
Fort William is a town in Lochaber in the Scottish Highlands, located on the eastern shore of Loch Linnhe. As of the 2011 Census, Fort William had a population of 10,459, making it the second largest settlement in the Highland council area, and the second largest settlement in the whole of the Scottish Highlands; only the city of Inverness has a larger population.

The Royal Pavilion, also known as the Brighton Pavilion, is a Grade I listed former royal residence located in Brighton, England. Beginning in 1787, it was built in three stages as a seaside retreat for George, Prince of Wales, who became the Prince Regent in 1811, and King George IV in 1820. It is built in the Indo-Saracenic style prevalent in India for most of the 19th century. The current appearance of the Pavilion, with its domes and minarets, is the work of architect John Nash, who extended the building starting in 1815. George IV's successors William IV, and Victoria, also used the Pavilion, but Queen Victoria decided that Osborne House should be the royal seaside retreat, and the Pavilion was sold to the city of Brighton in 1850.
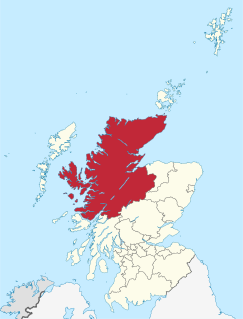
Highland is a council area in the Scottish Highlands and is the largest local government area in the United Kingdom. It was the 7th most populous council area in Scotland at the 2011 census. It shares borders with the council areas of Aberdeenshire, Argyll and Bute, Moray and Perth and Kinross. Their councils, and those of Angus and Stirling, also have areas of the Scottish Highlands within their administrative boundaries.
Glencoe was a place name used by Scottish immigrants to name several places in the world. It may also refer to:

Glencoe or Glencoe Village is the main settlement in Glen Coe in the Lochaber area of the Scottish Highlands. It lies at the north-west end of the glen, on the southern bank of the River Coe where it enters Loch Leven.

The Massacre of Glencoe took place in Glen Coe in the Highlands of Scotland on 13 February 1692. An estimated 30 members and associates of Clan MacDonald of Glencoe were killed by Scottish government forces, allegedly for failing to pledge allegiance to the new monarchs, William II and III and Mary II.

Dunfermline is a town and former Royal Burgh, and parish, in Fife, Scotland, on high ground 3 miles (5 km) from the northern shore of the Firth of Forth. The town recorded a population of 50,380 in 2012, making it the most populous locality in Fife and the 11th most populous in Scotland.

Jordanhill Campus is an historic 30.9-acre (12.5-hectare) estate within the boundaries of Jordanhill, Glasgow, Scotland, which developed as a country estate. It is best known and most recently used as the home to the Faculty of Education of the University of Strathclyde. Empty since 2012, after all previous educational activities were moved to the John Anderson Campus, the site which includes the Grade B listed David Stow building, is now up for sale with "minded to approve" planning permission for up to 364 new homes across 12 plots.
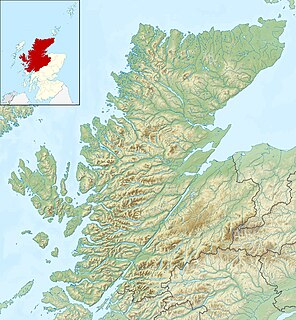
Glen Coe is a glen of volcanic origins, in the Highlands of Scotland. It lies in the north of the county of Argyll, close to the border with the historic province of Lochaber, within the modern council area of Highland. The glen is noted for its scenic beauty. A review by Scottish Natural Heritage in 2010 made reference to the "soaring, dramatic splendour of Glen Coe", and "the suddenness of the transition between high mountain pass and the lightly wooded strath" in the lower glen. It also described the journey through the glen on the main A82 road as "one of the classic Highland journeys". The main settlement is the village of Glencoe located at the foot of the glen. Glen Coe is regarded as the home of Scottish mountaineering and is popular with hillwalkers and climbers.

