Related Research Articles

In computing, a database is an organized collection of data stored and accessed electronically. Small databases can be stored on a file system, while large databases are hosted on computer clusters or cloud storage. The design of databases spans formal techniques and practical considerations including data modeling, efficient data representation and storage, query languages, security and privacy of sensitive data, and distributed computing issues including supporting concurrent access and fault tolerance.
A relational database is a digital database based on the relational model of data, as proposed by E. F. Codd in 1970. A system used to maintain relational databases is a relational database management system (RDBMS). Many relational database systems have an option of using the SQL for querying and maintaining the database.
Interoperability is a characteristic of a product or system to work with other products or systems. While the term was initially defined for information technology or systems engineering services to allow for information exchange, a broader definition takes into account social, political, and organizational factors that impact system-to-system performance.
Object–relational mapping in computer science is a programming technique for converting data between incompatible type systems using object-oriented programming languages. This creates, in effect, a "virtual object database" that can be used from within the programming language. There are both free and commercial packages available that perform object–relational mapping, although some programmers opt to construct their own ORM tools.
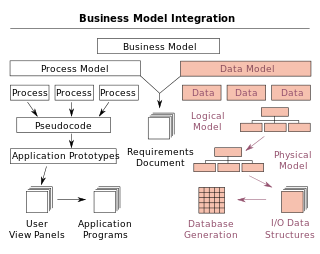
A data model is an abstract model that organizes elements of data and standardizes how they relate to one another and to the properties of real-world entities. For instance, a data model may specify that the data element representing a car be composed of a number of other elements which, in turn, represent the color and size of the car and define its owner.

Db2 is a family of data management products, including database servers, developed by IBM. They initially supported the relational model, but were extended to support object–relational features and non-relational structures like JSON and XML. The brand name was originally styled as DB/2, then DB2 until 2017 and finally changed to its present form.
Computer science is the study of the theoretical foundations of information and computation and their implementation and application in computer systems. One well known subject classification system for computer science is the ACM Computing Classification System devised by the Association for Computing Machinery.

Machine learning (ML) is the study of computer algorithms that can improve automatically through experience and by the use of data. It is seen as a part of artificial intelligence. Machine learning algorithms build a model based on sample data, known as training data, in order to make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed to do so. Machine learning algorithms are used in a wide variety of applications, such as in medicine, email filtering, speech recognition, and computer vision, where it is difficult or unfeasible to develop conventional algorithms to perform the needed tasks.

Theoretical computer science (TCS) is a subset of general computer science and mathematics that focuses on mathematical aspects of computer science such as the theory of computation, lambda calculus, and type theory.
Model Driven Architecture (MDA) is a software design approach for the development of software systems. It provides a set of guidelines for the structuring of specifications, which are expressed as models. Model Driven Architecture is a kind of domain engineering, and supports model-driven engineering of software systems. It was launched by the Object Management Group (OMG) in 2001.
Vasant G. Honavar is an Indian born American computer scientist, and artificial intelligence, machine learning, big data, data science, causal inference, knowledge representation, bioinformatics and health informatics researcher and professor.
JTS Topology Suite is an open-source Java software library that provides an object model for Euclidean planar linear geometry together with a set of fundamental geometric functions. JTS is primarily intended to be used as a core component of vector-based geomatics software such as geographical information systems. It can also be used as a general-purpose library providing algorithms in computational geometry.
A database model is a type of data model that determines the logical structure of a database. It fundamentally determines in which manner data can be stored, organized and manipulated. The most popular example of a database model is the relational model, which uses a table-based format.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to formal science:
The following is provided as an overview of and topical guide to databases:
This glossary of artificial intelligence is a list of definitions of terms and concepts relevant to the study of artificial intelligence, its sub-disciplines, and related fields. Related glossaries include Glossary of computer science, Glossary of robotics, and Glossary of machine vision.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to machine learning. Machine learning is a subfield of soft computing within computer science that evolved from the study of pattern recognition and computational learning theory in artificial intelligence. In 1959, Arthur Samuel defined machine learning as a "field of study that gives computers the ability to learn without being explicitly programmed". Machine learning explores the study and construction of algorithms that can learn from and make predictions on data. Such algorithms operate by building a model from an example training set of input observations in order to make data-driven predictions or decisions expressed as outputs, rather than following strictly static program instructions.
The Open Neural Network Exchange (ONNX) [] is an open-source artificial intelligence ecosystem of technology companies and research organizations that establish open standards for representing machine learning algorithms and software tools to promote innovation and collaboration in the AI sector. ONNX is available on GitHub.
References
- ↑ Tudor R. et al. "The Global Information Network Architecture (GINA) Technology Framework." [ permanent dead link ] Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey CA.