Related Research Articles
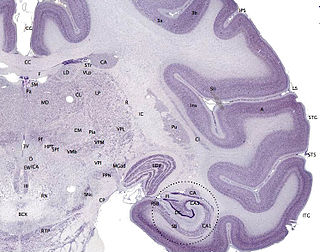
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. The cerebral cortex mostly consists of the six-layered neocortex, with just ten per cent consisting of allocortex. It is separated into two cortices, by the longitudinal fissure that divides the cerebrum into the left and right cerebral hemispheres. The two hemispheres are joined beneath the cortex by the corpus callosum. The cerebral cortex is the largest site of neural integration in the central nervous system. It plays a key role in attention, perception, awareness, thought, memory, language, and consciousness.

The cingulate cortex is a part of the brain situated in the medial aspect of the cerebral cortex. The cingulate cortex includes the entire cingulate gyrus, which lies immediately above the corpus callosum, and the continuation of this in the cingulate sulcus. The cingulate cortex is usually considered part of the limbic lobe.

A Brodmann area is a region of the cerebral cortex, in the human or other primate brain, defined by its cytoarchitecture, or histological structure and organization of cells.

The piriform cortex, or pyriform cortex, is a region in the brain, part of the rhinencephalon situated in the cerebrum. The function of the piriform cortex relates to the sense of smell.
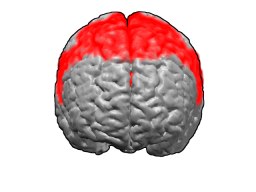
Brodmann area 6 (BA6) part of the frontal cortex in the human brain. Situated just anterior to the primary motor cortex (BA4), it is composed of the premotor cortex and, medially, the supplementary motor area (SMA). This large area of the frontal cortex is believed to play a role in planning complex, coordinated movements.

Brodmann area 10 is the anterior-most portion of the prefrontal cortex in the human brain. BA10 was originally defined broadly in terms of its cytoarchitectonic traits as they were observed in the brains of cadavers, but because modern functional imaging cannot precisely identify these boundaries, the terms anterior prefrontal cortex, rostral prefrontal cortex and frontopolar prefrontal cortex are used to refer to the area in the most anterior part of the frontal cortex that approximately covers BA10—simply to emphasize the fact that BA10 does not include all parts of the prefrontal cortex.

Brodmann area 19, or BA 19, is part of the occipital lobe cortex in the human brain. Along with area 18, it comprises the extrastriate cortex. In humans with normal sight, extrastriate cortex is a visual association area, with feature-extracting, shape recognition, attentional, and multimodal integrating functions.
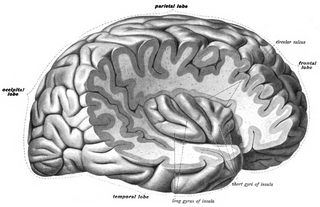
The insular cortex is a portion of the cerebral cortex folded deep within the lateral sulcus within each hemisphere of the mammalian brain.

Brodmann area 24 is part of the anterior cingulate in the human brain.
Brodmann Area 15 is one of Brodmann's subdivisions of the cerebral cortex in the brain.

Brodmann area 43, the subcentral area, is a structurally distinct area of the cerebral cortex defined on the basis of cytoarchitecture. Along with Brodmann Area 1, 2, and 3, Brodmann area 43 is a subdivision of the postcentral region of the brain, suggesting a somatosensory function. The histological structure of Area 43 was initially described by Korbinian Brodmann, but it was not labeled on his map of cortical areas.
In the rodent, the parasubiculum is a retrohippocampal isocortical structure, and a major component of the subicular complex. It receives numerous subcortical and cortical inputs, and sends major projections to the superficial layers of the entorhinal cortex.

