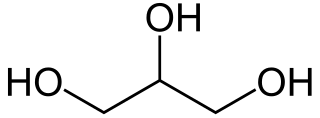
Glycerol, also called glycerine or glycerin, is a simple triol compound. It is a colorless, odorless, viscous liquid that is sweet-tasting and non-toxic. The glycerol backbone is found in lipids known as glycerides. Because it has antimicrobial and antiviral properties, it is widely used in wound and burn treatments approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Conversely, it is also used as a bacterial culture medium. Its presence in blood can be used as an effective marker to measure liver disease. It is also widely used as a sweetener in the food industry and as a humectant in pharmaceutical formulations. Because of its three hydroxyl groups, glycerol is miscible with water and is hygroscopic in nature.

Freezing-point depression is a drop in the maximum temperature at which a substance freezes, caused when a smaller amount of another, non-volatile substance is added. Examples include adding salt into water, alcohol in water, ethylene or propylene glycol in water, adding copper to molten silver, or the mixing of two solids such as impurities into a finely powdered drug.
This page provides supplementary chemical data on acetone.
This page provides supplementary data to the article properties of water.
This page provides supplementary chemical data on methanol.
This page provides supplementary chemical data on carbon dioxide.
This page provides supplementary chemical data on ammonia.
This page provides supplementary chemical data on benzene.
This page provides supplementary chemical data on p-xylene.
This page contains tables of azeotrope data for various binary and ternary mixtures of solvents. The data include the composition of a mixture by weight, the boiling point (b.p.) of a component, the boiling point of a mixture, and the specific gravity of the mixture. Boiling points are reported at a pressure of 760 mm Hg unless otherwise stated. Where the mixture separates into layers, values are shown for upper (U) and lower (L) layers.
This page provides supplementary chemical data on isopropanol.
This page provides supplementary chemical data on ethane.
This page provides supplementary chemical data on aniline.
This page provides supplementary chemical data on ethylene glycol.
This page provides supplementary chemical data on chloroform.
This page provides supplementary chemical data on carbon disulfide.
This page provides supplementary chemical data on o-Xylene.
This page provides supplementary chemical data on m-Xylene.
This page provides supplementary chemical data on 1,2-dichloroethane.
This page provides supplementary chemical data on tetrachloroethylene.




