Related Research Articles
Islamic banking, Islamic finance, or Sharia-compliant finance is banking or financing activity that complies with Sharia and its practical application through the development of Islamic economics. Some of the modes of Islamic banking/finance include Mudarabah, Wadiah (safekeeping), Musharaka, Murabahah (cost-plus), and Ijara (leasing).

The ING Group is a Dutch multinational banking and financial services corporation headquartered in Amsterdam. Its primary businesses are retail banking, direct banking, commercial banking, investment banking, wholesale banking, private banking, asset management, and insurance services. With total assets of US$1.1 trillion, it is one of the biggest banks in the world, and consistently ranks among the top 30 largest banks globally. It is among the top ten largest European companies by revenue.

The Asian financial crisis was a period of financial crisis that gripped much of East Asia and Southeast Asia beginning in July 1997 and raised fears of a worldwide economic meltdown due to financial contagion. However, the recovery in 1998–1999 was rapid and worries of a meltdown subsided. The crisis started in Thailand on 2 July, with the financial collapse of the Thai baht after the Thai government was forced to float the baht due to lack of foreign currency to support its currency peg to the U.S. dollar. Capital flight ensued almost immediately, beginning an international chain reaction. At the time, Thailand had acquired a burden of foreign debt. As the crisis spread, most of Southeast Asia and later South Korea and Japan saw slumping currencies, devalued stock markets and other asset prices, and a precipitous rise in private debt.

Second Life is an online multimedia platform that allows people to create an avatar for themselves and then interact with other users and user created content within a multi player online virtual world. Developed and owned by the San Francisco-based firm Linden Lab and launched on June 23, 2003, it saw rapid growth for some years and in 2013 it had approximately one million regular users. Growth eventually stabilized, and by the end of 2017 the active user count had declined to "between 800,000 and 900,000". In many ways, Second Life is similar to massively multiplayer online role-playing games; nevertheless, Linden Lab is emphatic that their creation is not a game: "There is no manufactured conflict, no set objective".
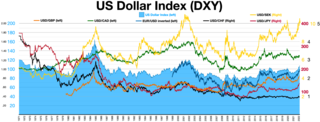
The foreign exchange market is a global decentralized or over-the-counter (OTC) market for the trading of currencies. This market determines foreign exchange rates for every currency. It includes all aspects of buying, selling and exchanging currencies at current or determined prices. In terms of trading volume, it is by far the largest market in the world, followed by the credit market.

The Argentine Great Depression was an economic depression in Argentina, which began in the third quarter of 1998 and lasted until the second quarter of 2002. It followed the fifteen years stagnation and a brief period of free-market reforms.

Philip Rosedale is an American entrepreneur who founded Linden Lab, which develops and hosts the virtual world Second Life.

Linden Research, Inc., doing business as Linden Lab, is an American technology company that is best known as the creator of Second Life.
Economic collapse, also called economic meltdown, is any of a broad range of bad economic conditions, ranging from a severe, prolonged depression with high bankruptcy rates and high unemployment, to a breakdown in normal commerce caused by hyperinflation, or even an economically caused sharp rise in the death rate and perhaps even a decline in population. Often economic collapse is accompanied by social chaos, civil unrest and a breakdown of law and order.
SBI Shinsei Bank, Limited is a leading diversified Japanese financial institution that provides a full range of financial products and services to both institutional and individual customers. It is owned by SBI Group and headquartered in Chuo, Tokyo.

Of all the precious metals, gold is the most popular as an investment. Investors generally buy gold as a way of diversifying risk, especially through the use of futures contracts and derivatives. The gold market is subject to speculation and volatility as are other markets. Compared to other precious metals used for investment, gold has been the most effective safe haven across a number of countries.

The Japanese asset price bubble was an economic bubble in Japan from 1986 to 1991 in which real estate and stock market prices were greatly inflated. In early 1992, this price bubble burst and Japan's economy stagnated. The bubble was characterized by rapid acceleration of asset prices and overheated economic activity, as well as an uncontrolled money supply and credit expansion. More specifically, over-confidence and speculation regarding asset and stock prices were closely associated with excessive monetary easing policy at the time. Through the creation of economic policies that cultivated the marketability of assets, eased the access to credit, and encouraged speculation, the Japanese government started a prolonged and exacerbated Japanese asset price bubble.

