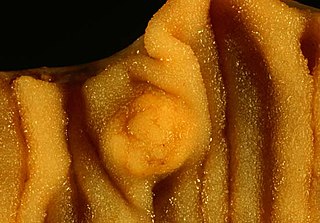
A carcinoid is a slow-growing type of neuroendocrine tumor originating in the cells of the neuroendocrine system. In some cases, metastasis may occur. Carcinoid tumors of the midgut are associated with carcinoid syndrome.

Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) are neoplasms that arise from cells of the endocrine (hormonal) and nervous systems. They most commonly occur in the intestine, where they are often called carcinoid tumors, but they are also found in the pancreas, lung and the rest of the body.
Appendix cancer are very rare cancers of the vermiform appendix.
In pathology, an apudoma is an endocrine tumour that arises from an APUD cell from structures such as the ampulla of Vater. They were historically thought to be derived from neural crest cells, but this has since been shown to be untrue.

An octreotide scan is a type of scintigraphy used to find carcinoid, pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors, and to localize sarcoidosis. It is also called somatostatin receptor scintigraphy (SRS). Octreotide, a drug similar to somatostatin, is radiolabeled with indium-111, and is injected into a vein and travels through the bloodstream. The radioactive octreotide attaches to tumor cells that have receptors for somatostatin. A gamma camera detects the radioactive octreotide, and makes pictures showing where the tumor cells are in the body.

In pathology, salt-and-pepper chromatin, also salt-and-pepper nuclei and stippled chromatin, refers to cell nuclei that demonstrate granular chromatin.
Large-cell carcinoma (LCC) is a heterogeneous group of undifferentiated malignant neoplasms that lack the cytologic and architectural features of small cell carcinoma and glandular or squamous differentiation. LCC is categorized as a type of NSCLC which originates from epithelial cells of the lung.

Fetal adenocarcinoma (FA) of the lung is a rare subtype of pulmonary adenocarcinoma that exhibits tissue architecture and cell characteristics that resemble fetal lung tissue upon microscopic examination. It is currently considered a variant of solid adenocarcinoma with mucin production.
Large cell lung carcinoma with rhabdoid phenotype (LCLC-RP) is a rare histological form of lung cancer, currently classified as a variant of large cell lung carcinoma (LCLC). In order for a LCLC to be subclassified as the rhabdoid phenotype variant, at least 10% of the malignant tumor cells must contain distinctive structures composed of tangled intermediate filaments that displace the cell nucleus outward toward the cell membrane. The whorled eosinophilic inclusions in LCLC-RP cells give it a microscopic resemblance to malignant cells found in rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS), a rare neoplasm arising from transformed skeletal muscle. Despite their microscopic similarities, LCLC-RP is not associated with rhabdomyosarcoma.
Epithelial-myoepithelial carcinoma of the lung is a very rare histologic form of malignant epithelial neoplasm ("carcinoma") arising from lung tissue.
Endocrine oncology refers to a medical speciality dealing with hormone producing tumors, i.e. a combination of endocrinology and oncology.
Adenosquamous lung carcinoma (AdSqLC) is a biphasic malignant tumor arising from lung tissue that is composed of at least 10% by volume each of squamous cell carcinoma (SqCC) and adenocarcinoma (AdC) cells.
A ceruminous adenoma is a benign glandular neoplasm which arises from the ceruminous glands located within the external auditory canal. These glands are found within the outer one third to one half of the external auditory canal, more common along the posterior surface; therefore, the tumor develops within a very specific location.
Neuroendocrine adenoma middle ear (NAME) is a tumor which arises from a specific anatomic site: middle ear. NAME is a benign glandular neoplasm of middle ear showing histologic and immunohistochemical neuroendocrine and mucin-secreting differentiation.

Typical pulmonary carcinoid tumour is a subtype of pulmonary carcinoid tumour. It is an uncommon low-grade malignant lung mass that is most often in the central airways of the lung.
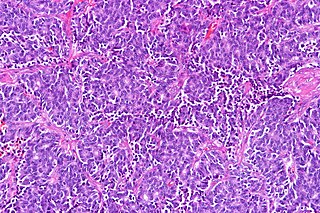
Atypical pulmonary carcinoid tumour is a subtype of pulmonary carcinoid tumor. It is an uncommon low-grade malignant lung mass that is most often in the central airways of the lung. It is also known as "atypical lung carcinoid tumour", " atypical lung carcinoid" or "moderately differentiated neuroendocrine carcinoma".
Pulmonary neuroendocrine tumors are neuroendocrine tumors localized to the lung: bronchus or pulmonary parenchyma.
Neuroendocrine differentiation is a term primarily used in relation to prostate cancers that display a significant neuroendocrine cell population on histopathological examination. These types of prostate cancer comprise true neuroendocrine cancers, such as small cell carcinoma, carcinoid and carcinoid-like tumors, as well as prostatic adenocarcinoma exhibiting focal neuroendocrine phenotype.

Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors, often referred to as "islet cell tumors", or "pancreatic endocrine tumors" are neuroendocrine neoplasms that arise from cells of the endocrine (hormonal) and nervous system within the pancreas.
Diffuse idiopathic pulmonary neuroendocrine cell hyperplasia (DIPNECH) is a diffuse parenchymal lung disease which often presents with symptoms of cough and shortness of breath. The pathological definition published by the World Health Organization is “a generalized proliferation of scattered single cells, small nodules, or linear proliferations of pulmonary neuroendocrine (PNE) cells that may be confined to the bronchial and bronchiolar epithelium.” The true prevalence of this disease is not known. To date, just under 200 cases have been reported in the literature. However, with an increase in recognition of this disease by radiologists and pulmonologists, the number of cases has been increasing. DIPNECH predominantly affects middle-aged women with slowly progressive lung obstruction. DIPNECH is usually discovered in one of two ways: 1) as an unexpected finding following a lung surgery; or 2) by evaluation of a patient in a pulmonary clinic with longstanding, unexplained symptoms.









