Arthur H. Vinal was an American architect who lived and worked in Boston, Massachusetts. Vinal was born in Quincy, Massachusetts, on July 1, 1855, to Howard Vinal and Clarissa J. Wentworth. Vinal apprenticed at the firm of Peabody & Stearns in Boston before leaving to start his own practice in 1875. Vinal started a partnership with Henry F. Starbuck in 1877; the firm broke up when Starbuck moved away. Vinal served as the third City Architect of Boston from 1884 to 1888. Vinal is principally known for his Richardsonian Romanesque High Service Building at the Chestnut Hill Reservoir (1887). In addition to his other public buildings, Vinal designed numerous residences in Boston and nearby suburbs.
R. H. Stearns & Company, or Stearns, as it was commonly called, was an upper-middle market department store based in Boston, Massachusetts, founded by R. H. Stearns in 1847.

The Boston Museum (1841–1903), also called the Boston Museum and Gallery of Fine Arts, was a theatre, wax museum, natural history museum, zoo, and art museum in 19th-century Boston, Massachusetts. Moses Kimball established the enterprise in 1841.

Court Street is located in the Financial District of Boston, Massachusetts. Prior to 1788, it was called Prison Lane (1634–1708) and then Queen Street (1708–1788). In the 19th century it extended beyond its current length, to Bowdoin Square. In the 1960s most of Court Street was demolished to make way for the construction of Government Center. The remaining street extends a few blocks, near the Old State House on State Street.

Franklin Street is located in the Financial District of Boston, Massachusetts, United States. It was developed at the end of the 18th century by Charles Bulfinch, and included the now-demolished Tontine Crescent and Franklin Place.

The Studio Building (1861–1906) on Tremont Street in Boston, Massachusetts, housed artists' studios, theater companies and other businesses in the 19th century. It "held the true Bohemia of Boston, where artists and literati delighted to gather." Among the tenants were portraitist E.T. Billings, architect George Snell, sculptor Martin Milmore, artists William Morris Hunt, William Rimmer, Edward Mitchell Bannister, Phoebe Jenks; gallerist Seth Morton Vose, and many others.

The Park Theatre (est.1879) was a playhouse in Boston, Massachusetts, in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. It later became the State cinema. Located on Washington Street, near Boylston Street, the building existed until 1990.

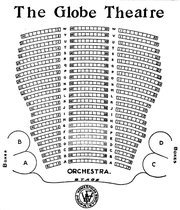
The Globe Theatre (est.1871) was a playhouse in Boston, Massachusetts, in the 19th century. It was located at 598 Washington Street, near the corner of Essex Street. Arthur Cheney oversaw the Globe until 1876. From 1871 to 1873 it occupied the former theatre of John H. Selwyn. After a fire in May 1873, the Globe re-opened on the same site in December 1874. Architect Benjamin F. Dwight designed the new building. From 1877 to 1893 John Stetson served as proprietor; some regarded him as "a theatrical producer with a reputation for illiteracy in his day such as Samuel Goldwyn has achieved" in the 1960s. The theatre burned down in January 1894.

The Columbia Theatre or Loew's New Columbia Theatre in Boston, Massachusetts, was a playhouse and cinema located in the South End at No. 978 Washington Street. Charles Frohman, Isaac Baker Rich and William Harris oversaw the theatre until 1895. Owners included J.J. Grace of New York and Loews. Staff included Harry Farren, Saul Hamilburg and Philip Shea. The Columbia existed until its demolition in 1957.

The Bowdoin Square Theatre (est.1892) in Boston, Massachusetts, was a playhouse and cinema. It was located on Bowdoin Square in the West End, in a building designed by architect C.H. Blackall. Personnel included Charles F. Atkinson and William Harris. Audience members included future magician Julius Linsky and future actor Joseph Sicari

The Tremont Theatre was a playhouse in Boston, Massachusetts, in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Henry E. Abbey and John B. Schoeffel established the enterprise and oversaw construction of its building at no.176 Tremont Street in the Boston Theater District area. Managers included Abbey, Schoeffel and Grau, Klaw & Erlanger, Thos. B. Lothan and Albert M. Sheehan.
The Grand Opera House (est.1888) of Boston, Massachusetts, was a theatre in the South End. Architect George Snell designed the 2,600-seat building on Washington Street. Managers and proprietors included Proctor & Mansfield, A.H. Dexter, George W. Magee, and Stair & Wilbur. Performances included Glyn's Three Weeks.

