Eccentricity or eccentric may refer to:
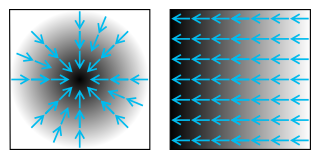
In vector calculus, the gradient of a scalar-valued differentiable function of several variables is the vector field whose value at a point gives the direction and the rate of fastest increase. The gradient transforms like a vector under change of basis of the space of variables of . If the gradient of a function is non-zero at a point , the direction of the gradient is the direction in which the function increases most quickly from , and the magnitude of the gradient is the rate of increase in that direction, the greatest absolute directional derivative. Further, a point where the gradient is the zero vector is known as a stationary point. The gradient thus plays a fundamental role in optimization theory, where it is used to minimize a function by gradient descent. In coordinate-free terms, the gradient of a function may be defined by:

A magnetometer is a device that measures magnetic field or magnetic dipole moment. Different types of magnetometers measure the direction, strength, or relative change of a magnetic field at a particular location. A compass is one such device, one that measures the direction of an ambient magnetic field, in this case, the Earth's magnetic field. Other magnetometers measure the magnetic dipole moment of a magnetic material such as a ferromagnet, for example by recording the effect of this magnetic dipole on the induced current in a coil.
Grade most commonly refers to:
Vector most often refers to:
Projection, projections or projective may refer to:
A temperature gradient is a physical quantity that describes in which direction and at what rate the temperature changes the most rapidly around a particular location. The temperature spatial gradient is a vector quantity with dimension of temperature difference per unit length. The SI unit is kelvin per meter (K/m).
Potential generally refers to a currently unrealized ability, in a wide variety of fields from physics to the social sciences.
Conservatism is a set of political philosophies that favour tradition.
Curl or CURL may refer to:
Geomorphometry, or geomorphometrics, is the science and practice of measuring the characteristics of terrain, the shape of the surface of the Earth, and the effects of this surface form on human and natural geography. It gathers various mathematical, statistical and image processing techniques that can be used to quantify morphological, hydrological, ecological and other aspects of a land surface. Common synonyms for geomorphometry are geomorphological analysis, terrain morphometry, terrain analysis, and land surface analysis. Geomorphometrics is the discipline based on the computational measures of the geometry, topography and shape of the Earth's horizons, and their temporal change. This is a major component of geographic information systems (GIS) and other software tools for spatial analysis.
The mathematics of general relativity is complicated. In Newton's theories of motion, an object's length and the rate at which time passes remain constant while the object accelerates, meaning that many problems in Newtonian mechanics may be solved by algebra alone. In relativity, however, an object's length and the rate at which time passes both change appreciably as the object's speed approaches the speed of light, meaning that more variables and more complicated mathematics are required to calculate the object's motion. As a result, relativity requires the use of concepts such as vectors, tensors, pseudotensors and curvilinear coordinates.
In vector calculus, the surface gradient is a vector differential operator that is similar to the conventional gradient. The distinction is that the surface gradient takes effect along a surface.
The histogram of oriented gradients (HOG) is a feature descriptor used in computer vision and image processing for the purpose of object detection. The technique counts occurrences of gradient orientation in localized portions of an image. This method is similar to that of edge orientation histograms, scale-invariant feature transform descriptors, and shape contexts, but differs in that it is computed on a dense grid of uniformly spaced cells and uses overlapping local contrast normalization for improved accuracy.
In mathematics and physics, vector is a term that refers to quantities that cannot be expressed by a single number, or to elements of some vector spaces. They have to be expressed by both magnitude and direction.
A spatial gradient is a gradient whose components are spatial derivatives, i.e., rate of change of a given scalar physical quantity with respect to the position coordinates in physical space. Homogeneous regions have spatial gradient vector norm equal to zero. When evaluated over vertical position, it is called vertical derivative or vertical gradient; the remainder is called horizontal gradient component, the vector projection of the full gradient onto the horizontal plane.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.

