Related Research Articles
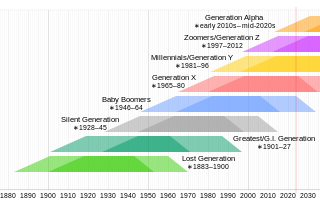
Generation X is the demographic cohort following the Baby Boomers and preceding Millennials. Researchers and popular media often use the mid-1960s as its starting birth years and the late 1970s as its ending birth years, with the generation being generally defined as people born from 1965 to 1980. By this definition and U.S. Census data, there are 65.2 million Gen Xers in the United States as of 2019. Most of Generation X are the children of the Silent Generation and early Baby Boomers; Xers are also often the parents of Millennials and Generation Z.

Baby boomers, often shortened to boomers, are the demographic cohort preceded by the Silent Generation and followed by Generation X. The generation is often defined as people born from 1946 to 1964 during the mid-20th century baby boom. The dates, the demographic context, and the cultural identifiers may vary by country. Most baby boomers are the children of either the Greatest Generation or the Silent Generation, and are often parents of Millennials.

A generation is all of the people born and living at about the same time, regarded collectively. It also is "the average period, generally considered to be about 20–30 years, during which children are born and grow up, become adults, and begin to have children." In kinship, generation is a structural term, designating the parent–child relationship. In biology, generation also means biogenesis, reproduction, and procreation.

Millennials, also known as Generation Y or Gen Y, are the demographic cohort following Generation X and preceding Generation Z. Researchers and popular media use the early 1980s as starting birth years and the mid-1990s to early 2000s as ending birth years, with the generation typically being defined as people born from 1981 to 1996. Most Millennials are the children of Baby Boomers and older Generation X. In turn Millennials are often the parents of Generation Alpha.
A generation gap or generational gap is a difference of opinions and outlooks between one generation and another. These differences may relate to beliefs, politics, language, work, demographics and values. The differences between generations can cause misunderstandings, but it is possible for generations to overcome their differences and maintain functional relationships.
A baby boom is a period marked by a significant increase of births. This demographic phenomenon is usually ascribed within certain geographical bounds of defined national and cultural populations. The cause of baby booms involves various fertility factors. The best-known baby boom occurred in the mid-twentieth century, sometimes considered to have started after the end of the Second World War, sometimes from the late 1940s, and ending in the 1960s. People born during this period are often called baby boomers.

The Silent Generation, also known as the Traditionalist Generation, is the Western demographic cohort following the Greatest Generation and preceding the baby boomers. The generation is generally defined as people born from 1928 to 1945. By this definition and U.S. Census data, there were 23 million Silents in the United States as of 2019.

Generation Jones is the generation or social cohort between the Baby Boom generation and Generation X. The term was coined by American cultural commentator Jonathan Pontell, who argues that the term refers to a full distinct generation born from 1954 to 1965. Media coverage of Generation Jones typically has described it as a distinct generation, using Pontell's dates. Others see this as a subset of the Baby Boom Generation, primarily its second half. A third view is that Generation Jones is a cusp or micro-generation between the Boomers and Xers.
In Western culture the Boomerang Generation refers to the generation of young adults graduating high school and college in the 21st century. They are so named for the percentage of whom choose to share a home with their parents after previously living on their own—thus boomeranging back to their parents' residence. This arrangement can take many forms, ranging from situations that mirror the high dependency of pre-adulthood to highly independent, separate-household arrangements.

Generation Z, also known as Zoomers, is the demographic cohort succeeding Millennials and preceding Generation Alpha. Researchers and popular media use the mid-to-late 1990s as starting birth years and the early 2010s as ending birth years, with the generation most frequently being defined as people born from 1997 to 2012. Most members of Generation Z are the children of younger Baby Boomers or Generation X.

