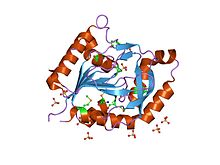
Aspartate carbamoyltransferase catalyzes the first step in the pyrimidine biosynthetic pathway.
Biosynthesis, i.e., chemical synthesis occurring in biological contexts, is a term most often referring to multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed processes where chemical substances absorbed as nutrients serve as enzyme substrates, with conversion by the living organism either into simpler or more complex products. Examples of biosynthetic pathways include those for the production of amino acids, lipid membrane components, and nucleotides, but also for the production of all classes of biological macromolecules, and of acetyl-coenzyme A, adenosine triphosphate, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and other key intermediate and transactional molecules needed for metabolism. Thus, in biosynthesis, any of an array of compounds, from simple to complex, are converted into other compounds, and so it includes both the catabolism and anabolism of complex molecules. Biosynthetic processes are often represented via charts of metabolic pathways. A particular biosynthetic pathway may be located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located across an array of cellular organelles and structures.
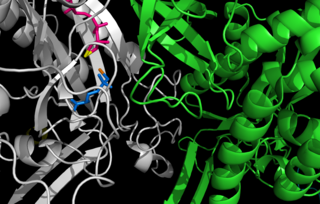
Glutamine synthetase (GS) is an enzyme that plays an essential role in the metabolism of nitrogen by catalyzing the condensation of glutamate and ammonia to form glutamine:
Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I is a ligase enzyme located in the mitochondria involved in the production of urea. Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I transfers an ammonia molecule to a molecule of bicarbonate that has been phosphorylated by a molecule of ATP. The resulting carbamate is then phosphorylated with another molecule of ATP. The resulting molecule of carbamoyl phosphate leaves the enzyme.

Amino acid biosynthesis is the set of biochemical processes by which the amino acids are produced. The substrates for these processes are various compounds in the organism's diet or growth media. Not all organisms are able to synthesize all amino acids. For example, humans can synthesize 11 of the 20 standard amino acids. These 11 are called the non-essential amino acids.

CAD protein is a trifunctional multi-domain enzyme involved in the first three steps of pyrimidine biosynthesis. De-novo synthesis starts with cytosolic carbamoylphosphate synthetase II which uses glutamine, carbon dioxide and ATP. This enzyme is inhibited by uridine triphosphate.
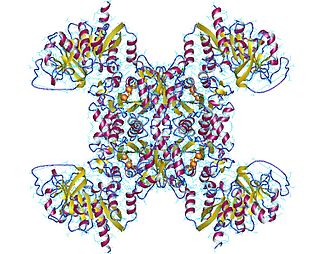
CTP synthase is an enzyme involved in pyrimidine biosynthesis that interconverts UTP and CTP.

Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase catalyzes the ATP-dependent synthesis of carbamoyl phosphate from glutamine or ammonia and bicarbonate. This ATP-grasp enzyme catalyzes the reaction of ATP and bicarbonate to produce carboxy phosphate and ADP. Carboxy phosphate reacts with ammonia to give carbamic acid. In turn, carbamic acid reacts with a second ATP to give carbamoyl phosphate plus ADP.
Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase (glutamine-hydrolysing) is an enzyme that catalyzes the reactions that produce carbamoyl phosphate in the cytosol. Its systemic name is hydrogen-carbonate:L-glutamine amido-ligase .

Guanosine monophosphate synthetase, also known as GMPS is an enzyme that converts xanthosine monophosphate to guanosine monophosphate.

Amidophosphoribosyltransferase (ATase), also known as glutamine phosphoribosylpyrophosphate amidotransferase (GPAT), is an enzyme responsible for catalyzing the conversion of 5-phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate (PRPP) into 5-phosphoribosyl-1-amine (PRA), using the amine group from a glutamine side-chain. This is the committing step in de novo purine synthesis. In humans it is encoded by the PPAT gene. ATase is a member of the purine/pyrimidine phosphoribosyltransferase family.

Isopenicillin N synthase (IPNS) is a non-heme iron protein belonging to the 2-oxoglutarate (2OG)-dependent dioxygenases oxidoreductase family. This enzyme catalyzes the formation of isopenicillin N from δ-(L-α-aminoadipoyl)-L-cysteinyl-D-valine (LLD-ACV).

The enzyme anthranilate synthase catalyzes the chemical reaction
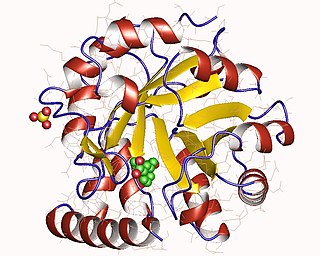
The enzyme indole-3-glycerol-phosphate synthase (IGPS) (EC 4.1.1.48) catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, an aminodeoxychorismate synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a NAD+ synthase (glutamine-hydrolysing) (EC 6.3.5.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a trypanothione synthase (EC 6.3.1.9) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme chorismate synthase catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an aminoacylase (EC 3.5.1.14) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase III is one of the three isoforms of the carbamoyl phosphate synthetase, an enzyme that catalyzes the active production of carbamoyl phosphate in many organisms.