Related Research Articles

Gram stain, is a method of staining used to classify bacterial species into two large groups: gram-positive bacteria and gram-negative bacteria. It may also be used to diagnose a fungal infection. The name comes from the Danish bacteriologist Hans Christian Gram, who developed the technique in 1884.

In bacteriology, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria that give a positive result in the Gram stain test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall.

Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that, unlike gram-positive bacteria, do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. Their defining characteristic is their cell envelope, which consists of a thin peptidoglycan cell wall sandwiched between an inner (cytoplasmic) membrane and an outer membrane. These bacteria are found in all environments that support life on Earth.

An agar plate is a Petri dish that contains a growth medium solidified with agar, used to culture microorganisms. Sometimes selective compounds are added to influence growth, such as antibiotics.

Staining is a technique used to enhance contrast in samples, generally at the microscopic level. Stains and dyes are frequently used in histology, in cytology, and in the medical fields of histopathology, hematology, and cytopathology that focus on the study and diagnoses of diseases at the microscopic level. Stains may be used to define biological tissues, cell populations, or organelles within individual cells.

Acute septic arthritis, infectious arthritis, suppurative arthritis, pyogenic arthritis, osteomyelitis, or joint infection is the invasion of a joint by an infectious agent resulting in joint inflammation. Generally speaking, symptoms typically include redness, heat and pain in a single joint associated with a decreased ability to move the joint. Onset is usually rapid. Other symptoms may include fever, weakness and headache. Occasionally, more than one joint may be involved, especially in neonates, younger children and immunocompromised individuals. In neonates, infants during the first year of life, and toddlers, the signs and symptoms of septic arthritis can be deceptive and mimic other infectious and non-infectious disorders.
The cell envelope comprises the inner cell membrane and the cell wall of a bacterium. In Gram-negative bacteria an outer membrane is also included. This envelope is not present in the Mollicutes where the cell wall is absent.
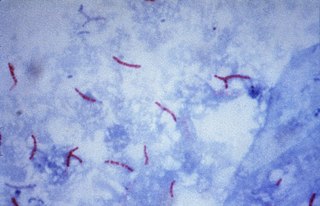
The Ziehl-Neelsen stain, also known as the acid-fast stain, is a bacteriological staining technique used in cytopathology and microbiology to identify acid-fast bacteria under microscopy, particularly members of the Mycobacterium genus. This staining method was initially introduced by Paul Ehrlich (1854–1915) and subsequently modified by the German bacteriologists Franz Ziehl (1859–1926) and Friedrich Neelsen (1854–1898) during the late 19th century.

A blood culture is a medical laboratory test used to detect bacteria or fungi in a person's blood. Under normal conditions, the blood does not contain microorganisms: their presence can indicate a bloodstream infection such as bacteremia or fungemia, which in severe cases may result in sepsis. By culturing the blood, microbes can be identified and tested for resistance to antimicrobial drugs, which allows clinicians to provide an effective treatment.
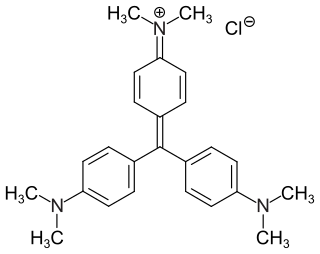
Crystal violet or gentian violet, also known as methyl violet 10B or hexamethyl pararosaniline chloride, is a triarylmethane dye used as a histological stain and in Gram's method of classifying bacteria. Crystal violet has antibacterial, antifungal, and anthelmintic (vermicide) properties and was formerly important as a topical antiseptic. The medical use of the dye has been largely superseded by more modern drugs, although it is still listed by the World Health Organization.

A growth medium or culture medium is a solid, liquid, or semi-solid designed to support the growth of a population of microorganisms or cells via the process of cell proliferation or small plants like the moss Physcomitrella patens. Different types of media are used for growing different types of cells.

A counterstain is a stain with colour contrasting to the principal stain, making the stained structure easily visible using a microscope.
Differential staining is a staining process which uses more than one chemical stain. Using multiple stains can better differentiate between different microorganisms or structures/cellular components of a single organism.

Acridine orange is an organic compound that serves as a nucleic acid-selective fluorescent dye with cationic properties useful for cell cycle determination. Acridine orange is cell-permeable, which allows the dye to interact with DNA by intercalation, or RNA via electrostatic attractions. When bound to DNA, acridine orange is very similar spectrally to an organic compound known as fluorescein. Acridine orange and fluorescein have a maximum excitation at 502nm and 525 nm (green). When acridine orange associates with RNA, the fluorescent dye experiences a maximum excitation shift from 525 nm (green) to 460 nm (blue). The shift in maximum excitation also produces a maximum emission of 650 nm (red). Acridine orange is able to withstand low pH environments, allowing the fluorescent dye to penetrate acidic organelles such as lysosomes and phagolysosomes that are membrane-bound organelles essential for acid hydrolysis or for producing products of phagocytosis of apoptotic cells. Acridine orange is used in epifluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry. The ability to penetrate the cell membranes of acidic organelles and cationic properties of acridine orange allows the dye to differentiate between various types of cells. The shift in maximum excitation and emission wavelengths provides a foundation to predict the wavelength at which the cells will stain.

Löwenstein–Jensen medium, more commonly known as LJ medium, is a growth medium specially used for culture of Mycobacterium species, notably Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Cardiobacterium hominis /ˌkɑːrdiəʊbækˈtɪəriəm ˈhɒmɪnɪs/ is a microaerophilic, pleomorphic, fastidious, Gram-negative bacterium part of the Cardiobacteriaceae family and the HACEK group. It is most commonly found in the human microbiota, specifically the oropharyngeal region including the mouth and upper part of the respiratory tract. It is one of the causes of endocarditis, a life-threatening inflammation close to the heart's inner lining and valves. While infections caused by Cardiobacterium hominis are uncommon, various clinical manifestations are linked to the bacterium, including meningitis, septicemia, and bone infections.
A fastidious organism is any organism that has complex or particular nutritional requirements. In other words, a fastidious organism will only grow when specific nutrients are included in its medium. The more restrictive term fastidious microorganism is used in microbiology to describe microorganisms that will grow only if special nutrients are present in their culture medium. Thus fastidiousness is often practically defined as being difficult to culture, by any method yet tried.
Cardiobacterium valvarum is a Gram-negative species of bacteria belonging to the Cardiobacterium genus. It belongs to the HACEK group of fastidious bacteria that are present in normal oropharyngeal flora and can develop into infective endocarditis.
In microbiology, the term isolation refers to the separation of a strain from a natural, mixed population of living microbes, as present in the environment, for example in water or soil, or from living beings with skin flora, oral flora or gut flora, in order to identify the microbe(s) of interest. Historically, the laboratory techniques of isolation first developed in the field of bacteriology and parasitology, before those in virology during the 20th century.
Columbia Nalidixic Acid (CNA) agar is a growth medium used for the isolation and cultivation of bacteria from clinical and non-clinical specimens. CNA agar contains antibiotics that inhibit Gram-negative organisms, aiding in the selective isolation of Gram-positive bacteria. Gram-positive organisms that grow on the media can be differentiated on the basis of hemolysis.
References
- P. Bruneval et al.. "Detection of fastidious bacteria in cardiac valves in cases of blood culture negative endocarditis." Journal of Clinical Pathology. 54:238-240 (2001).
- D.F. Gimenez. "Staining Rickettsiae in yolksack cultures". Stain Technol39:135–40 (1964).