
Juvénal Habyarimana was a Rwandan politician and military officer who was the second president of Rwanda, from 1973 until his assassination in 1994. He was nicknamed Kinani, a Kinyarwanda word meaning "invincible".
The Republican Democratic Movement was a political party in Rwanda.

The Interahamwe is a Hutu paramilitary organization active in the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Uganda. The Interahamwe was formed around 1990 as the youth wing of the National Republican Movement for Democracy and Development, the then-ruling party of Rwanda, and enjoyed the backing of the Hutu Power government. The Interahamwe, led by Robert Kajuga, were the main perpetrators of the Rwandan genocide, during which an estimated 500,000 to 1,000,000 Tutsi, Twa, and moderate Hutus were killed from April to July 1994, and the term "Interahamwe" was widened to mean any civilian militias or bands killing Tutsi.

The Rwandan genocide, also known as the genocide against the Tutsi, occurred between 7 April and 19 July 1994 during the Rwandan Civil War. During this period of around 100 days, members of the Tutsi minority ethnic group, as well as some moderate Hutu and Twa, were killed by armed Hutu militias. Although the Constitution of Rwanda states that more than 1 million people perished in the genocide, the actual number of fatalities is unclear, and some estimates suggest that the real number killed was likely lower. The most widely accepted scholarly estimates are around 500,000 to 800,000 Tutsi deaths.
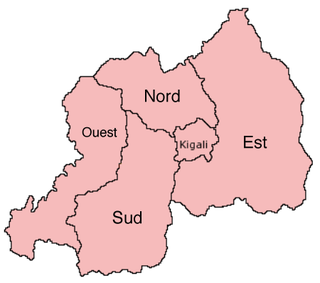
The provinces of Rwanda are divided into districts (akarere) and municipalities (umujyi). Prior to January 1, 2006, Rwanda was composed of 12 provinces. The Rwandan government decided to establish new provinces in an attempt to address issues that arose from the Rwandan genocide. The new provinces were to be "ethnically-diverse administrative areas".

The National Revolutionary Movement for Development was the ruling political party of Rwanda from 1975 to 1994 under President Juvénal Habyarimana, running with first Vice President Édouard Karemera. From 1978 to 1991, the MRND was the only legal political party in the country. It was dominated by Hutus, particularly from President Habyarimana's home region of Northern Rwanda. The elite group of MRND party members who were known to have influence on the President and his wife are known as the akazu. In 1991, the party was renamed the National Republican Movement for Democracy and Development.

Butare was a province (prefecture) of Rwanda prior to its dissolution in January 2006. Butare city was the second largest city in Rwanda and one of the nation's former twelve provinces. It is located in south-central region of the country and borders Burundi to the south. It had a population of 77.449 as of January 2006.
The Rwandan Civil War was a large-scale civil war in Rwanda which was fought between the Rwandan Armed Forces, representing the country's government, and the rebel Rwandan Patriotic Front (RPF) from 1 October 1990 to 18 July 1994. The war arose from the long-running dispute between the Hutu and Tutsi groups within the Rwandan population. A 1959–1962 revolution had replaced the Tutsi monarchy with a Hutu-led republic, forcing more than 336,000 Tutsi to seek refuge in neighbouring countries. A group of these refugees in Uganda founded the RPF which, under the leadership of Fred Rwigyema and Paul Kagame, became a battle-ready army by the late 1980s.
Simon Bikindi was a Rwandan musician and singer who was formerly very popular in Rwanda. His patriotic and nationalist songs were playlist staples on the national radio station Radio Rwanda during the Rwandan Civil War. For his actions during the Rwandan genocide, he was tried and convicted for incitement to genocide by the International Criminal Tribunal for Rwanda (ICTR) in 2008. He died of diabetes at a Beninese hospital in December 2018.

