Agribusiness is the industry, enterprises, and the field of study of value chains in agriculture and in the bio-economy, in which case it is also called bio-business or bio-enterprise. The primary goal of agribusiness is to maximize profit while satisfying the needs of consumers for products related to natural resources such as biotechnology, farms, food, forestry, fisheries, fuel, and fiber.

Tnuva, or Tenuvah, is an Israeli food creation and marketing company. The company holds in Israel a significant market share in the field of drinking milk production, dairy products and its marketing. It was for its first seventy years an Israeli food processing cooperative (co-op) owned by the kibbutzim and moshavim, and historically specializing in milk and dairy products; it was subsequently sold by its members as a limited company and, since 2014, has been controlled by a Chinese state company, Bright Food. Tnuva is the largest food manufacturer in Israel; its sales account for 70% of the country's dairy market as well as sales of meat, eggs and packaged food.

An agricultural cooperative, also known as a farmers' co-op, is a producer cooperative in which farmers pool their resources in certain areas of activities.

Vegetables are parts of plants that are consumed by humans or other animals as food. The original meaning is still commonly used and is applied to plants collectively to refer to all edible plant matter, including the flowers, fruits, stems, leaves, roots, and seeds. An alternative definition of the term is applied somewhat arbitrarily, often by culinary and cultural tradition. It may exclude foods derived from some plants that are fruits, flowers, nuts, and cereal grains, but include savoury fruits such as tomatoes and courgettes, flowers such as broccoli, and seeds such as pulses.

Agricultural research in Israel is based on close cooperation and interaction between scientists, consultants, farmers and agriculture-related industries. Israel's climate ranges from Mediterranean (Csa) to semi-arid and arid. Shortage of irrigation water and inadequate precipitation in some parts of the country are major constraints facing Israeli agriculture. Through extensive greenhouses production, vegetables, fruits and flowers are grown for export to the European markets during the winter off-season.
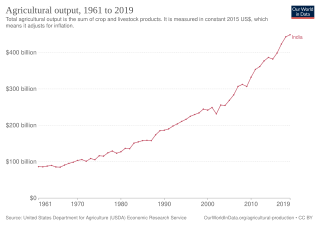
The history of agriculture in India dates back to the Neolithic period. India ranks second worldwide in farm outputs. As per the Indian economic survey 2020 -21, agriculture employed more than 50% of the Indian workforce and contributed 20.2% to the country's GDP.

Jain Irrigation Systems, or Jains, is an Indian multinational conglomerate based in Jalgaon. It develops, manufactures, supports and sells diversified products, including drip and sprinkler irrigation systems and its components, integrated irrigation automation systems for monitoring and control, dosing systems, PVC and PE piping systems, plastic sheets, greenhouses, bio-fertilizers, solar power, solar water heating systems, solar water pumps, turnkey biogas plants, photovoltaic systems and tissue culture plants. JISL also processes dehydrated vegetables, spices, concentrated & frozen fruits or pulp. It also provides turnkey projects and agronomical support services.

Agriculture in South Korea is a sector of the economy of South Korea. Korean agriculture is the basic industry of the Korean economy, consisting of farming, animal husbandry, forestry and fishing. At the time of its founding, Korea was a typical agricultural country, with more than 80% of the population engaged in agricultural production. After land reform under the Lee Seung-man administration, economic revitalization under the Park Chung-hee military government and the wave of world trade liberalization that began in the 1980s, Korean agriculture has undergone dramatic changes. Through the Green Revolution, Korea became self-sufficient in rice, the staple food, in 1978, and in 1996, Korea became the first Asian country after Japan to mechanize its agriculture with fine-grained cultivation. The development of Korean agriculture has also led to the development of agriculture-related industries such as fertilizer, agricultural machinery and seed.

Israeli cuisine primarily comprises dishes brought from the Jewish diaspora, and has more recently been defined by the development of a notable fusion cuisine characterized by the mixing of Jewish cuisine and Arab cuisine. It also blends together the culinary traditions of the various diaspora groups, namely those of Middle Eastern Jews with roots in Southwest Asia and North Africa, Sephardi Jews from Iberia, and Ashkenazi Jews from Central and Eastern Europe.

