
A semi-trailer truck, also known as a semitruck, is the combination of a tractor unit and one or more semi-trailers to carry freight. A semi-trailer attaches to the tractor with a type of hitch called a fifth wheel.
A railway air brake is a railway brake power braking system with compressed air as the operating medium. Modern trains rely upon a fail-safe air brake system that is based upon a design patented by George Westinghouse on April 13, 1869. The Westinghouse Air Brake Company was subsequently organized to manufacture and sell Westinghouse's invention. In various forms, it has been nearly universally adopted.
A Controller Area Network is a robust vehicle bus standard designed to allow microcontrollers and devices to communicate with each other's applications without a host computer. It is a message-based protocol, designed originally for multiplex electrical wiring within automobiles to save on copper, but it can also be used in many other contexts. For each device, the data in a frame is transmitted sequentially but in such a way that if more than one device transmits at the same time, the highest priority device can continue while the others back off. Frames are received by all devices, including by the transmitting device.

The vacuum brake is a braking system employed on trains and introduced in the mid-1860s. A variant, the automatic vacuum brake system, became almost universal in British train equipment and in countries influenced by British practice. Vacuum brakes also enjoyed a brief period of adoption in the United States, primarily on narrow-gauge railroads. Their limitations caused them to be progressively superseded by compressed air systems starting in the United Kingdom from the 1970s onward. The vacuum brake system is now obsolete; it is not in large-scale usage anywhere in the world, other than in South Africa, largely supplanted by air brakes.
Rail terminology is a form of technical terminology. The difference between the American term railroad and the international term railway is the most significant difference in rail terminology. There are also others, due to the parallel development of rail transport systems in different parts of the world.

A kill switch, also known as an emergency stop (E-stop), emergency off (EMO) and as an emergency power off (EPO), is a safety mechanism used to shut off machinery in an emergency, when it cannot be shut down in the usual manner. Unlike a normal shut-down switch or shut-down procedure, which shuts down all systems in order and turns off the machine without damage, a kill switch is designed and configured to abort the operation as quickly as possible and to be operated simply and quickly. Kill switches are usually designed to be noticeable, even to an untrained operator or a bystander.

A trailer is an unpowered vehicle towed by a powered vehicle. It is commonly used for the transport of goods and materials.

A hose is a flexible hollow tube designed to carry fluids from one location to another. Hoses are also sometimes called pipes, or more generally tubing. The shape of a hose is usually cylindrical.
In electrical and mechanical trades and manufacturing, each half of a pair of mating connectors or fasteners is conventionally assigned the designation male or female. The female connector is generally a receptacle that receives and holds the male connector. Sometimes the terms plug and socket or jack are used, particularly in reference to electrical connectors. In some cases, the pins on the connector may have the opposite nominal gender to the mounted connector, such as the RCA connector.
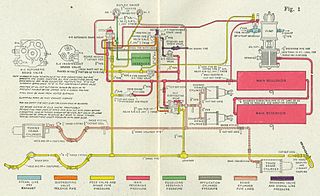
A relay valve is an air-operated valve typically used in air brake systems to remotely control the brakes at the rear of a heavy truck or semi-trailer in a tractor-trailer combination. Relay valves are necessary in heavy trucks in order to speed-up rear-brake application and release, since air takes longer to travel to the rear of the vehicle than the front of the vehicle, where the front service brakes, foot-valve, parking-control valve, and trailer-supply valve are located.
An air line is a tube, or hose, that contains and carries a compressed air supply. In industrial usage, this may be used to inflate car or bicycle tyres or power tools worked by compressed air, for breathing apparatus in hazardous environments and to operate many other pneumatic systems.
This is a glossary of firefighting equipment.

A tow hitch is a device attached to the chassis of a vehicle for towing, or a towbar to an aircraft nose gear. It can take the form of a tow ball to allow swiveling and articulation of a trailer, or a tow pin, or a tow hook with a trailer loop, often used for large or agricultural vehicles where slack in the pivot pin allows similar movements. Another category is the towing pintle used on military vehicles worldwide.

An air brake or, more formally, a compressed-air-brake system, is a type of friction brake for vehicles in which compressed air pressing on a piston is used to apply the pressure to the brake pad or brake shoe needed to stop the vehicle. Air brakes are used in large heavy vehicles, particularly those having multiple trailers which must be linked into the brake system, such as trucks, buses, trailers, and semi-trailers, in addition to their use in railroad trains. George Westinghouse first developed air brakes for use in railway service. He patented a safer air brake on March 5, 1872. Westinghouse made numerous alterations to improve his air pressured brake invention, which led to various forms of the automatic brake. In the early 20th century, after its advantages were proven in railway use, it was adopted by manufacturers of trucks and heavy road vehicles.
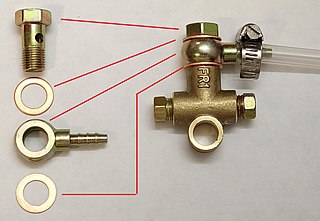
A banjo fitting is a hydraulic fitting consisting of a perforated hollow bolt, or internally relieved bolt, and a spherical union for fluid transfer. It is typically used to connect a fluid line to a rigid, internally threaded hydraulic component. The bolt is assembled through the center of the union, usually with face seals on either side of the union, to create a fluid path between the external ports on the union and bolt. A flexible hose or a rigid pipe may be connected to the union port.
A specialized set of jargon describe the tools, equipment, and employment sectors used in the trucking industry in the United States. Some terms may be used within other English-speaking countries, or within the freight industry in general. For example, shore power is a term borrowed from shipping terminology, in which electrical power is transferred from shore to ship, instead of the ship relying upon idling its engines. Drawing power from land lines is more efficient than engine idling and eliminates localized air pollution. Another borrowed term is "landing gear", which refers to the legs which support the front end of a semi-trailer when it is not connected to a semi-truck. Some nicknames are obvious wordplay, such as "portable parking lot", in reference to a truck that carries automobiles.
Ekebergbanen has operated a series of similar trams for use on the Ekeberg Line, the Simensbråten Line and the line in towards the city center. The trams were in use between 1917 and 1974.
A number of ISO standards cover trailer connectors, the electrical connectors between vehicles and the trailers they tow that provide a means of control for the trailers. These are listed below, with notes on significant deviations from them that can cause problems.

A number of standards prevail in North America, or parts of it, for trailer connectors, the electrical connectors between vehicles and the trailers they tow that provide a means of control for the trailers.

The Mack NJU 5- to 6-ton 4x4 Ponton tractor (G639) was a semi-tractor designed to haul bridging equipment during World War II. Of the 700 built 119 were supplied to the British in Egypt, 8 were built with van bodies, and the rest were used as a substitute standard by the US Army.













