Related Research Articles
Temple names are posthumous titles accorded to monarchs of the Sinosphere for the purpose of ancestor worship. The practice of honoring monarchs with temple names began during the Shang dynasty in China and had since been adopted by other dynastic regimes in the Sinosphere,with the notable exception of Japan. Temple names should not be confused with era names (年號),regnal names (尊號) or posthumous names (謚號).

Wu,known in historiography as Eastern Wu or Sun Wu,was a dynastic state of China and one of the three major states that competed for supremacy over China in the Three Kingdoms period. It previously existed from 220 to 222 as a vassal kingdom nominally under Cao Wei,its rival state,but declared complete independence from Cao Wei in November 222. It was elevated to an empire in May 229 after its founding ruler,Sun Quan,declared himself emperor. Its name was derived from the place it was based in—the Jiangnan region,which was also historically known as "Wu". It was referred to as "Dong Wu" or "Sun Wu" by historians to distinguish it from other Chinese historical states with similar names which were also located in that region,such as the Wu state in the Spring and Autumn period and the Wuyue kingdom in the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. It was called "Eastern Wu" because it occupied most of eastern China in the Three Kingdoms period,and "Sun Wu" because the family name of its rulers was "Sun". During its existence,Wu's capital was at Jianye,but at times it was also at Wuchang.

The Baiyue,Hundred Yue,or simply Yue,were various ethnic groups who inhabited the regions of Southern China and Northern Vietnam during the 1st millennium BC and 1st millennium AD. They were known for their short hair,body tattoos,fine swords,and naval prowess.

The Tây Sơn dynasty (Vietnamese:[təjʂəːn],Vietnamese:NhàTây Sơn,ChữNôm:茹西山,lit. 'House of Tây Sơn';Vietnamese:Tây Sơn triều,officially Great Việt,was a dynasty of Vietnam. It was founded after three Nguyễn brothers from the village of Tây Sơn rebelled against the Lêdynasty,Nguyễn lords,and Trịnh lords. The Tây Sơn were led by these three brothers,referred to by modern Vietnamese historians as the Tây Sơn brothers because of their origin in the district of Tây Sơn. The Tây Sơn was later succeeded by the Nguyễn dynasty.

Son of Heaven,or Tianzi,was the sacred monarchial and imperial title of the Chinese sovereign. It originated with the Zhou dynasty and was founded on the political and spiritual doctrine of the Mandate of Heaven. Since the Qin dynasty,the secular imperial title of the Son of Heaven was "Huangdi".

Ma Yuan,courtesy name Wenyuan,also known by his official title Fubo Jiangjun,was a Chinese military general and politician of the Eastern Han dynasty. He played a prominent role in defeating the Trung sisters' rebellion.

Nanyue was an ancient kingdom founded by the Chinese general Zhao Tuo,whose family continued to rule until 111 BC. Nanyue's geographical expanse covered the modern Chinese subdivisions of Guangdong,Guangxi,Hainan,Hong Kong,Macau,southern Fujian and central to northern Vietnam. Zhao Tuo,then Commander of Nanhai Commandery of the Qin dynasty,established Nanyue in 204 BC after the collapse of the Qin dynasty. At first,it consisted of the commanderies of Nanhai,Guilin,and Xiang.
The Three Ducal Ministers,also translated as the Three Dukes,Three Excellencies,or the Three Lords,was the collective name for the three highest officials in Ancient China and Imperial China. These posts were abolished by Cao Cao in 208 AD and replaced with the position of Grand Chancellor. When Cao Cao's son Cao Pi became King of Wei after his father's death,he reinstated the three positions. Hua Xin was made Chancellor,Jia Xu was made Grand Commandant and Wang Lang was made Grand Secretary. When Cao Pi declared himself emperor in late 220,Hua Xin was made Cao Wei's first Minister of the Masses,Jia Xu remained as Grand Commandant,and Wang Lang was made the first Minister of Works.