Agriculture is one of the main industries in Taiwan. It contributes to the food security, rural development and conservation of Taiwan. Around 24% of Taiwan's land is used for farming.

Agriculture in Israel is a highly developed industry. Israel is an exporter of fresh produce and a leader in agricultural technologies. The southern one-half of Israel is desert and irrigation is required for growing crops. The northern one-half is more conducive to rain-fed agriculture. According to the World Bank, 29.7 percent of Israel is agricultural land. The shortage of water is a constraint. In 2008, agriculture represented 2.5% of total GDP and 3.6% of exports. Israel is not self-sufficient in growing food. In 2021, Israel's agricultural imports totaled 8,791 million and agricultural exports totaled 2,445 million dollars. Grains, oilseeds, meat, coffee, cocoa, and sugar were among the imports.

Benin is predominantly a rural society, and agriculture in Benin supports more than 70% of the population. Agriculture contributes around 35% of the country's gross domestic product (GDP) and 80% of export income. While the Government of Benin (GOB) aims to diversify its agricultural production, Benin remains underdeveloped, and its economy is underpinned by subsistence agriculture. Approximately 93% of total agricultural production goes into food production. The proportion of the population living in poverty is about 35.2%, with more rural households in poverty (38.4%) than urban households (29.8%). 36% of households depend solely upon agricultural (crop) production for income, and another 30% depend on crop production, livestock, or fishing for income.

Agriculture in Lebanon is the third most productive sector in the country after the tertiary and industrial sectors. It contributes 3.1% of GDP and 8 percent of the effective labor force. The sector includes an informal Syrian labor and is dependent on foreign labor for its productivity. Main crops include cereals, fruits and vegetables, olives, grapes, and tobacco, along with sheep and goat herding. Mineral resources are limited and are only exploited for domestic consumption. Lebanon, which has a variety of agricultural lands, from the interior plateau of the Beqaa Valley to the narrow valleys leading downward to the sea, enables farmers to grow both European and tropical crops. Tobacco and figs are grown in the south, citrus fruits and bananas along the coast, olives in the north and around the Shouf Mountains, and fruits and vegetables in the Beqaa Valley. More exotic crops include avocados, grown near Byblos, and hashish. Although the country benefits from favorable farming conditions and diverse microclimates, it relies on food imports, which make up 80% of its consumption.

Agriculture in Cyprus constituted the backbone of its economy when it achieved its independence in 1960. It mostly consisted of small farms, and sometimes even subsistence farms. During the 1960s, irrigation projects made possible vegetable and fruit exports; increasingly commercialized farming was able to meet the demands for meat, dairy products, and wine from the British and United Nations troops stationed on the island and from the growing number of tourists.

Agriculture in Spain is important to the national economy. The primary sector activities accounting for agriculture, husbandry, fishing and silviculture represented a 2.7% of the Spanish GDP in 2017, with an additional 2.5% represented by the agrofood industry.
Al Dahra Agricultural Company is an agribusiness firm specializing in the cultivation, production, and trading of animal feed and human food commodities such as rice, flour, fruits and vegetables. The group owns and operates a land bank of 200 thousand acres, 8 forage pressing and production plants, 4 rice milling plants, and 2 flour milling plants.

Post-harvest losses of vegetables and fruits occur at all points in the value chain from production in the field to the food being placed on a plate for consumption. Post-harvest activities include harvesting, handling, storage, processing, packaging, transportation and marketing.

Fruit waxing is the process of covering fruits with artificial waxing material. Natural wax is removed first, usually by washing, followed by a coating of a biological or petroleum derived wax. Potentially allergenic proteins may be combined with shellac.
The horticulture industry embraces the production, processing and shipping of and the market for fruits and vegetables. As such it is a sector of agribusiness and industrialized agriculture. Industrialized horticulture sometimes also includes the floriculture industry and production and trade of ornamental plants.

Apeel Sciences is an American food technology company based in Goleta, California. Its edible coating product Apeel or Edipeel can make avocados, citrus and other types of fruit last twice as long as usual by using a tasteless edible coating, and reduces food loss and waste as well as reliance on single-use plastic packaging.

















