Income tax in the Netherlands is regulated by the Wet inkomstenbelasting 2001.

In the United Kingdom, taxation may involve payments to at least three different levels of government: central government, devolved governments and local government. Central government revenues come primarily from income tax, National Insurance contributions, value added tax, corporation tax and fuel duty. Local government revenues come primarily from grants from central government funds, business rates in England, Council Tax and increasingly from fees and charges such as those for on-street parking. In the fiscal year 2014–15, total government revenue was forecast to be £648 billion, or 37.7 per cent of GDP, with net taxes and National Insurance contributions standing at £606 billion.
A gift tax, known originally as inheritance tax, is a tax imposed on the transfer of ownership of property during the giver's life. The United States Internal Revenue Service says that a gift is "Any transfer to an individual, either directly or indirectly, where full compensation is not received in return."

Taxation in Ireland in 2017 came from Personal Income taxes, and Consumption taxes, being VAT and Excise and Customs duties. Corporation taxes represents most of the balance, but Ireland's Corporate Tax System (CT) is a central part of Ireland's economic model. Ireland summarises its taxation policy using the OECD's Hierarchy of Taxes pyramid, which emphasises high corporate tax rates as the most harmful types of taxes where economic growth is the objective. The balance of Ireland's taxes are Property taxes and Capital taxes.
A gift, in the law of property, is the voluntary and immediate transfer of property from one person to another without consideration. There are several type of gifts in property law, most notably inter vivos gifts which are made in the donor's lifetime and causa mortis (deathbed) gifts which are made in expectation of the donor's imminent death. Both types of gifts share three elements which must be met in order for the gift to be legally effective: donative intent, the delivery of the gift to the donee, and the acceptance of the gift. In addition to those elements, causa mortis gifts require that the donor must die of the impending peril that he or she had contemplated when making the gift.
International tax law distinguishes between an estate tax and an inheritance tax. An inheritance tax is a tax paid by a person who inherits money or property of a person who has died, whereas an estate tax is a levy on the estate of a person who has died. However, this distinction is not always observed; for example, the UK's "inheritance tax" is a tax on the assets of the deceased, and strictly speaking is therefore an estate tax.

Income tax in India is governed by Entry 82 of the Union List of the Seventh Schedule to the Constitution of India, empowering the central government to tax non-agricultural income; agricultural income is defined in Section 10(1) of the Income-tax Act, 1961. Income-tax law consists of the 1961 act, Income Tax Rules 1962, Notifications and Circulars issued by the Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT), annual Finance Acts, and judicial pronouncements by the Supreme and high courts.
Tax on cash withdrawal is a form of advance taxation and is a strategy to keep tax evasion in check. This mode of tax collection is also called the presumptive tax regime. Globally, 3 countries are known to consider this approach namely, Pakistan, India and Greece.
Tax deduction at source (TDS) is an Indian withholding tax that is a means of collecting tax on income, dividends, or asset sales by requiring the payer to deduct tax due before paying the balance to the payee.
Taxes in India are levied by the Central Government and the State Governments by virtue of powers conferred to them from the Constitution of India. Some minor taxes are also levied by the local authorities such as the Municipality.
A unit-linked insurance plan is a product offered by insurance companies that, unlike a pure insurance policy, gives investors both insurance and investment under a single integrated plan.
In economics, a gift tax is the tax on money or property that one living person or corporate entity gives to another. A gift tax is a type of transfer tax that is imposed when someone gives something of value to someone else. The transfer must be gratuitous or the receiving party must pay a lesser amount than the item's full value to be considered a gift. Items received upon the death of another are considered separately under the inheritance tax. Many gifts are not subject to taxation because of exemptions given in tax laws. The gift tax amount varies by jurisdiction, and international comparison of rates is complex and fluid.
In the United States, the estate tax is a federal tax on the transfer of the estate of a person who dies. The tax applies to property that is transferred by will or, if the person has no will, according to state laws of intestacy. Other transfers that are subject to the tax can include those made through a trust and the payment of certain life insurance benefits or financial accounts. The estate tax is part of the federal unified gift and estate tax in the United States. The other part of the system, the gift tax, applies to transfers of property during a person's life.
The National Pension System (NPS) is a defined-contribution pension system in India regulated by the Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (PFRDA) which is under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Finance of the Government of India. National Pension System Trust was established by PFRDA as per the provisions of the Indian Trusts Act of 1882 to take care of the assets and funds under this scheme for the best interest of the subscriber.
Taxes in Germany are levied at various government levels: the federal government, the 16 states (Länder), and numerous municipalities (Städte/Gemeinden). The structured tax system has evolved significantly, since the reunification of Germany in 1990 and the integration within the European Union, which has influenced tax policies. Today, income tax and Value-Added Tax (VAT) are the primary sources of tax revenue. These taxes reflect Germany's commitment to a balanced approach between direct and indirect taxation, essential for funding extensive social welfare programs and public infrastructure. The modern German tax system accentuate on fairness and efficiency, adapting to global economic trends and domestic fiscal needs.
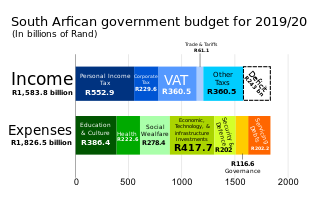
Taxation may involve payments to a minimum of two different levels of government: central government through SARS or to local government. Prior to 2001 the South African tax system was "source-based", where in income is taxed in the country where it originates. Since January 2001, the tax system was changed to "residence-based" wherein taxpayers residing in South Africa are taxed on their income irrespective of its source. Non residents are only subject to domestic taxes.
A recurring deposit is a special kind of term deposit in India that is offered by Indian banks and India Post which helps people with regular incomes to deposit a fixed amount every month into their recurring deposit account and earn interest at the rate applicable to fixed deposits.
The tax system of the Czech Republic is similar in its main features to the systems of developed and especially European countries.

Black Money and Imposition of Tax Act, 2015 is an Act of the Parliament of India. It aims to curb black money, or undisclosed foreign assets and income and imposes tax and penalty on such income. The Act has been passed by both the Houses of the Parliament. The Act has received the assent of the President of India on 26 May 2015. It came into effect from 1 July 2015.

Income tax return is the form in which assesses file information about his/her income and tax thereon to Income Tax Department. Various forms are ITR 1, ITR 2, ITR 3, ITR 4, ITR 5, ITR 6 and ITR 7. When you file a belated return, you are not allowed to carry forward certain losses.





