Related Research Articles

A rocket is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to accelerate without using the surrounding air. A rocket engine produces thrust by reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entirely from propellant carried within the vehicle; therefore a rocket can fly in the vacuum of space. Rockets work more efficiently in a vacuum and incur a loss of thrust due to the opposing pressure of the atmosphere.
Altitude or height is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum and a point or object. The exact definition and reference datum varies according to the context. Although the term altitude is commonly used to mean the height above sea level of a location, in geography the term elevation is often preferred for this usage.


Robert Hutchings Goddard was an American engineer, professor, physicist, and inventor who is credited with creating and building the world's first liquid-fueled rocket. Goddard successfully launched his rocket on March 16, 1926, which ushered in an era of space flight and innovation. He and his team launched 34 rockets between 1926 and 1941, achieving altitudes as high as 2.6 km (1.6 mi) and speeds as fast as 885 km/h (550 mph).

The Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) is a major NASA space research laboratory located approximately 6.5 miles (10.5 km) northeast of Washington, D.C. in Greenbelt, Maryland, United States. Established on May 1, 1959 as NASA's first space flight center, GSFC employs approximately 10,000 civil servants and contractors. Named in recognition of American rocket propulsion pioneer Robert H. Goddard, it is one of ten major NASA field centers. GSFC is partially within the former Goddard census-designated place; it has a Greenbelt mailing address.

The Bell X-2 was an X-plane research aircraft built to investigate flight characteristics in the Mach 2–3 range. The X-2 was a rocket-powered, swept-wing research aircraft developed jointly in 1945 by Bell Aircraft Corporation, the United States Air Force and the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) to explore aerodynamic problems of supersonic flight and to expand the speed and altitude regimes obtained with the earlier X-1 series of research aircraft.

Terra is a multi-national, NASA scientific research satellite in a Sun-synchronous orbit around the Earth that takes simultaneous measurements of Earth's atmosphere, land, and water to understand how Earth is changing and to identify the consequences for life on Earth. It is the flagship of the Earth Observing System (EOS) and the first satellite of the system which was followed by Aqua and Aura. Terra was launched in 1999.
A geocentric orbit, Earth-centered orbit, or Earth orbit involves any object orbiting Earth, such as the Moon or artificial satellites. In 1997, NASA estimated there were approximately 2,465 artificial satellite payloads orbiting Earth and 6,216 pieces of space debris as tracked by the Goddard Space Flight Center. More than 16,291 objects previously launched have undergone orbital decay and entered Earth's atmosphere.

Space launch is the earliest part of a flight that reaches space. Space launch involves liftoff, when a rocket or other space launch vehicle leaves the ground, floating ship or midair aircraft at the start of a flight. Liftoff is of two main types: rocket launch, and non-rocket spacelaunch.

Cabin pressurization is a process in which conditioned air is pumped into the cabin of an aircraft or spacecraft in order to create a safe and comfortable environment for humans flying at high altitudes. For aircraft, this air is usually bled off from the gas turbine engines at the compressor stage, and for spacecraft, it is carried in high-pressure, often cryogenic, tanks. The air is cooled, humidified, and mixed with recirculated air by one or more environmental control systems before it is distributed to the cabin.

Operation Fishbowl was a series of high-altitude nuclear tests in 1962 that were carried out by the United States as a part of the larger Operation Dominic nuclear test program. Flight-test vehicles were designed and manufactured by Avco Corporation.

Samuel Pearson "Terry" Goddard III is an American attorney and politician who served as the mayor of Phoenix, Arizona from 1984 to 1990 and as the 24th attorney general of Arizona from 2003 to 2011. He is a member of the Democratic Party.

The Goddard Rocket Launching Site is a National Historic Landmark commemorating the launch site of the world's first successful liquid-fueled rocket.

The Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) is a NASA mission which has been observing the Sun since 2010. Launched on 11 February 2010, the observatory is part of the Living With a Star (LWS) program.

A medium Earth orbit (MEO) is an Earth-centered orbit with an altitude above a low Earth orbit (LEO) and below a high Earth orbit (HEO) – between 2,000 and 35,786 km above sea level.

Project Highwater was an experiment carried out as part of two of the test flights of NASA's Saturn I launch vehicle, successfully launched into a sub-orbital trajectory from Cape Canaveral, Florida. The Highwater experiment sought to determine the effect of a large volume of water suddenly released into the ionosphere. The project answered questions about the effect of the diffusion of propellants in the event that a rocket was destroyed at high altitude.

George William Goddard was a United States Air Force brigadier general and a pioneer in aerial photography.

Vertical takeoff, vertical landing (VTVL) is a form of takeoff and landing for rockets. Multiple VTVL craft have flown. The most widely known and commercially successful VTVL rocket is SpaceX's Falcon 9 first stage.
The Particle Astrophysics Magnet Facility is a NASA project that was designed to investigate anti-matter. It consisted of a series of experiments which would culminate in an experiment launched in 1995 to be externally attached to the Freedom Space Station
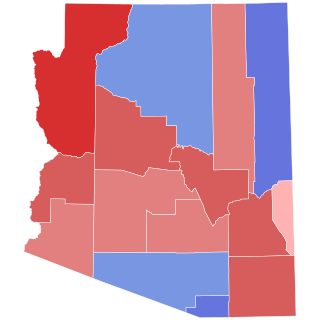
The 2010 Arizona gubernatorial election was held on November 2, 2010, to elect the Governor of Arizona. Incumbent Republican Jan Brewer ran for a full term. Party primaries were held on August 24, 2010. Jan Brewer won a full term, defeating Arizona Attorney General and Democratic nominee Terry Goddard 54% to 42%.
References
- ↑ E.M. Cliff. "Goddard Problem (slides)" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2010-06-24. Retrieved 2010-04-29.
- ↑ Boris Garfinkel. A Solution of the Goddard Problem (Report). Archived from the original on September 27, 2021.