Plön district in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany, and has about 8,700 inhabitants. It lies right on the shores of Schleswig-Holstein's biggest lake, the Great Plön Lake, as well as on several smaller lakes, touching the town on virtually all sides. The town's landmark is Plön Castle, a chateau built in the 17th century on a hill overlooking the town.

Otto Ernst Lindemann was a German Kapitän zur See. He was the only commander of the battleship Bismarck during its eight months of service in World War II.

Karl-Friedrich Merten commanded the U-boat U-68 in Nazi Germany's Kriegsmarine during World War II. He received the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross with Oak Leaves. Merten was credited with the sinking of 27 ships for a total of 170,151 gross register tons (GRT) of Allied shipping. Merten joined the Reichsmarine in 1926. He served on the light cruisers Karlsruhe and Leipzig during the Spanish Civil War patrols.

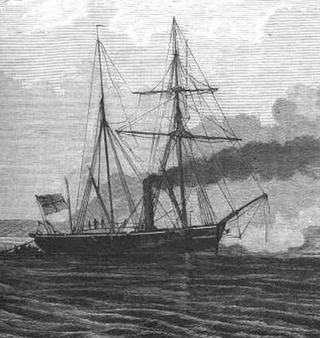
Von der Tann was a steam-powered 120 ton gunboat built in 1849 at Conradi shipyards in Kiel for the small joint navy of the two duchies of Schleswig and Holstein. She was the first propeller-driven gunboat in the world.

Eduard Karl Emanuel von Jachmann was the first Vizeadmiral of the Prussian Navy. He entered the navy in the 1840s after initially serving in the merchant marine. In 1848, Jachmann received his first command, the corvette SMS Amazone; through the 1850s and early 1860s, he held several other commands, including the frigates Thetis—aboard which he took part in the Eulenburg expedition to East Asia—and Arcona. During the Second Schleswig War in 1864, he commanded Prussian naval forces in the Baltic from Arcona, and led a small squadron at the Battle of Jasmund on 17 March. Though defeated in that battle, he was promoted to Konteradmiral for his aggressive handling of the Prussian fleet.

The Naval Academy Mürwik is the main training establishment for all German Navy officers and in 1910 replaced the German Imperial Naval Academy in Kiel

The Schleswig-Holstein Landtag is the state parliament of the German state of Schleswig-Holstein. It convenes in the state's capital Kiel and currently consists of 69 members of five parties. The current majority consists of coalition of the Christian Democratic Union and the Greens, supporting the cabinet of Minister President Daniel Günther.

The German Imperial Admiralty Staff was one of four command agencies for the administration of the Imperial German Navy from 1899 to 1918. While the German Emperor Wilhelm II as commander-in-chief exercised supreme operational command and control of the naval forces, the military staff was split into the Admiralty, the Naval Office, the Naval Cabinet, and the Inspector-General. The command structure had a negative impact on German naval warfare in World War I, as a professional head of the Imperial Navy, similar to the First Sea Lord, was not established until August 1918. After the war and the German Revolution of 1918–19, the Admiralty Staff became subordinate to the Naval Office and was finally disestablished by order of the German President.

Günter Luther was a German admiral who became Inspector of the Navy and Deputy Supreme Allied Commander Europe for NATO. During World War II, he served as a military pilot in the Kriegsmarine and a paratrooper in the Luftwaffe. After the war, he joined the newly founded West German Bundesmarine in 1956.
Klaus von Dambrowski is a Konteradmiral of the German Navy and Chief of Staff of the Navy Command.

Otto Daniel Livonius was a Vizeadmiral of the German Imperial Navy, serving in the predecessor Prussian Navy and the Navy of the North German Confederation.

Mürwik is a community of Flensburg in the north of the German state of Schleswig-Holstein. Situated on the east side of the Flensburg Firth, it is on the Angeln peninsula. Mürwik is the location of the Naval Academy at Mürwik, which is the main academy that trains German Navy officers. Nazi Germany's final government, the Flensburg government, was located in Mürwik.
SMS Camäleon was the lead ship of the Camäleon class of steam-powered gunboats of the Prussian Navy that was launched in 1860. A small vessel, armed with only three light guns, Camäleon saw little active use. She served during the Second Schleswig War of 1864 and the Franco-Prussian War of 1870–1871, but saw no action in either conflict. Her peacetime career was limited to survey work in 1865 and limited tender duties in and around Kiel in 1867–1868. In poor condition by 1872, she was stricken from the naval register and used as a storage hulk in Kiel. She was broken up for scrap some time after 1878.

SMS Delphin was a Camäleon-class gunboat of the Prussian Navy that was launched in 1860. A small vessel, armed with only three light guns, Delphin served during the Second Schleswig War of 1864 and the Austro-Prussian War of 1866, part of the conflicts that unified Germany. The ship was present at, but was only lightly engaged in the Battle of Jasmund during the Second Schleswig War. The ship spent much of the rest of her career in the Mediterranean Sea, going on three lengthy deployments there in 1865–1866, 1867–1870, and 1871–1873. During the last tour, she took part in operations off the coast of Spain with an Anglo-German squadron during the Third Carlist War, where she helped to suppress forces rebelling against the Spanish government. For the rest of the 1870s, she served as a survey vessel in the North and Baltic Seas before being decommissioned in August 1881, stricken from the naval register the following month, and subsequently broken up for scrap.
Fritz Krauss was a German naval officer, most recently a Konteradmiral in the World War II. Between 16 August 1944 – 22 July 1945, Fritz Krauss was Director of Department of Naval Intelligence, specifically 3 SKL/MND IV of the German Navy.

SMS Nymphe was the lead ship of the Nymphe class of steam corvettes, the first ship of that type to be built for the Prussian Navy. She had one sister ship, Medusa, and the vessels were wooden-hulled ships armed with a battery of sixteen guns. She was ordered as part of a naval expansion program to counter the Danish Navy over the disputed ownership of Schleswig and Holstein. Nymphe was laid down in January 1862, was launched in April 1863, and was completed in October that year.

SMS Preussischer Adler was a paddle steamer originally built in the mid-1840s for use on a packet route between the Kingdom of Prussia and the Russian Empire in the Baltic Sea. She was requisitioned by the Prussian Navy during the First Schleswig War in 1848 and converted into an aviso, the first vessel of the type commissioned by Prussia. During the war, she took part in an inconclusive action with the Danish brig St. Croix, the first naval battle of the Prussian fleet. After the war, she was disarmed and returned to her commercial role, operating uneventfully on the Stettin–St. Petersburg route until 1862, when the expansion of the Prussian Eastern Railway had rendered the maritime route superfluous. The ship was purchased by the Prussian Navy that year and rearmed, once again as an aviso.

SMS Grille was an aviso of the Prussian Navy built in France in the mid-1850s as part of a naval expansion program directed by Prince Adalbert of Prussia, who saw the need for a stronger fleet. She was authorized in 1855 in the aftermath of the First Schleswig War, which had demonstrated the weakness of the Prussian fleet. Grille was the first screw propeller-driven steamship to be built for Prussia; all earlier steam-powered vessels had been paddle steamers.


















