
Lewy bodies are the inclusion bodies – abnormal aggregations of protein – that develop inside nerve cells affected by Parkinson's disease (PD), the Lewy body dementias, and some other disorders. They are also seen in cases of multiple system atrophy, particularly the parkinsonian variant (MSA-P).

Alpha-synuclein(aSyn) is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the SNCA gene. Alpha-synuclein is a neuronal protein that regulates synaptic vesicle trafficking and subsequent neurotransmitter release.

Frontotemporal dementia (FTD), or frontotemporal degeneration disease, or frontotemporal neurocognitive disorder, encompasses several types of dementia involving the progressive degeneration of frontal and temporal lobes. FTDs broadly present as behavioral or language disorders with gradual onsets. Common signs and symptoms include significant changes in social and personal behavior, apathy, blunting of emotions, and deficits in both expressive and receptive language. Currently, there is no cure for FTD, but there are treatments that help alleviate symptoms.

Progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) is a late-onset neurodegenerative disease involving the gradual deterioration and death of specific volumes of the brain. The condition leads to symptoms including loss of balance, slowing of movement, difficulty moving the eyes, and cognitive impairment. PSP may be mistaken for other types of neurodegeneration such as Parkinson's disease, frontotemporal dementia and Alzheimer's disease. The cause of the condition is uncertain, but involves the accumulation of tau protein within the brain. Medications such as levodopa and amantadine may be useful in some cases.

The tau proteins are a group of six highly soluble protein isoforms produced by alternative splicing from the gene MAPT. They have roles primarily in maintaining the stability of microtubules in axons and are abundant in the neurons of the central nervous system (CNS), where the cerebral cortex has the highest abundance. They are less common elsewhere but are also expressed at very low levels in CNS astrocytes and oligodendrocytes.

Frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD) is a pathological process that occurs in frontotemporal dementia. It is characterized by atrophy in the frontal lobe and temporal lobe of the brain, with sparing of the parietal and occipital lobes.

Neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) are aggregates of hyperphosphorylated tau protein that are most commonly known as a primary biomarker of Alzheimer's disease. Their presence is also found in numerous other diseases known as tauopathies. Little is known about their exact relationship to the different pathologies.

Hippocampal sclerosis (HS) or mesial temporal sclerosis (MTS) is a neuropathological condition with severe neuronal cell loss and gliosis in the hippocampus. Neuroimaging tests such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and positron emission tomography (PET) may identify individuals with hippocampal sclerosis. Hippocampal sclerosis occurs in 3 distinct settings: mesial temporal lobe epilepsy, adult neurodegenerative disease and acute brain injury.

Corticobasal degeneration (CBD) is a rare neurodegenerative disease involving the cerebral cortex and the basal ganglia. CBD symptoms typically begin in people from 50 to 70 years of age, and the average disease duration is six years. It is characterized by marked disorders in movement and cognition, and is classified as one of the Parkinson plus syndromes. Diagnosis is difficult, as symptoms are often similar to those of other disorders, such as Parkinson's disease, progressive supranuclear palsy, and dementia with Lewy bodies, and a definitive diagnosis of CBD can only be made upon neuropathologic examination.

Tauopathy belongs to a class of neurodegenerative diseases involving the aggregation of tau protein into neurofibrillary or gliofibrillary tangles in the human brain. Tangles are formed by hyperphosphorylation of the microtubule protein known as tau, causing the protein to dissociate from microtubules and form insoluble aggregates. The mechanism of tangle formation is not well understood, and whether tangles are a primary cause of Alzheimer's disease or play a peripheral role is unknown.
The biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease, the most common cause of dementia, is not yet very well understood. Alzheimer's disease (AD) has been identified as a proteopathy: a protein misfolding disease due to the accumulation of abnormally folded amyloid beta (Aβ) protein in the brain. Amyloid beta is a short peptide that is an abnormal proteolytic byproduct of the transmembrane protein amyloid-beta precursor protein (APP), whose function is unclear but thought to be involved in neuronal development. The presenilins are components of proteolytic complex involved in APP processing and degradation.

Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) is a neurodegenerative disease linked to repeated trauma to the head. The encephalopathy symptoms can include behavioral problems, mood problems, and problems with thinking. The disease often gets worse over time and can result in dementia.

