
Veins are blood vessels in the circulatory system of humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are those of the pulmonary and fetal circulations which carry oxygenated blood to the heart. In the systemic circulation, arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart, and veins return deoxygenated blood to the heart, in the deep veins.
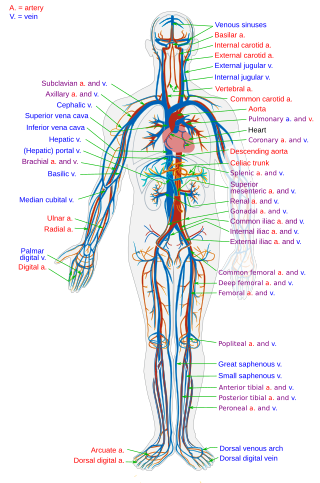
The circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart and blood vessels. The circulatory system has two divisions, a systemic circulation or circuit, and a pulmonary circulation or circuit. Some sources use the terms cardiovascular system and vascular system interchangeably with circulatory system.

The brachial artery is the major blood vessel of the (upper) arm. It is the continuation of the axillary artery beyond the lower margin of teres major muscle. It continues down the ventral surface of the arm until it reaches the cubital fossa at the elbow. It then divides into the radial and ulnar arteries which run down the forearm. In some individuals, the bifurcation occurs much earlier and the ulnar and radial arteries extend through the upper arm. The pulse of the brachial artery is palpable on the anterior aspect of the elbow, medial to the tendon of the biceps, and, with the use of a stethoscope and sphygmomanometer, often used to measure the blood pressure.

The left and right brachiocephalic veins are major veins in the upper chest, formed by the union of the ipsilateral internal jugular vein and subclavian vein behind the sternoclavicular joint. The left brachiocephalic vein is more than twice the length of the right brachiocephalic vein.

Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) or heart-lung machine also called the pump or CPB pump is a machine that temporarily takes over the function of the heart and lungs during open-heart surgery by maintaining the circulation of blood and oxygen throughout the body. As such it is an extracorporeal device.

Cardiac catheterization is the insertion of a catheter into a chamber or vessel of the heart. This is done both for diagnostic and interventional purposes.

The renal veins in the renal circulation, are large-calibre veins that drain blood filtered by the kidneys into the inferior vena cava. There is one renal vein draining each kidney. Each renal vein is formed by the convergence of the interlobar veins of one kidney.

In human anatomy, the hepatic veins are the veins that drain venous blood from the liver into the inferior vena cava. There are usually three large upper hepatic veins draining from the left, middle, and right parts of the liver, as well as a number (6-20) of lower hepatic veins. All hepatic veins are valveless.

The coronary sinus is the largest vein of the heart. It drains over half of the deoxygenated blood from the heart muscle into the right atrium. It begins on the backside of the heart, in between the left atrium, and left ventricle; it begins at the junction of the great cardiac vein, and oblique vein of the left atrium. It receives multiple tributaries. It passes across the backside of the heart along a groove between left atrium and left ventricle, then drains into the right atrium at the orifice of the coronary sinus.
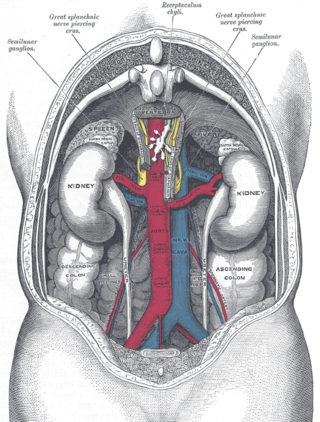
In medicine, gonadal vein refers to the blood vessel that carries blood away from the gonad toward the heart. These are different arteries in women and men, but share the same embryological origin.
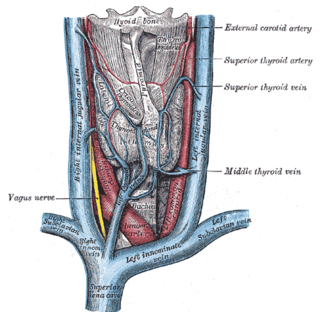
The superior thyroid vein is the vena comitans of the superior thyroid artery. It is formed by the union of deep and superficial tributaries that correspond to the arterial branches of the superior thyroid artery. Its tributaries are the superior laryngeal vein, and the cricothyroid veins. The vein empties into either the internal jugular vein, or the facial vein.

The inferior phrenic artery is a bilaterally paired artery of the abdominal cavity which represents the main source of arterial supply to the diaphragm. Each artery usually arises either from the coeliac trunk or the abdominal aorta, however, their origin is highly variable and the different sites of origin are different for the left artery and right artery. The superior suprarenal artery is a branch of the inferior phrenic artery.

The right colic artery is an artery of the abdomen, a branch of the superior mesenteric artery supplying the ascending colon. It divides into two terminal branches - an ascending branch and a descending branch - which form anastomoses with the middle colic artery, and ileocolic artery (respectively).

The middle suprarenal artery is a paired artery in the abdomen. It is a branch of the aorta. It supplies the adrenal gland.
The sinus venarum is the portion of the right atrium in the adult human heart where the inner surface of the right atrium is smooth, whereas the rest of the inner surface is rough (trabeculated) due to the presence of pectinate muscles. The sinus venarum represents the portion of the adult heart that develops from the right sinus horn of the foetal sinus venosus. The sinus venarum is demarcated from the rest of the right atrium by the crista terminalis (internally) and the sulcus terminalis (externally).

The dorsal nasal artery is an artery of the face. It is one of the two terminal branches of the ophthalmic artery. It contributes arterial supply to the lacrimal sac, and outer surface of the nose.

The supratrochlear artery is one of the terminal branches of the ophthalmic artery. It arises within the orbit. It exits the orbit alongside the supratrochlear nerve. It contributes arterial supply to the skin, muscles and pericranium of the forehead.

The crista terminalis is a vertical ridge on the posterolateral inner surface of the adult right atrium extending between the superior vena cava, and the inferior vena cava. The crista terminalis denotes where the junction of the embryologic sinus venosus and the right atrium occurred during embryonic development. It forms a boundary between the rough trabecular portion and the smooth, sinus venosus-derived portion of the internal surface of the right atrium. The sinoatrial node is located within the crista terminalis.

The lumbar veins are four pairs of veins running along the inside of the posterior abdominal wall, and drain venous blood from parts of the abdominal wall. Each lumbar vein accompanies a single lumbar artery. The lower two pairs of lumbar veins all drain directly into the inferior vena cava, whereas the fate of the upper two pairs is more variable.

The sinoatrial nodal artery, sinoatrial nodal artery or sinoatrial artery is an artery of the heart which supplies the sinoatrial node, the natural pacemaker center of the heart. It is usually a branch of the right coronary artery. It passes between the right atrium, and the opening of the superior vena cava.



