The sandwich generation is a group of middle-aged adults who care for both their aging parents and their own children. It is not a specific generation or cohort in the sense of the Greatest Generation or the Baby boomer generation, but a phenomenon that can affect anyone whose parents and children need support at the same time.
The working environment has gone through a major transformation over the last decades, particularly in terms of population in the workforce. The generations dominating the workforce in 2024 are baby boomers, Generation X, millennials and Generation Z. The coming decades will see further changes with emergence of newer generations, and slower removal of older generations from organisations as pension age is pushed out. Many reports, including a publication by Therese Kinal and Olga Hypponen of Unleash, warn that understanding differences between the generations, and learning to adapt their management practices is critical to building a successful multigenerational workplace.
A cusper is a person born near the end of one generation and the beginning of another. People born in these circumstances tend to have a mix of characteristics common to their adjacent generations, but do not closely resemble those born in the middle of their adjacent generations, and thus these cusper groups can be considered micro generations. Generational profiles are built based on people born in the middle of a generation rather than those on the tails of a generation. Generations may overlap by five to eight years. As such, many people identify with aspects of at least two generations. The precise birth years defining when generations start and end vary. Lancaster and Stillman (2002) introduced the term, cusper, in reference to those who are born at either end of a generation, and consequently, may identify to some extent with the generation before or after it. The authors observed that such individuals can often play an important role in mediating dialogue between members of different generations. Other authors like Ubl, Walden and Arbit (2017) observed something similar: "the truth is that they play a pivotal role in ensuring seamless communication across generations. Cuspers are natural translators because they often speak the language of two generations. Sometimes we even call them generationally bilingual!"

Generation Z, colloquially known as Zoomers, is the demographic cohort succeeding Millennials and preceding Generation Alpha.
A group where we all pretend to be boomers is a Facebook group created in May 2019, for users – the majority of whom are millennials and in Generation Z – to pretend to be baby boomers. The group has been described as "digital larping". The members of the group post in the manner of a stereotypical internet user from the baby boomer generation.

Zillennials is the demographic cohort on the cusp of the Millennial and Generation Z cohorts. Their adjacency between the two generations and limited age set has led to their characterization as a "micro-generation." They are generally the children of younger Baby Boomers and Generation X. Estimates of the U.S. population in this cohort range from 30 million to 48 million.
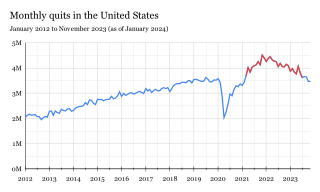
The Great Resignation, also known as the Big Quit and the Great Reshuffle, was a mainly American economic trend in which employees voluntarily resigned from their jobs en masse, beginning in early 2021 during the COVID-19 pandemic. Among the most cited reasons for resigning included wage stagnation amid rising cost of living, limited opportunities for career advancement, hostile work environments, lack of benefits, inflexible remote-work policies, and long-lasting job dissatisfaction. Most likely to quit were workers in hospitality, healthcare, and education. In addition, many of the resigning workers were retiring Baby Boomers, who are one of the largest demographic cohorts in the United States.

In recent decades, the fertility rate of the United States has declined below replacement level, prompting projections of an aging population and workforce, as is already happening elsewhere in the developed world and some developing countries. The decline has been most noticeable since after the Great Recession of the late 2000s. Nevertheless, the rate of aging in the United States remains slower than that seen in many other countries, including some developing ones, giving the nation a significant competitive advantage. Unintentional pregnancies have become less common; in particular, teenage pregnancies have dropped to record lows.

Millennials, also known as Generation Y or Gen Y, are the demographic cohort following Generation X and preceding Generation Z.
Millennials, also known as Generation Y, are the demographic cohort following Generation X and preceding Generation Z. The generation is typically defined as people born between 1981 and 1996.
References
- 1 2 Wolfe, Ira (2012-07-16). "Gray Ceiling Darkens Job Hopes for Millennials". HuffPost . Retrieved 2024-07-30.
- ↑ "The gray ceiling". The Journal Record . Oklahoma City. 2009-10-07. Retrieved 2024-07-30.
- ↑ BehindTheLines-The Gray Ceiling on YouTube
- ↑ Fisher, Anne (15 August 2006). "Are you stuck in middle management hell?". Cable News Network. Retrieved 31 March 2024.
- ↑ Smith, David (2015-12-09). "One gray ceiling is one gray floor". taxcreditadvisor.com. National Housing & Rehabilitation Association. Retrieved 2024-07-30.