Related Research Articles

Hannibal was a Carthaginian general and statesman who commanded the forces of Carthage in their battle against the Roman Republic during the Second Punic War.
This article concerns the period 219 BC – 210 BC.

Year 216 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Varro and Paullus. The denomination 216 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

The gens Livia was an illustrious plebeian family at ancient Rome. The first of the Livii to obtain the consulship was Marcus Livius Denter in 302 BC, and from his time the Livii supplied the Republic with eight consuls, two censors, a dictator, and a master of the horse. Members of the gens were honoured with three triumphs. In the reign of Augustus, Livia Drusilla was Roman empress, and her son was the emperor Tiberius.

Lucius Cornelius Scipio Asiaticus was a general and statesman of the Roman Republic. He was the son of Publius Cornelius Scipio and the younger brother of Scipio Africanus. He was elected consul in 190 BC, and later that year led the Roman forces to victory at the Battle of Magnesia.
Publius Sulpicius Galba Maximus was a Roman military officer and Senator who was elected Roman consul twice, and appointed dictator once. He fought in the Second Punic War and the First and Second Macedonian Wars.

Titus Quinctius Flamininus was a Roman politician and general instrumental in the Roman conquest of Greece.
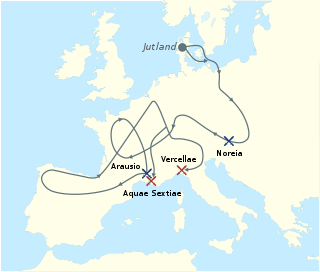
The Battle of Arausio took place on 6 October 105 BC, at a site between the town of Arausio, now Orange, Vaucluse, and the Rhône river. Two Roman armies, commanded by proconsul Quintus Servilius Caepio and consul Gnaeus Mallius Maximus, clashed with the migratory tribes of the Cimbri under Boiorix and the Teutons under Teutobod.
Gaius Norbanus, nicknamed Balbus was a Roman politician who was elected consul in 83 BC alongside Lucius Cornelius Scipio Asiaticus. He committed suicide in exile at Rhodes after being proscribed by Lucius Cornelius Sulla shortly after the latter's victory in the civil war.

Gaius Claudius Nero was a Roman general active during the Second Punic War against the invading Carthaginian force, led by Hannibal Barca. During a military career that began as legate in 214 BC, he was praetor in 212 BC, propraetor in 211 BC during the siege of Capua, before being sent to Spain that same year. He became consul in 207 BC.
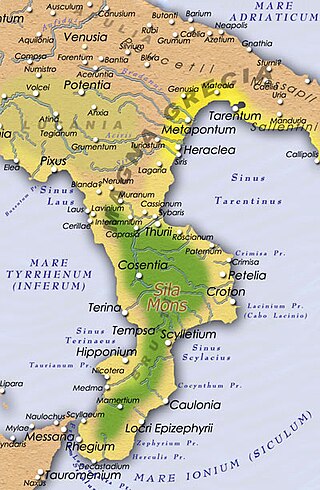
The Battles of Kroton in 204 and 203 BC were, as well as the raid in Cisalpine Gaul, the last larger scale engagements between the Romans and the Carthaginians in Italy during the Second Punic War. After Hannibal’s retreat to Bruttium due to the Metaurus debacle, the Romans continuously tried to block his forces from gaining access to the Ionian Sea and cut his eventual escape to Carthage by capturing Kroton, the last port which had remained in his hands after years of fighting.
Quintus Servilius Caepio was a Roman patrician, statesman and soldier. He was the son of Quintus Servilius Caepio who was consul in 106 BCE and who lost his army during the Battle of Arausio. He was elected praetor some time in the last 90s BC and fought for Rome during the Social War. He was killed in the second year of the war while fighting the Marsi by Quintus Poppaedius Silo.
Marcus Livius Drusus was a Roman politician and reformer. He is most famous for his legislative programme during his term as tribune of the plebs in 91 BC. During his year in office, Drusus proposed wide-ranging legislative reforms, including offering citizenship to Rome's Italian allies.
The gens Sempronia was one of the most ancient and noble houses of ancient Rome. Although the oldest branch of this gens was patrician, with Aulus Sempronius Atratinus obtaining the consulship in 497 BC, the thirteenth year of the Republic, but from the time of the Samnite Wars onward, most if not all of the Sempronii appearing in history were plebeians. Although the Sempronii were illustrious under the Republic, few of them attained any importance or notice in imperial times.

The Roman–Seleucid war (192–188 BC), also called the Aetolian war, Antiochene war, Syrian war, and Syrian-Aetolian war was a military conflict between two coalitions, one led by the Roman Republic and the other led by the Seleucid king Antiochus III. The fighting took place in modern-day southern Greece, the Aegean Sea, and Asia Minor.
The gens Servilia was a patrician family at ancient Rome. The gens was celebrated during the early ages of the Republic, and the names of few gentes appear more frequently at this period in the consular Fasti. It continued to produce men of influence in the state down to the latest times of the Republic, and even in the imperial period. The first member of the gens who obtained the consulship was Publius Servilius Priscus Structus in 495 BC, and the last of the name who appears in the consular Fasti is Quintus Servilius Silanus, in AD 189, thus occupying a prominent position in the Roman state for nearly seven hundred years.

Publius Cornelius Scipio Africanus was a Roman general and statesman, most notable as one of the main architects of Rome's victory against Carthage in the Second Punic War. Often regarded as one of the greatest military commanders and strategists of all time, his greatest military achievement was the defeat of Hannibal at the Battle of Zama in 202 BC. This victory in Africa earned him the honorific epithet Africanus, literally meaning "the African," but meant to be understood as a conqueror of Africa.
Gaius Servilius Geminus was a Roman statesman who served as Consul in 203 BC, Dictator in 202 BC, and Pontifex Maximus from 183 BC to 180 BC.
Gnaeus Servilius Caepio was a Roman statesman. The son of the consul of 203 BC, Gnaeus Servilius Caepio, he also served as Roman consul in 169 BC alongside Quintus Marcius Philippus. He also served as Curule Aedile in 179 BC and as Praetor in 174, when he obtained the province of Further Spain.
Livia Drusa was a Roman matron. She was the daughter of Marcus Livius Drusus, consul in 112 BC, and sister of Marcus Livius Drusus, tribune of the plebs in 91 BC. She was the mother of Cato the Younger, and grandmother of Marcus Junius Brutus, through her oldest daughter Servilia.
References
- ↑ J.C. Yardley (2009). Hannibal's War:, Books 21-30 (Google eBook). Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-162330-1.
- ↑ Livy, XXV, 2
- ↑ Livy, XXVIII, 10
- ↑ Livy, XXVIII, 38 and 46
- ↑ Livy 30 19
- ↑ Livy, XXX, 24
- ↑ Livy, XXXIII, 47 & 49
- ↑ Smith, William (1870). Dictionary of Greek and Roman biography and mythology. Vol. 1. Boston, Little. p. 533.
- ↑ Livy, XLI, 21