Transmembrane protein 106B is a protein that is encoded by the TMEM106B gene. It is found primarily within neurons and oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system with its subcellular location being in lysosomal membranes. TMEM106B helps facilitate important functions for maintaining a healthy lysosome, and therefore certain mutations and polymorphisms can lead to issues with proper lysosomal function. Lysosomes are in charge of clearing out mis-folded proteins and other debris, and thus, play an important role in neurodegenerative diseases that are driven by the accumulation of various mis-folded proteins and aggregates. Due to its impact on lysosomal function, TMEM106B has been investigated and found to be associated to multiple neurodegenerative diseases.
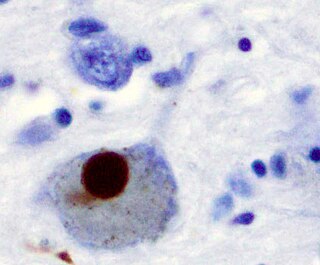
Synucleinopathies are neurodegenerative diseases characterised by the abnormal accumulation of aggregates of alpha-synuclein protein in neurons, nerve fibres or glial cells. There are three main types of synucleinopathy: Parkinson's disease (PD), dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), and multiple system atrophy (MSA). Other rare disorders, such as various neuroaxonal dystrophies, also have α-synuclein pathologies. Additionally, autopsy studies have shown that around 6% of sporadic Alzheimer's Disease exhibit α-synuclein positive Lewy pathology, and are sub-classed as Alzheimer's Disease with Amygdalar Restricted Lewy Bodies (AD/ALB).
Primary age-related tauopathy (PART) is a neuropathological designation introduced in 2014 to describe the neurofibrillary tangles (NFT) that are commonly observed in the brains of normally aged and cognitively impaired individuals that can occur independently of the amyloid plaques of Alzheimer's disease (AD). The term and diagnostic criteria for PART were developed by a large group of neuropathologists, spearheaded by Drs. John F. Crary and Peter T. Nelson. Despite some controversy, the term PART has been widely adopted, with the consensus criteria cited over 1130 times as of April 2023 according to Google Scholar.

Virginia Man-Yee Lee is a Chinese-born American biochemist and neuroscientist who specializes in the research of Alzheimer's disease. She is the current John H. Ware 3rd Endowed Professor in Alzheimer's Research at the Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, and the director of the Center for Neurodegenerative Disease Research and co-director of the Marian S. Ware Alzheimer Drug Discovery Program at the Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania. She received the 2020 Breakthrough Prize in Life Sciences.
Benjamin Wolozin is an American pharmacologist and neurologist currently at Boston University School of Medicine and an Elected Fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science. Benjamin Wolozin, M.D., Ph.D. received his B.A. from Wesleyan University and his M.D., Ph.D. from the Albert Einstein College of Medicine. He is currently a professor of Pharmacology, Neurology and the Program in Neuroscience at Boston University School of Medicine. He is also co-founder and Chief Scientific Officer (CSO) of Aquinnah Pharmaceuticals Inc., a biotechnology company developing novel therapeutics to treat Alzheimer's disease and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis.

Neurotubules are microtubules found in neurons in nervous tissues. Along with neurofilaments and microfilaments, they form the cytoskeleton of neurons. Neurotubules are undivided hollow cylinders that are made up of tubulin protein polymers and arrays parallel to the plasma membrane in neurons. Neurotubules have an outer diameter of about 23 nm and an inner diameter, also known as the central core, of about 12 nm. The wall of the neurotubules is about 5 nm in width. There is a non-opaque clear zone surrounding the neurotubule and it is about 40 nm in diameter. Like microtubules, neurotubules are greatly dynamic and the length of them can be adjusted by polymerization and depolymerization of tubulin.

LATE is a term that describes a prevalent condition with impaired memory and thinking in advanced age, often culminating in the dementia clinical syndrome. In other words, the symptoms of LATE are similar to those of Alzheimer's disease.

Eva Braak (1939-2000) was a German anatomist, mostly known for the Braak and Braak Alzheimer disease stages. She was professor at the Institute of Clinical Neuroanatomy, Johann Wolfgang Goethe-University, Frankfurt am Main.

















