
A golem is an animated anthropomorphic being in Jewish folklore, which is created entirely from inanimate matter, usually clay or mud. The most famous golem narrative involves Judah Loew ben Bezalel, the late 16th-century rabbi of Prague. According to Moment magazine, "the golem is a highly mutable metaphor with seemingly limitless symbolism. It can be a victim or villain, man or woman—or sometimes both. Over the centuries, it has been used to connote war, community, isolation, hope, and despair."

Philip R. Zimmermann is an American computer scientist and cryptographer. He is the creator of Pretty Good Privacy (PGP), the most widely used email encryption software in the world. He is also known for his work in VoIP encryption protocols, notably ZRTP and Zfone. Zimmermann is co-founder and Chief Scientist of the global encrypted communications firm Silent Circle.

Norbert Wiener was an American computer scientist, mathematician and philosopher. He became a professor of mathematics at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). A child prodigy, Wiener later became an early researcher in stochastic and mathematical noise processes, contributing work relevant to electronic engineering, electronic communication, and control systems.
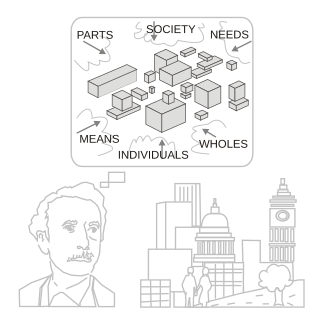
Systems thinking is a way of making sense of the complexity of the world by looking at it in terms of wholes and relationships rather than by splitting it down into its parts. It has been used as a way of exploring and developing effective action in complex contexts, enabling systems change. Systems thinking draws on and contributes to systems theory and the system sciences.

The Hyperion Cantos is a series of science fiction novels by Dan Simmons. The title was originally used for the collection of the first pair of books in the series, Hyperion and The Fall of Hyperion, and later came to refer to the overall storyline, including Endymion, The Rise of Endymion, and a number of short stories. More narrowly, inside the fictional storyline, after the first volume, the Hyperion Cantos is an epic poem written by the character Martin Silenus covering in verse form the events of the first two books.

William Ross Ashby was an English psychiatrist and a pioneer in cybernetics, the study of the science of communications and automatic control systems in both machines and living things. His first name was not used: he was known as Ross Ashby.

Walter Harry Pitts, Jr. was an American logician who worked in the field of computational neuroscience. He proposed landmark theoretical formulations of neural activity and generative processes that influenced diverse fields such as cognitive sciences and psychology, philosophy, neurosciences, computer science, artificial neural networks, cybernetics and artificial intelligence, together with what has come to be known as the generative sciences. He is best remembered for having written along with Warren Sturgis McCulloch, a seminal paper in scientific history, titled A Logical Calculus of Ideas Immanent in Nervous Activity (1943). This paper proposed the first mathematical model of a neural network. The unit of this model, a simple formalized neuron, is still the standard of reference in the field of neural networks. It is often called a McCulloch–Pitts neuron. Prior to that paper, he formalized his ideas regarding the fundamental steps to building a Turing machine in "The Bulletin of Mathematical Biophysics" in an essay titled "Some observations on the simple neuron circuit".
A Himmelsbrief, also known as a "heaven's letter" or "heavenly letter", is a religious documents said to have been written by God or a divine agent. Their purpose is to protect the bearer or place from all evil and danger; however, there is a price for their protection. Bearers will only be protected so long as they abide by the moral covenants detailed in the letter.

Warren Weaver was an American scientist, mathematician, and science administrator. He is widely recognized as one of the pioneers of machine translation and as an important figure in creating support for science in the United States.

Robert Wright is an American author and journalist known for his wide-ranging interests in philosophy, society, science, history, politics, international relations, and religion. He has published five books: Three Scientists and Their Gods: Looking for Meaning in an Age of Information (1988), The Moral Animal (1994), Nonzero: The Logic of Human Destiny (1999), The Evolution of God (2009), and Why Buddhism is True (2017). Wright has taught at Princeton University and the University of Pennsylvania; more recently, in 2019 he was Visiting Professor of Science and Religion at Union Theological Seminary, New York.
Norman Levinson was an American mathematician. Some of his major contributions were in the study of Fourier transforms, complex analysis, non-linear differential equations, number theory, and signal processing. He worked closely with Norbert Wiener in his early career. He joined the faculty of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in 1937. In 1954, he was awarded the Bôcher Memorial Prize of the American Mathematical Society and in 1971 the Chauvenet Prize of the Mathematical Association of America for his paper A Motivated Account of an Elementary Proof of the Prime Number Theorem. In 1974 he published a paper proving that more than a third of the zeros of the Riemann zeta function lie on the critical line, a result later improved to two fifths by Conrey.

MIT Technology Review is a bimonthly magazine wholly owned by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. It was founded in 1899 as The Technology Review, and was re-launched without "The" in its name on April 23, 1998, under then publisher R. Bruce Journey. In September 2005, it was changed, under its then editor-in-chief and publisher, Jason Pontin, to a form resembling the historical magazine.

Jon Kabat-Zinn is an American professor emeritus of medicine and the creator of the Stress Reduction Clinic and the Center for Mindfulness in Medicine, Health Care, and Society at the University of Massachusetts Medical School. Kabat-Zinn was a student of Zen Buddhist teachers such as Philip Kapleau, Thich Nhat Hanh, and Seung Sahn, and a founding member of Cambridge Zen Center. His practice of hatha yoga, Vipassanā and appreciation of the teachings of Soto Zen and Advaita Vedanta led him to integrate their teachings with scientific findings. He teaches mindfulness, which he says can help people cope with stress, anxiety, pain, and illness. The stress reduction program created by Kabat-Zinn, mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR), is offered by medical centers, hospitals, and health maintenance organizations, and is described in his book Full Catastrophe Living.

Arturo Rosenblueth Stearns was a Mexican researcher, physician and physiologist, who is known as one of the pioneers of cybernetics.
Thomas B. Sheridan is an American professor of mechanical engineering and Applied Psychology Emeritus at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. He is a pioneer of robotics and remote control technology.
David Alexander Vogan Jr. is a mathematician at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology who works on unitary representations of simple Lie groups.

Cybernetics is the transdisciplinary study of circular causal processes such as feedback and recursion, where the effects of a system's actions return as inputs to that system, influencing subsequent action. It is concerned with general principles that are relevant across multiple contexts, including in ecological, technological, economic, biological, cognitive and social systems and also in practical activities such as designing, learning, and managing. Cybernetics' transdisciplinary character has meant that it intersects with a number of other fields, leading to it having both wide influence and diverse interpretations.

David Leigh Donoho is an American statistician. He is a professor of statistics at Stanford University, where he is also the Anne T. and Robert M. Bass Professor in the Humanities and Sciences. His work includes the development of effective methods for the construction of low-dimensional representations for high-dimensional data problems, development of wavelets for denoising and compressed sensing. He was elected a Member of the American Philosophical Society in 2019.
Robert Horton Cameron was an American mathematician, who worked on analysis and probability theory. He is known for the Cameron–Martin theorem.

Cybernetics: Or Control and Communication in the Animal and the Machine is a book written by Norbert Wiener and published in 1948. It is the first public usage of the term "cybernetics" to refer to self-regulating mechanisms. The book laid the theoretical foundation for servomechanisms, automatic navigation, analog computing, artificial intelligence, neuroscience, and reliable communications.