The premotor cortex is an area of motor cortex lying within the frontal lobe of the brain just anterior to the primary motor cortex. It occupies part of Brodmann's area 6. It has been studied mainly in primates, including monkeys and humans. The functions of the premotor cortex are diverse and not fully understood. It projects directly to the spinal cord and therefore may play a role in the direct control of behavior, with a relative emphasis on the trunk muscles of the body. It may also play a role in planning movement, in the spatial guidance of movement, in the sensory guidance of movement, in understanding the actions of others, and in using abstract rules to perform specific tasks. Different subregions of the premotor cortex have different properties and presumably emphasize different functions. Nerve signals generated in the premotor cortex cause much more complex patterns of movement than the discrete patterns generated in the primary motor cortex.
The perirhinal cortex is a cortical region in the medial temporal lobe that is made up of Brodmann areas 35 and 36. It receives highly processed sensory information from all sensory regions, and is generally accepted to be an important region for memory. It is bordered caudally by postrhinal cortex or parahippocampal cortex and ventrally and medially by entorhinal cortex.
In the rodent, the parasubiculum is a retrohippocampal isocortical structure, and a major component of the subicular complex. It receives numerous subcortical and cortical inputs, and sends major projections to the superficial layers of the entorhinal cortex.

The line of Gennari is a band of myelinated axons that run parallel to the surface of the cerebral cortex on the banks of the calcarine fissure in the occipital lobe. This formation is visible to the naked eye as a white strip running through the cortical grey matter, and is the reason the V1 in primates is also referred to as "striate cortex." The line of Gennari is due to dense axonal input from the thalamus to layer IV of visual cortex. The structure is named for its discoverer, Francesco Gennari, who first observed it in 1776 as a medical student at the University of Parma. He described it in a book which he published six years later. Although non-primate species have areas that are designated primary visual cortex, some lack a stria of Gennari.
The accessory facial motor nucleus is a small cluster of neurons dorsal to the facial motor nucleus in the pontine tegmentum. It has been reported for the human, rat, and mouse.
Nonprimary motor cortex is a functionally defined portion of the frontal lobe. It includes two subdivisions, the premotor cortex and the supplementary motor cortex. Largely coincident with the cytoarchitecturally defined area 6 of Brodmann (human), it is located primarily in the rostral portion of the precentral gyrus and caudal portions of the superior frontal gyrus and the middle frontal gyrus, It aids in cerebral control of movement. Anatomically speaking, several nonmprimary areas exist, and make direct connections with the spinal cord.
Agranular insula is a portion of the cerebral cortex defined on the basis of internal structure in the human, the macaque, the rat, and the mouse. Classified as allocortex (periallocortex), it is in primates distinguished from adjacent neocortex (proisocortex) by absence of the external granular layer (II) and of the internal granular layer (IV). It occupies the anterior part of the insula, the posterior portion of the orbital gyri and the medial part of the temporal pole. In rodents it is located on the ventrolateral surface of the cortex rostrally, between the piriform area ventrally and the gustatory area or the visceral area dorsally.
Dopaminergic cell groups are collections of neurons in the central nervous system that synthesize the neurotransmitter dopamine. In the 1960s, dopamine neurons were first identified and named by Annica Dahlström and Kjell Fuxe, who used histochemical fluorescence. The subsequent discovery of genes encoding enzymes that synthesize dopamine, and transporters that incorporate dopamine into synaptic vesicles or reclaim it after synaptic release, enabled scientists to identify dopaminergic neurons by labeling gene or protein expression that is specific to these neurons.
References
- ↑ Mesulam M-M; Mufson EJ (1985). "5: The insula of Reil in man and monkey: Architectonics, connectivity, and function". In Peters A, Jones EG (eds.). Cerebral Cortex. pp. 179–226. OCLC 277149053.
- ↑ Swanson LW (1998). Brain Maps: Structure of the Rat Brain (2nd Revised ed.). Amsterdam: Elsevier Science. OCLC 640898561.
- ↑ Paxinos G; Franklin KBJ (2001). The Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates (2nd ed.). San Diego: Academic Press. OCLC 493265554.
- ↑ Zilles K (2004). "27: Architecture of the human cerebral cortex". In Paxinos G, Mai JK (eds.). The Human Nervous System (2nd ed.). Amsterdam: Elsevier. OCLC 54767534.
- ↑ Mesulam M-M, Mufson EJ (1984). "5: The insula of Reil in man and monkey: Architectonics, connectivity, and function". In Peters A, Jones EG (eds.). Cerebral Cortex. pp. 179–226. OCLC 277149053.
- ↑ Swanson LW (2004). Brain Maps: Structure of the Rat Brain (3rd ed.). Oxford: Elsevier Academic Press. OCLC 225608577.