MUFG Bank, Ltd. is the largest bank in Japan. It was established on January 1, 2006, following the merger of the Bank of Tokyo-Mitsubishi, Ltd. and UFJ Bank Ltd. MUFG is one of the three so-called Japanese "megabanks". As such, it is considered a systemically important bank by the Financial Stability Board.

The Hokkaidō Takushoku Bank, Ltd., literally Hokkaidō Exploitation Bank, was a major commercial bank in Japan, founded in 1899 as a "Special Bank" to promote capitalism on the island of Hokkaidō. Its nickname was Takugin; it was also known in the media and business world as Hokutaku (北拓). It was the City Bank in its stronghold of Hokkaidō until it went bankrupt in November 1997, and the following year it transferred its business to the North Pacific Bank, which is another bank in Hokkaidō, and others. Its unified financial institution code was 0012.
Teen Second Life was a version of Second Life reserved for teenagers, running on the so-called "Teen Grid." It was officially opened to the public on February 14, 2005 for people aged 13–17 to use Second Life, without entering false information to participate in Second Life . On January 1, 2006, Teen Second Life's operating hours were increased to 24 hours a day, whereas it was previously open only from noon to 10 pm Pacific Time.
The virtual world Second Life has its own economy and a virtual token referred to as Linden Dollars (L$). In the SL economy, users buy from and sell to one another directly, using the Linden, which is a closed-loop virtual token for use only within the Second Life platform. Linden Dollars have no monetary value and are not redeemable for monetary value from Linden Lab. A resident with a surplus of Linden Dollars earned via a Second Life business or experiential play can offer to exchange with other users via the LindeX exchange provided by Linden Lab. This economy is independent of the price of the game, which users pay to Linden Lab, not to each other. Linden Lab reports that the Second Life economy generated US$3,596,674 in economic activity during the month of September 2005, and in September 2006 Second Life was reported to have a GDP of US$64,000,000.
The interbank lending market is a market in which banks lend funds to one another for a specified term. Most interbank loans are for maturities of one week or less, the majority being over day. Such loans are made at the interbank rate. A sharp decline in transaction volume in this market was a major contributing factor to the collapse of several financial institutions during the financial crisis of 2007–2008.
Vancouver City Savings Credit Union, commonly referred to as Vancity, is a member-owned financial co-operative headquartered in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. By asset size, Vancity is the largest community credit union in Canada as of 2019, with CA$28.2 billion in assets plus assets under administration, 60 branches and more than 543,000 members.

The 2007–2008 financial crisis, or Global Financial Crisis (GFC), was a severe worldwide economic crisis that occurred in the early 21st century. It was the most serious financial crisis since the Great Depression (1929). Predatory lending targeting low-income homebuyers, excessive risk-taking by global financial institutions, and the bursting of the United States housing bubble culminated in a "perfect storm." Mortgage-backed securities (MBS) tied to American real estate, as well as a vast web of derivatives linked to those MBS, collapsed in value. Financial institutions worldwide suffered severe damage, reaching a climax with the bankruptcy of Lehman Brothers on September 15, 2008, and a subsequent international banking crisis.
The 2003 banking crisis of Myanmar was a major bank run in private banking that hit Myanmar (Burma) in February 2003. It started with a decline in the trust for private financial institutions following the collapse of small financial enterprises and proliferating rumors about the liquidity of major private banks. Leading to a bank run on the Asia Wealth Bank, the crisis quickly spread to all major private banks in the country. It led to severe liquidity problems for private banks and scarcity of the kyat. Though exact data is not available, it is believed that the crisis caused major economic hardship for many in Myanmar.
References
- 1 2 3 "Ginko's Going...Going?"
- 1 2 The Alphaville Herald, "Ginko Financial’s End-Game", August 6, 2007
- ↑ Linden Labs, "New Policy Regarding Inworld Banks", January 2008