Related Research Articles

Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced in a specific time period. GDP (nominal) per capita does not, however, reflect differences in the cost of living and the inflation rates of the countries; therefore, using a basis of GDP per capita at purchasing power parity (PPP) is arguably more useful when comparing living standards between nations, while nominal GDP is more useful comparing national economies on the international market. Total GDP can also be broken down into the contribution of each industry or sector of the economy. The ratio of GDP to the total population of the region is the per capita GDP and the same is called Mean Standard of Living.

The economy of the United States is a highly developed mixed economy. It is the world's largest economy by nominal GDP and net wealth and the second-largest by purchasing power parity (PPP). It has the world's fifth-highest per capita GDP (nominal) and the seventh-highest per capita GDP (PPP) in 2021. The United States has the most technologically powerful economy in the world and its firms are at or near the forefront in technological advances, especially in artificial intelligence, computers, pharmaceuticals, and medical, aerospace, and military equipment. The U.S. dollar is the currency most used in international transactions and is the world's foremost reserve currency, backed by its economy, its military, the petrodollar system and its linked eurodollar and large U.S. treasuries market. Several countries use it as their official currency and in others it is the de facto currency. The largest U.S. trading partners are China, Canada, Mexico, India, Japan, Germany, South Korea, United Kingdom, France and Taiwan. The U.S. is the world's largest importer and the second-largest exporter. It has free trade agreements with several nations, including the USMCA, Australia, South Korea, Israel, and few others that are in effect or under negotiation.
A variety of measures of national income and output are used in economics to estimate total economic activity in a country or region, including gross domestic product (GDP), gross national product (GNP), net national income (NNI), and adjusted national income. All are specially concerned with counting the total amount of goods and services produced within the economy and by various sectors. The boundary is usually defined by geography or citizenship, and it is also defined as the total income of the nation and also restrict the goods and services that are counted. For instance, some measures count only goods & services that are exchanged for money, excluding bartered goods, while other measures may attempt to include bartered goods by imputing monetary values to them.

The Second World is a term used during the Cold War for the industrial socialist states that were under the influence of the Soviet Union. In the first two decades following World War II, 19 communist states emerged; all of these were at least originally within the Soviet sphere of influence, though some broke with Moscow and developed their own path of socialism while retaining Communist governments. But most communist states remained part of this bloc until the fall of the Soviet Union in 1991; afterwards, only five Communist states remained: China, North Korea, Cuba, Laos, and Vietnam. Along with "First World" and "Third World", the term was used to divide the states of Earth into three broad categories.

The category of newly industrialized country (NIC), newly industrialized economy (NIE) or middle income country is a socioeconomic classification applied to several countries around the world by political scientists and economists. They represent a subset of developing countries whose economic growth is much higher than other developing countries; and where the social consequences of industrialization, such as urbanization, are reorganizing society.

The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistic composite index of life expectancy, education, and per capita income indicators, which are used to rank countries into four tiers of human development. A country scores a higher HDI when the lifespan is higher, the education level is higher, and the gross national income GNI (PPP) per capita is higher. It was developed by Pakistani economist Mahbub ul Haq and was further used to measure a country's development by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)'s Human Development Report Office.

The Index of Economic Freedom is an annual index and ranking created in 1995 by conservative think-tank The Heritage Foundation and The Wall Street Journal to measure the degree of economic freedom in the world's nations. The creators of the index claim to take an approach inspired by Adam Smith's in The Wealth of Nations, that "basic institutions that protect the liberty of individuals to pursue their own economic interests result in greater prosperity for the larger society".
The economies of Canada and the United States are similar because they are both developed countries and are each other's largest trading partners. However, key differences in population makeup, geography, government policies and productivity all result in different economies. While both countries are in the list of top ten economies in the world in 2018, the US is the largest economy in the world, with US$20.4 trillion, with Canada ranking tenth at US$1.8 trillion. The population of Canada in July 2018 was 37,058,856 while the population of the United States was 328,928,146 in November 2018. According to the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD)'s 2018 report, Canadians pay lower personal income taxes than Americans. According to KPMG the corporate tax rate in Canada was 26.50% compared to 27% in the United States based in January 2018 data. Canada's 2017 debt-to-GDP ratio was 89.7%, compared to the United States at 107.8%. In 2016, Canada ranked 24th and the US 30th out of 35 OECD countries in terms of tax revenue to GDP ratio. In the U.S. News & World Report's "2019 Best Countries Report", which ranked 80 countries, Canada ranked 7th on Open for Business compared to the United States which ranked 48th out of the 80 countries. Canada placed first on Quality of Life, 2nd on Citizenship, 6th on Entrepreneurship, and 3rd overall. The US ranked first in terms of Power and fourth in terms of Cultural Influence. The United States on "health outcomes, education levels and other such metrics" scores lower than other rich nations. The United States ranks 2nd and Canada ranks 14th out of 135 countries in terms of economic competitiveness according to the World Economic Forum .https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Global_Competitiveness_Report.

The Kerala model of development refers to the practices adopted in the state of Kerala, India. It is characterized by results showing strong social indicators such as high literacy, improved access to healthcare, high life expectancy, low infant mortality and low birth rate, often at all levels comparable to developed countries despite having a lower per capita income. These achievements along with the factors responsible for such achievements have been considered characteristic results of the Kerala model.

