Related Research Articles

A tomb is a repository for the remains of the dead. It is generally any structurally enclosed interment space or burial chamber, of varying sizes. Placing a corpse into a tomb can be called immurement, although this word mainly means entombing people alive, and is a method of final disposition, as an alternative to cremation or burial.
Tourism in Bulgaria is a significant contributor to the country's economy. Situated at the crossroads of the East and West, Bulgaria has been home to many civilizations: Thracians, Greeks, Romans, Eastern Romans or Byzantines, Slavs, Bulgars, and Ottomans. The country is rich in tourist sights and historical artifacts, scattered through a relatively small and easily accessible territory. Bulgaria is internationally known for its seaside and winter resorts.
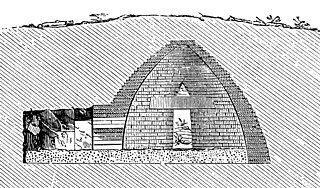
A beehive tomb, also known as a tholos tomb, is a burial structure characterized by its false dome created by corbelling, the superposition of successively smaller rings of mudbricks or, more often, stones. The resulting structure resembles a beehive, hence the traditional English name.

The Thracian Tomb of Svestari is 2.5 kilometers (1.6 mi) southwest of the village of Sveshtari, Razgrad Province, which is 42 kilometers (26 mi) northeast of Razgrad, in northeast Bulgaria. The tomb is probably the grave of Dromichaetes who was a king of the Getae on both sides of the lower Danube around 300 BCE, and his wife, the daughter of King Lysimachus who was a general and diadochus of Alexander the Great. The tomb is a UNESCO World Heritage Site.

The Thracian Tomb of Kazanlak is a vaulted-brickwork "beehive" (tholos) tomb that is located near the town of Kazanlak in central Bulgaria.

The Ludogorie or Deliorman, is a region in northeastern Bulgaria stretching over the plateau of the same name. Major cities in the region are Targovishte, Razgrad, Dulovo, Novi Pazar, Pliska, Preslav and Isperih. Part of the Danubian Plain, the region is hilly in the east, reaching up to 485.70 metres (1,593.5 ft) in height near the village of Samuil, but merges with the plains of Dobruja and the Danube to the north, with the lowest point near Yuper. The region is bordered to the west by the Provadiya River and the Beli Lom; to the east it transitions into the Dobruja plateau.

Isperih is a town in northeastern Bulgaria, part of Razgrad Province, situated in the central part of the Ludogorie region. It is the administrative centre of the eponymous Isperih Municipality. As of December 2009, the town has a population of 9,017 inhabitants.
The Thracians were a group of Indo-European tribes inhabiting a large area in Central and Southeastern Europe, centred in modern Bulgaria. They were bordered by the Scythians to the north, the Celts and the Illyrians to the west, the Greeks to the south, and the Black Sea to the east.

Demir Baba Teke is a 16th-century Alevi mausoleum (türbe) near the village of Sveshtari, Isperih municipality, Razgrad Province in northeastern Bulgaria. As part of the Sboryanovo historical and archaeological reserve, Demir Baba Teke is one of the 100 Tourist Sites of Bulgaria.
Thracian may refer to:

The Aleksandrovo tomb is a Thracian burial mound and tomb excavated near Aleksandrovo, Haskovo Province, South-Eastern Bulgaria, dated to c. 4th century BCE.

The Tomb of Seuthes III is located near Kazanlak, Bulgaria. Seuthes III was the King of the Odrysian Kingdom of Thrace from c. 331 to c. 300 BC and founder of the nearby Thracian city of Seuthopolis.

The Ostrusha mound is a Thracian burial tumulus near the Bulgarian town of Shipka. It was constructed in the middle of the 4th century BCE. The stone structures under the more than 18 meters high mound form one of the biggest representative tomb-cult complexes with 6 rooms on an area of 100 square meters. It was professionally excavated in 1993.

The Thracian tomb at Shushmanets is a mound located in the Valley of the Thracian Rulers. It was built as a temple in the 4th century BC and later used as a tomb.

The Thracian tomb "Helvetia" mound near Shipka, Bulgaria, was built in the middle of the 4th century BC.

Golyama Arsenalka mound is a Thracian burial tumulus with a subterranean stone building near the Bulgarian town of Shipka. It dates from the end of 5th century BCE.

The Thracian tomb Griffins, found in Bulgaria, has a façade decorated with plastic columns and with a pediment above them. The pediment`s ends are semi-palmettes, the lower leaves of which are elongated and look like heads of griffins. The temple was built in the 5th century BC. There is a corridor made from river stones, floored with earth. The façade, the antechamber and the circular chamber are built of granite blocks. The entrances to the antechamber and the dome chamber had been closed by stone doors which were found broken during the research of the facility. The antechamber is of rectangular shape and has a double-pitched roof. The round chamber is covered with fine-made dome. The floors of both rooms are made of plastered granite slabs. Opposite the entrance of the circular chamber is situated a ritual stone bed with decorations. On a stone block in front of the bed were found gold paws. A funeral took place in the temple in the 4th century BC. The corridor was filled with river stones and soil. It was robbed in antiquity.

The Roman Tomb of Silistra is an Ancient Roman burial tomb in the town of Silistra in northeastern Bulgaria. Dating to the mid-4th century AD, the Roman Tomb is the best-preserved architectural monument of the Ancient Roman city of Durostorum. The tomb is considered "one of the most investigated and most discussed monuments of the late antique art in Bulgaria" and the Balkans, owing in large part to the quality and extent of its interior frescoes.

The Mogilan mound or Mogilanska mound is a burial mound in the center of Vratsa, Bulgaria.
References
- ↑ "Ancient Thracian gold hoard unearthed in Bulgaria". Reuters. 2012-11-08. Retrieved 2023-01-28.