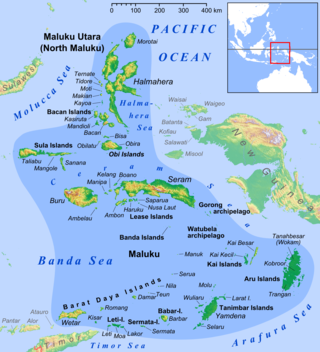
The Maluku Islands or the Moluccas are an archipelago in the eastern part of Indonesia. Tectonically they are located on the Halmahera Plate within the Molucca Sea Collision Zone. Geographically they are located east of Sulawesi, west of New Guinea, and north and east of Timor. Lying within Wallacea, the Moluccas have been considered a geographical and cultural intersection of Asia and Oceania.

The Bacan Islands, formerly also known as the Bachans, Bachians, and Batchians, are a group of islands in the Moluccas in Indonesia. They are mountainous and forested, lying south of Ternate and southwest of Halmahera. The islands are administered by the South Halmahera Regency of North Maluku Province. They formerly constituted the Sultanate of Bacan.

The Malay Archipelago is the archipelago between Mainland Southeast Asia and Australia, and is also called Insulindia or the Indo-Australian Archipelago. The name was taken from the 19th-century European concept of a Malay race, later based on the distribution of Austronesian languages. It has also been called the "Malay world," "Nusantara", "East Indies" over time. The name is controversial in Indonesia due to its ethnic connotations and colonial undertones, which can overshadow the country's diverse cultures.

Seram is the largest and main island of Maluku province of Indonesia, despite Ambon Island's historical importance. It is located just north of the smaller Ambon Island and a few other adjacent islands, such as Saparua, Haruku, Nusa Laut and the Banda Islands.

Halmahera, formerly known as Jilolo, Gilolo, or Jailolo, is the largest island in the Maluku Islands. It is part of the North Maluku province of Indonesia, and Sofifi, the capital of the province, is located on the west coast of the island.
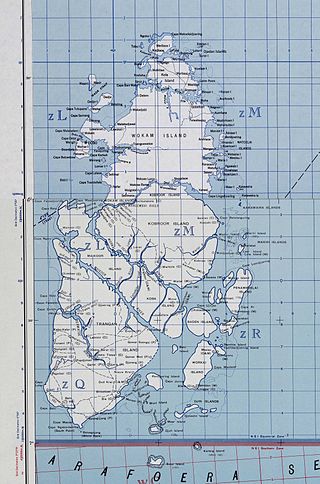
The Aru Islands Regency is a group of about 95 low-lying islands in the Maluku Islands of eastern Indonesia. It also forms a regency of Maluku Province, with a land area of 6,426.77 km2 (2,481.39 sq mi). At the 2011 Census the Regency had a population of 84,138; the 2020 Census produced a total of 102,237, and the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 108,834. Some sources regard the archipelago as part of Asia, while others regard it as part of Melanesia.

Wallacea is a biogeographical designation for a group of mainly Indonesian islands separated by deep-water straits from the Asian and Australian continental shelves. Wallacea includes Sulawesi, the largest island in the group, as well as Lombok, Sumbawa, Flores, Sumba, Timor, Halmahera, Buru, Seram, and many smaller islands. The islands of Wallacea lie between the Sunda Shelf to the west, and the Sahul Shelf including Australia and New Guinea to the south and east. The total land area of Wallacea is 347,000 km2 (134,000 sq mi).

The Babar Islands(Indonesian: Kepulauan Babar) are located in Maluku Province, Indonesia between latitudes 7 degrees 31 minutes South to 8 degrees 13 minutes South and from longitudes 129 degrees 30 minutes East to 130 degrees 05 minutes East. The group now constitutes five districts (kecamatan) within the Maluku Barat Daya Regency of Maluku province.

The Obi Islands are a group of 42 islands in the Indonesian province of North Maluku, north of Buru and Ceram, and south of Halmahera. With a total area of 3,048.08 km2, they had a population of 41,455 at the 2010 Census and 50,760 at the 2020 Census. The official estimate as at mid 2023 was 53,182.