Grundmann Studios (1893–1917) in Boston, Massachusetts, was a building on Clarendon Street in the Back Bay. It contained artist's workspaces and multipurpose function rooms Copley Hall and Allston Hall. Prior to 1893, it functioned as a skating rink; after the Boston Art Students' Association leased the building it was renamed in honor of local art educator Emil Otto Grundmann. The Massachusetts Institute of Technology, whose campus was adjacent, owned the property. Tenants included the Copley Society ; artists Henry R. Blaney, Herman Dudley Murphy, Frank Richmond, Mary Bradish Titcomb; sculptor John A. Wilson, architect Josephine Wright Chapman; and the College Club.
Chickering Hall (est.1883) was a concert auditorium in Boston, Massachusetts, in the late 19th century. It occupied the second floor of Chickering and Sons showrooms on Tremont Street, near the corner of West Street. "Bradlee, Winslow and Wetherell were the architects, and Mr. E.P. Treadwell, the decorator. The hall [was] lighted by the Edison electric light." By 1895: "Tremont St., towards Boylston, for some years has been called Piano Row, for a long row of piano agencies occupied a good portion of the block; but of late most of these have migrated to Boylston St. Chickering Hall, at 152 Tremont St., was for many years a favorite place for fashionable musicales, and the headquarters of the musical profession."

Chickering Hall (1901–1912) was an auditorium in Boston, Massachusetts, located on Huntington Avenue in the Back Bay. It stood adjacent to Horticultural Hall. Tenants included the Emerson College of Oratory and D.M. Shooshan's "Ladies' and Gents' Cafe." In 1912 it became the St. James Theatre, and later the Uptown Theatre. The building existed until 1963, when it was demolished.

The Park Square Theatre was a theatre in Park Square in Boston, Massachusetts, designed by architect Clarence Blackall. It opened January 19, 1914, as the Cort Theatre, named for impresario John Cort. It was his first theatrical venue in Boston.
The Plymouth Theatre (1911–1957) of Boston, Massachusetts, was located on Stuart Street in today's Boston Theater District. Architect Clarence Blackall designed the building for Liebler & Co. Performers included Henry Jewett, Bill "Bojangles" Robinson, 8-year-old Sammy Davis Jr., and Bette Davis. In October 1911, the touring Abbey Theatre presented Synge's Playboy of the Western World at the Plymouth; in the audience were W. B. Yeats, Isabella Stewart Gardner and Rose Fitzgerald Kennedy.
The Palace Theatre (ca.1891-1931) of Boston, Massachusetts, United States, was a variety theatre on Court Street in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Acts which performed there included Rose Hill Folly Co., Clifford & Dixon, Murry & Murry, Behler & Stone, and the Adamless Eden Burlesquers. It also showed photo-plays such as The Exploits of Elaine, The Master Key, and "Charles Chaplin comedies." Among its managers and proprietors were William Austin, F. J. Pilling, George Milbank, and Dunn & Waldron. The Palace occupied the building of the former Nickelodeon. It existed until 1931, when it was demolished.

The Gaiety Theatre (1908–1949) or Gayety Theatre of Boston, Massachusetts, was located at no.661 Washington Street near Boylston Street in today's Boston Theater District. The theatre was designed by architect Clarence H. Blackall. The Lyceum Theatre was demolished in June 1908 to make way for the Gaiety Theatre which was built on the same site.
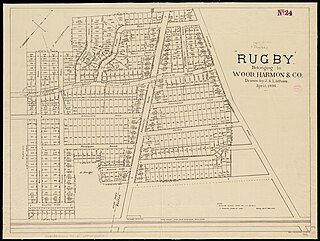
Rugby was a 1894 residential development of 60 acres straddling the border between what was then the western section of the Dorchester district of Boston and the eastern part of the town of Hyde Park, Massachusetts. Described by the developer Wood, Harmon & Co. as a "new Dorchester suburb, commands fine views of Blue Hills", the area was purchased from the estate of Charles L. Flint and others. The area is now part of the Boston neighborhoods of Mattapan and Hyde Park.