The Aonach Eagach is a rocky ridge lying to the north of Glen Coe in the Scottish Highlands, boasting two Munro summits. In length the full ridge continues for 10 km from the Pap of Glencoe at the west to the eastern end at the Devil's Staircase. The central section, some 2 km in length, is very rocky and the route along it requires scrambling ability. The slopes to each side are extremely dangerous, with steep grass and scree slopes hiding even steeper slopes which end in cliffs on both north and south sides of the ridge.

Glencoe is situated in the Umzinyathi District, District of KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa.

Clan Donald, also known as Clan MacDonald, is a Highland Scottish clan and one of the largest Scottish clans. The Lord Lyon King of Arms, who is the Scottish official with responsibility for regulating heraldry in that country, issuing new grants of coats of arms, and serving as the judge of the Court of the Lord Lyon, recognizes under Scottish law the High Chief of Clan Donald. Historically the chiefs of the Clan Donald held the title of Lord of the Isles until 1493 and two of those chiefs also held the title of Earl of Ross until 1476.

The Royal United Hospital (RUH) is a major acute-care hospital in the Weston suburb of Bath, England, which lies approximately 1.5 miles (2.4 km) west of the city centre. The hospital has 565 beds and occupies a 52 acres (21 ha) site. It is the area's major accident and emergency hospital, with a helicopter landing point on the adjacent Lansdown Cricket Club field. The hospital is operated by the Royal United Hospitals Bath NHS Foundation Trust.

The Independence Seaport Museum was founded in 1961 and is located in the Penn's Landing complex along the Delaware River in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. The collections at the Independence Seaport Museum document maritime history and culture along the Delaware River. At the museum are two National Historic Landmark ships and the J. Welles Henderson Archives and Library.

Dumfries House is a Palladian country house in Ayrshire, Scotland. It is located within a large estate, around two miles (3 km) west of Cumnock. Noted for being one of the few such houses with much of its original 18th-century furniture still present, including specially commissioned Thomas Chippendale pieces, the house and estate is now owned by The Prince's Foundation, a charity which maintains it as a visitor attraction and hospitality and wedding venue. Both the house and the gardens are listed as significant aspects of Scottish heritage.

NHS Highland is one of the fourteen regions of NHS Scotland. Geographically, it is the largest Health Board, covering an area of 32,500 km2 (12,500 sq mi) from Kintyre in the south-west to Caithness in the north-east, serving a population of 320,000 people. In 2016–17 it had an operating budget of £780 million.

Craig House is a historic house and estate located on Easter Craiglockhart Hill, between the Craiglockhart and Morningside areas of Edinburgh, Scotland. Old Craig House dates from the 16th century, and succeeded an earlier building. In the late 19th century it was purchased by the Royal Edinburgh Hospital, and the site was developed as Craig House Hospital, a psychiatric hospital, including substantial new buildings. Following refurbishment, the site was opened in 1996 as the Craighouse Campus of Edinburgh Napier University.

The Royal Hospital for Sick Children was a hospital in Edinburgh, Scotland, specialising in paediatric healthcare. Locally, it was commonly referred to simply as the Sick Kids. The hospital provided emergency care for children from birth to the 13th birthday, including a specialist Accident and Emergency facility. Some in patient specialties will see children up to the 16th birthday. The hospital was located on Sciennes Road in the Sciennes area of Edinburgh's South Side and was managed by NHS Lothian.
The Lochaber hydroelectric scheme is a hydroelectric power generation project constructed in the Lochaber area of the western Scottish Highlands after the First World War. Like its predecessor at Kinlochleven, it was intended to provide electricity for aluminium production, this time at Fort William, a little further north. It is still in operation.

The West Highland Museum tells the story of the Scottish Highlands and the Islands. It aims to cover every aspect of West Highland history, including that of Fort William, where it is located in a listed building in the centre of the town. It also hosts other exhibits for archaeology and wildlife. The museum, which has always been independent, is a member of Museums Galleries Scotland.




















