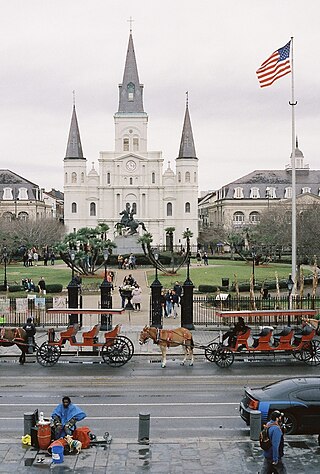The French Quarter, also known as the Vieux Carré, is the oldest neighborhood in the city of New Orleans. After New Orleans was founded in 1718 by Jean-Baptiste Le Moyne de Bienville, the city developed around the Vieux Carré, a central square. The district is more commonly called the French Quarter today, or simply "The Quarter", related to changes in the city with American immigration after the 1803 Louisiana Purchase. Most of the extant historic buildings were constructed either in the late 18th century, during the city's period of Spanish rule, or were built during the first half of the 19th century, after U.S. purchase and statehood.

Esteban Rodríguez Miró y Sabater, also known as Esteban Miro and Estevan Miro, was a Spanish army officer and governor of the Spanish provinces of Louisiana and Florida. He was one of the most popular of the Spanish governors, largely because of his prompt response to the New Orleans Fire of 1788, which destroyed almost all of the city.

The history of New Orleans, Louisiana traces the city's development from its founding by the French in 1718 through its period of Spanish control, then briefly back to French rule before being acquired by the United States in the Louisiana Purchase in 1803. During the War of 1812, the last major battle was the Battle of New Orleans in 1815. Throughout the 19th century, New Orleans was the largest port in the Southern United States, exporting most of the nation's cotton output and other farm products to Western Europe and New England. As the largest city in the South at the start of the Civil War (1861–1865), it was an early target for capture by Union forces. With its rich and unique cultural and architectural heritage, New Orleans remains a major destination for live music, tourism, conventions, and sporting events and annual Mardi Gras celebrations. After the significant destruction and loss of life resulting from Hurricane Katrina in 2005, the city would bounce back and rebuild in the ensuing years.

The Cathedral-Basilica of Saint Louis, King of France, also called St. Louis Cathedral, is a Catholic cathedral and basilica in New Orleans, Louisiana. It is the seat of the Archdiocese of New Orleans and is the oldest cathedral in continuous use in the United States alongside the Royal Presidio Chapel in Monterey, California. It is dedicated to Saint Louis, also known as King Louis IX of France. The first church on the site was built in 1718; the third, under the Spanish rule, built in 1789, was raised to cathedral rank in 1793. The second St. Louis Cathedral was burned during the great fire of 1788 and was expanded and largely rebuilt and completed in the 1850s, with little of the 1789 structure remaining.

DonAndrés Almonaster y Roxas de Estrada was a Spanish civil servant and philanthropist of New Orleans, today chiefly remembered for his numerous charitable benefactions made to the city of New Orleans.

The Cabildo, originally called "Casa Capitular", is a historical building in New Orleans, Louisiana. Originally the seat of Spanish colonial city hall, the building now forms part of the Louisiana State Museum. It is located along Jackson Square, adjacent to St. Louis Cathedral.

The Louisiana State Museum (LSM), founded in New Orleans in 1906, is a statewide system of National Historic Landmarks and modern structures across Louisiana, housing thousands of artifacts and works of art reflecting Louisiana's legacy of historic events and cultural diversity.
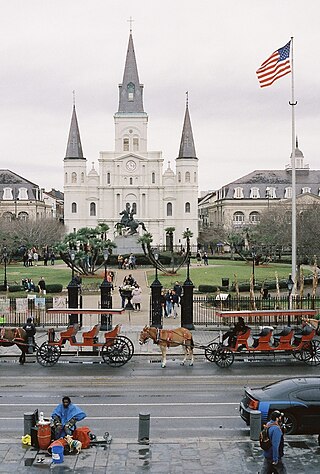
Jackson Square, formerly the Place d'Armes (French) or Plaza de Armas (Spanish), is a historic park in the French Quarter of New Orleans, Louisiana. It was declared a National Historic Landmark in 1960, for its central role in the city's history, and as the site where in 1803 Louisiana was made United States territory pursuant to the Louisiana Purchase. In 2012 the American Planning Association designated Jackson Square as one of the Great Public Spaces in the United States.
Gilbert Antoine de St. Maxent was a French merchant and military officer who played a major role in the development of French and Spanish Louisiana.

The Great New Orleans Fire (1788) was a fire that destroyed 856 of the 1,100 structures in New Orleans, Louisiana, on March 21, 1788, spanning the south central Vieux Carré from Burgundy to Chartres Street, almost to the Mississippi River front buildings. An additional 212 buildings were destroyed in a later citywide fire on December 8, 1794.

Louisiana, or the Province of Louisiana, was a province of New Spain from 1762 to 1801 primarily located in the center of North America encompassing the western basin of the Mississippi River plus New Orleans. The area had originally been claimed and controlled by France, which had named it La Louisiane in honor of King Louis XIV in 1682. Spain secretly acquired the territory from France near the end of the Seven Years' War by the terms of the Treaty of Fontainebleau (1762). The actual transfer of authority was a slow process, and after Spain finally attempted to fully replace French authorities in New Orleans in 1767, French residents staged an uprising which the new Spanish colonial governor did not suppress until 1769. Spain also took possession of the trading post of St. Louis and all of Upper Louisiana in the late 1760s, though there was little Spanish presence in the wide expanses of what they called the "Illinois Country".

The Presbytère is an architecturally important building in the French Quarter of New Orleans, Louisiana. It stands facing Jackson Square, adjacent to the St. Louis Cathedral. Built in 1813 as a matching structure for the Cabildo, which flanks the cathedral on the other side, it is one of the nation's best examples of formal colonial Spanish architecture. It was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1970, and is now a property of the Louisiana State Museum.

The buildings and architecture of New Orleans reflect its history and multicultural heritage, from Creole cottages to historic mansions on St. Charles Avenue, from the balconies of the French Quarter to an Egyptian Revival U.S. Customs building and a rare example of a Moorish revival church.

The Historic New Orleans Collection (THNOC) is a museum, research center, and publisher dedicated to the study and preservation of the history and culture of New Orleans and the Gulf South region of the United States. It is located in New Orleans' French Quarter. The institution was established in 1966 by General and Mrs. L. Kemper Williams to keep their collection of Louisiana materials intact and available for research and exhibition to the public.

Micaela Leonarda Antonia de Almonester Rojas y de la Ronde, Baroness de Pontalba was a wealthy New Orleans-born Creole aristocrat, businesswoman, and real estate designer and developer, who endures as one of the most recalled and dynamic personalities in the city's history, though she lived most of her life in Paris.

The Louisiana State Museum's 1850 House is an antebellum row house furnished to represent life in mid-nineteenth-century New Orleans. It is located at 523 St. Ann Street on Jackson Square in the French Quarter.
Events from the year 1788 in the United States.

William Woodward was a U.S. artist and educator, best known for his impressionist paintings of New Orleans and the Gulf Coast of the United States.
José Francisco Xavier de Salazar y Mendoza (1750–1802) was a portrait painter from New Spain known for being the first painter of significance to work in Spanish colonial New Orleans, Louisiana.

In New Orleans, a gallery is a wide platform projecting from the wall of a building supported by posts or columns. Galleries are typically constructed from cast iron with ornate balusters, posts, and brackets.