Alfur, Alfurs, Alfuros, Alfures, Aliforoes, Alifuru or Horaforas people is a broad term recorded at the time of the Portuguese seaborne empire to refer all the non-Muslim, non-Christian peoples living in inaccessible areas of the interior in the eastern portion of Maritime Southeast Asia, mainly from the Arafura Sea area.

The Seram Sea or Ceram Sea is one of several small seas between the scattered islands of Indonesia. It is a section of the Pacific Ocean with an area of approximately 120,000 km2 (46,000 sq mi) located between Buru and Seram, which are two of the islands once called the South Moluccas. These islands are the native habitat of plants long coveted for their use as spices, such as nutmeg, cloves, and black peppercorns, and the seas surrounding them were busy shipping routes. The Seram Sea is also the habitat of several species of tropical goby and many other fish. Like many other small Indonesian seas, the Seram Sea is rocky and very tectonically active.

The Malay Archipelago is a book by the British naturalist Alfred Russel Wallace which chronicles his scientific exploration, during the eight-year period 1854 to 1862, of the southern portion of the Malay Archipelago including Malaysia, Singapore, the islands of Indonesia, then known as the Dutch East Indies, and the island of New Guinea. It was published in two volumes in 1869, delayed by Wallace's ill health and the work needed to describe the many specimens he brought home. The book went through ten editions in the nineteenth century; it has been reprinted many times since, and has been translated into at least twelve languages.

The common paradise kingfisher, also known as the Galatea paradise kingfisher and the racquet-tailed kingfisher, is a species of bird in the family Alcedinidae. It is found in subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests of the Maluku Islands and New Guinea. Like all paradise kingfishers, it has a red bill and colourful plumage. The species is common and the IUCN has assessed its conservation status as being of "least concern".

Watubela is an archipelago in the Maluku Islands, east of Ceram and north of Kai Islands, southeast of the Gorong archipelago, and southwest of the Bomberai Peninsula of Papua, Indonesia. It includes the islands of Watubela itself, Kesui and Teor. The total land area is 60.99 km2, of which Watubela and Kesui together cover 37.58 km2 and Teor covers 23.41 km2.

Central Maluku Regency is a regency of Maluku Province of Indonesia. The Regency covers an area of 11,595.57 km2, and had a population of 361,698 at the 2010 Census, and 423,094 at the 2020 Census. The official estimate as at mid 2023 was 430,798. The principal town lies at Masohi, on Seram Island. The regency (kebupaten) is composed of the central part of the island of Seram, the Banda Islands, and the Lease Islands, together with those parts of Ambon Island which are outside the City of Ambon.

Southwest Maluku Regency is a regency of Maluku Province, Indonesia. Geographically it forms the most eastern portion of the Lesser Sunda Islands, although it has never been administratively included with them, and politically has always comprised a part of the Maluku Province. It comprises a number of islands and island groups in the south of the province, including Lirang Island, Wetar Island, Kisar Island, Romang Island, the Letti Islands, the Damer Islands, the Sermata Islands and the Babar Islands. The total land area is 4,581.06 km2, and the population was 70,714 at the 2010 Census and 81,928 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 93,766.

East Seram Regency is a regency of Maluku (province), in Indonesia. It is mainly located on the island of Seram, but also includes smaller islands to the southeast comprising the Gorom and Watubela archipelagoes. The regency covers a land area of 5,779.12 km2, and had a population of 99,065 at the 2010 Census and 137,972 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 138,580. The principal town lies at Bula, on Seram Island.

Kayoa, or in the native language Pulau Urimatiti, is a group of 66 islands, part of the Maluku Islands. It is located in South Halmahera Regency, part of North Maluku Province of Indonesia.

Manipa Island is an island in West Seram Regency, Maluku Province, Indonesia. It is located 8 km off the western coast of Kelang at the western end of Seram Island and 25 km off the western coast of Buru. Including adjacent small islands, it forms an administrative district (kecamatan) within the regency, with its district centre at Masawoi. The district covers an area of 159.71 km2 and had a population of 7,165 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 7,793.
