The Hutu Emancipation Movement Party, also known as the Republican Democratic Movement – Parmehutu, was a political party in Rwanda. The movement emphasised the right of the majority ethnicity to rule and asserted the supremacy of Hutus over Tutsis. It was the most important party of the "Hutu Revolution" of 1959–61 that led to Rwanda becoming an independent republic and Hutus superseding Tutsis as the ruling group.

Hassan Ngeze is a Rwandan journalist and convicted war criminal best known for spreading anti-Tutsi propaganda and Hutu superiority through his newspaper, Kangura, which he founded in 1990. Ngeze was a founding member and leadership figure in the Coalition for the Defence of the Republic (CDR), a Rwandan Hutu Power political party that is known for helping to incite the genocide.

The Impuzamugambi was a Hutu militia in Rwanda formed in 1992. Together with the Interahamwe militia, which formed earlier and had more members, the Impuzamugambi was responsible for many of the deaths of Tutsis and moderate Hutus during the Rwandan genocide of 1994.
Callixte Nzabonimana is a former Rwandan politician who is accused of participating in the Rwandan genocide.

The five provinces of Rwanda are divided into 30 districts. Each district is in turn divided into sectors, which are in turn divided into cells, which are in turn divided into villages.

Kangura was a Kinyarwanda and French-language magazine in Rwanda that served to stoke ethnic hatred in the run-up to the Rwandan genocide. The magazine was established in 1990, following the invasion of the rebel Rwandan Patriotic Front (RPF), and continued publishing up to the genocide. Edited by Hassan Ngeze, the magazine was a response to the RPF-sponsored Kanguka, adopting a similar informal style. "Kangura" was a Rwandan word meaning "wake others up", as opposed to "Kanguka", which meant "wake up". The journal was based in Gisenyi.

The Coalition for the Defence of the Republic was a Rwandan far-right Hutu Power political party that took a major role in inciting the Rwandan genocide.

Christianity is the largest organisedreligionin Rwanda. The most recent 2022 census indicated that 92% of Rwanda's population is Christian: 48% is Protestant, 40% is Catholic, 4% belongs to other Christian denominations. 3% claims no religious affiliation. 3% practices other religions including traditional faiths. 2% is Muslim.
These are some of the articles related to Rwanda on the English Wikipedia pages:
Jean-Baptiste Habyalimana was a Rwandan academic and politician who served as the Prefect of Butare and was killed during the Rwandan genocide in 1994. He was the only Tutsi prefect at the time of the genocide, and also the only prefect belonging to the Liberal Party. He had resisted the genocide.
The Bugesera invasion, also known as the Bloody Christmas, was a military attack which was conducted against Rwanda by Inyenzi rebels who aimed to overthrow the government in December 1963. The Inyenzi were a collection of ethnically Tutsi exiles who were affiliated with the Rwandan political party Union Nationale Rwandaise (UNAR), which had supported Rwanda's deposed Tutsi monarchy. The Inyenzi opposed Rwanda's transformation upon independence from Belgium into a state run by the ethnic Hutu majority through the Parti du Mouvement de l'Emancipation Hutu (PARMEHUTU), an anti-Tutsi political party led by President Grégoire Kayibanda. In late 1963, Inyenzi leaders decided to launch an invasion of Rwanda from their bases in neighbouring countries to overthrow Kayibanda. While an attempted assault in November was stopped by the government of Burundi, early in the morning on 21 December 1963, several hundred Inyenzi crossed the Burundian border and captured the Rwandan military in camp in Gako, Bugesera. Bolstered with seized arms and recruited locals, the Iyenzi—numbering between 1,000 and 7,000—marched on the Rwandan capital, Kigali. They were stopped 12 miles south of the city at Kanzenze Bridge along the Nyabarongo River by multiple units of the Garde Nationale Rwandaise (GNR). The GNR routed the rebels with their superior firepower, and in subsequent days repelled further Inyenzi attacks launched from the Republic of the Congo and Uganda.