The Đinh dynasty,officially Great CồViệt,was a Vietnamese dynasty. It was founded in 968 when Đinh BộLĩnh vanquished the upheavals of Twelve warlords and ended when the son of Đinh BộLĩnh,Đinh Toàn,ceded the throne to LêHoàn in 980.
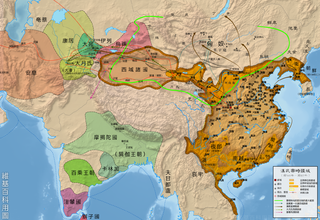
The First Era of Northern Domination refers to the period of Vietnamese history during which present-day northern Vietnam was under the rule of the Han dynasty and the Xin dynasty. It is considered the first of four periods of Chinese rule over Vietnam,and the first of the three in which were almost continuous and was referred to as Bắc thuộc.
Đại Việt,often known as Annam,was a monarchy in eastern Mainland Southeast Asia from the 10th century AD to the early 19th century,centered around the region of present-day Hanoi,Northern Vietnam. Its early name,Đại CồViệt,was established in 968 by Vietnamese ruler Đinh BộLĩnh after he ended the Anarchy of the 12 Warlords,until the beginning of the reign of LýThánh Tông,the third emperor of the Lýdynasty. Đại Việt lasted until the reign of Gia Long,the first emperor of the Nguyễn dynasty,when the name was changed to Việt Nam.
Emperor Cảnh Thịnh,born Nguyễn Quang Toản,was the third and last emperor of the Tây Sơn dynasty. He followed his father Quang Trung at the age of 9,and reigned for 10 years.

Literary Chinese was the medium of all formal writing in Vietnam for almost all of the history of the country up to the early 20th century,when it was replaced by vernacular writing in Vietnamese using the Latin-based Vietnamese alphabet. The language was the same as that used in China,as well as in Korea and in Japan,and used the same standard Chinese characters. It was used for official business,historical annals,fiction,verse,scholarship and even for declarations of Vietnamese determination to resist Chinese invaders.

Li or Lee is a common Chinese surname,it is the 4th name listed in the famous Hundred Family Surnames. Li is one of the most common surnames in Asia,shared by 92.76 million people in China,and more than 100 million in Asia. It is the second-most common surname in China as of 2018,the second-most common surname in Hong Kong,the most common surname in Macau and the 5th most common surname in Taiwan,where it is usually romanized as "Lee". The surname is pronounced as in Cantonese,Lí (poj) in Taiwanese Hokkien,but is often spelled as "Lee" in Hong Kong,Macau,Taiwan and many overseas Chinese communities. In Macau,it is also spelled as "Lei". In Indonesia it is commonly spelled as "Lie". The common Korean surname,"Lee",and the Vietnamese surname,"Lý",are both derived from Li and written with the same Chinese character (李). The character also means "plum" or "plum tree".
A xunfu was an important imperial Chinese provincial office under both the Ming and Qing dynasties. However,the purview of the office under the two dynasties differed markedly. Under the Ming dynasty,the post originated around 1430 as a kind of inspector-general and ad hoc provincial-level administrator;such a xunfu is usually translated as a grand coordinator. However,since the mid-17th century,xunfu became the title of a regular provincial governor overseeing civil administration in the Qing dynasty.
The Imperial Preceptor,or Dishi,was a high title and powerful post created by Kublai Khan,founder of the Yuan dynasty. It was established as part of Mongol patronage of Tibetan Buddhism and the Yuan administrative rule of Tibet.

Zhang Fu,courtesy name Wenbi,was a Chinese military general of the Ming dynasty. He was the eldest son of general Zhang Yu,one of Zhu Di's finest generals. Zhang Yu was killed in the Jingnan campaign,Zhang Fu succeeded his father's title. After Zhu Di crowned the Yongle Emperor,Zhang Fu was granted the title "Count of Xin'an" (信安伯). In 1405,he was elevated to the title "Marquis of Xincheng" (新成侯).
Emperor at home,king abroad was a system of conducting relations between states within the Chinese cultural sphere. Rulers of lesser regimes would adopt the title of emperor and/or other imperial titles domestically,and adopt the title of king when dealing with the dominant Chinese regime. Instead of using the styles Imperial Majesty and Majesty (陛下),rulers of lesser realms were styled as Highness (殿下). This system was applicable to Japan,Korea and Vietnam,as well as less powerful Chinese states,among others.

Minh Hương refers to descendants of Ming dynasty immigrants who settled in southern Vietnam during the 16th and 18th centuries. They were among the first wave of ethnic Han who came to southern Vietnam.
References
- ↑ "Official Titles of the Han Dynasty: A Tentative List Compiled for The Han Dynasty History Project" (PDF). University of Washington. p. 34. Archived from the original (PDF) on January 17, 2013. Retrieved March 4, 2013.
- ↑ de Crespigny, Rafe (1996). To Establish Peace: being the Chronicle of the Later Han dynasty for the years 189 to 220 AD as recorded in Chapters 59 to 69 of the Zizhi tongjian of Sima Guang (PDF). Canberra: Australian National University. ISBN 978-0-7315-2526-3. Section Cp2:192 C