Genuine progress indicator (GPI) is a metric that has been suggested to replace, or supplement, gross domestic product (GDP). The GPI is designed to take fuller account of the well-being of a nation, only a part of which pertains to the size of the nation's economy, by incorporating environmental and social factors which are not measured by GDP. For instance, some models of GPI decrease in value when the poverty rate increases. The GPI separates the concept of societal progress from economic growth.
An emerging market is a market that has some characteristics of a developed market, but does not fully meet its standards. This includes markets that may become developed markets in the future or were in the past. The term "frontier market" is used for developing countries with smaller, riskier, or more illiquid capital markets than "emerging". As of 2006, the economies of China and India are considered to be the largest emerging markets. According to The Economist, many people find the term outdated, but no new term has gained traction. Emerging market hedge fund capital reached a record new level in the first quarter of 2011 of $121 billion. The nine largest emerging and developing economies by either nominal or PPP-adjusted GDP are 4 of the 5 BRICS countries along with Indonesia, South Korea, Mexico, Saudi Arabia and Turkey.

BRIC is a grouping acronym which refers to the countries of Brazil, Russia, India and China deemed to be developing countries at a similar stage of newly advanced economic development, on their way to becoming developed countries. It is typically rendered as "the BRIC," "the BRIC countries," "the BRIC economies," or alternatively as the "Big Four". The name has since been changed to BRICS after the addition of South Africa in 2010.

Global Peace Index (GPI) is a report produced by the Institute for Economics & Peace (IEP) which measures the relative position of nations' and regions' peacefulness. The GPI ranks 172 independent states and territories according to their levels of peacefulness. In the past decade, the GPI has presented trends of increased global violence and less peacefulness.
The Economist Intelligence Unit’s where-to-be-born index attempts to measure which country will provide the best opportunities for a healthy, safe and prosperous life in the years ahead. It is based on a method that links the results of subjective life-satisfaction surveys to the objective determinants of quality of life across countries along with a forward-looking element.
India's per capita net national income or NNI was around 135 thousand rupees in 2020. The per-capita income is a crude indicator of the prosperity of a country. In contrast, the gross national income at constant prices stood at over 128 trillion rupees. The same year, GNI growth rate at constant prices was around 6.6 percent. While GNI and NNI are both indicators for a country's economic performance and welfare, the GNI is related to the GDP or the gross domestic product plus the net receipts from abroad, including wages and salaries, property income, net taxes and subsidies receivable from abroad. On the other hand, the NNI of a country is equal to its GNI net of depreciation.
The Ministry of Public Health in Cameroon is responsible for the maintenance of all public health services. Many missionaries maintain health and leprosy centers. The government is pursuing a vigorous policy of public health improvement, with considerable success in reducing sleeping sickness, leprosy, and other endemic diseases.

Times Higher Education World University Rankings is an annual publication of university rankings by Times Higher Education (THE) magazine. The publisher had collaborated with Quacquarelli Symonds (QS) to publish the joint THE-QS World University Rankings from 2004 to 2009 before it turned to Thomson Reuters for a new ranking system from 2010–2013. The magazine signed a new deal with Elsevier in 2014 who now provide them with the data used to compile the rankings.
3G countries or Global Growth Generating countries are 11 countries which have been identified as sources of growth potential and of profitable investment opportunities.
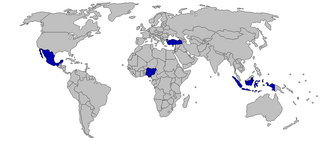
MINT is an acronym referring to the economies of Mexico, Indonesia, Nigeria, and Turkey. The term was originally coined in 2014 by Fidelity Investments, a Boston-based asset management firm, and was popularized by Jim O'Neill of Goldman Sachs, who had created the term BRIC. The term is primarily used in the economic and financial spheres as well as in academia. Its usage has grown specially in the investment sector, where it is used to refer to the bonds issued by these governments. These four countries are also part of the "Next Eleven".
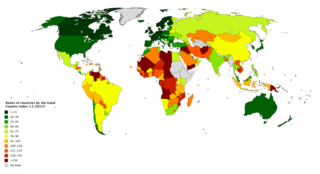
The Good Country Index measures how much each of the 163 countries on the list contribute to the planet, and to the human race, through their policies and behaviors.
References
- 1 2 "Global Retirement Index". Natixis. NGAM. 2017. Retrieved 1 September 2017.
- ↑ "Canada Ranks 11th in 2017 Natixis Global Retirement Index". BusinessWire. 19 July 2017. Retrieved 1 September 2017.
- ↑ "India ranks 43rd in 2017 Global Retirement Index". General Knowledge Today. GKToday. 9 August 2017. Retrieved 1 September 2017.
- ↑ Wooley, Suzanne (19 July 2017). "The U.S. Falls in a Global Retirement Security Ranking". Bloomberg. Retrieved 1 September 2017.
- ↑ Satter, Marlene Y. (21 June 2017). "10 countries topping the global retirement index". BenefitsPro. ALM Media. Retrieved 1 September 2017.