Related Research Articles

Transportation planning is the process of defining future policies, goals, investments, and spatial planning designs to prepare for future needs to move people and goods to destinations. As practiced today, it is a collaborative process that incorporates the input of many stakeholders including various government agencies, the public and private businesses. Transportation planners apply a multi-modal and/or comprehensive approach to analyzing the wide range of alternatives and impacts on the transportation system to influence beneficial outcomes.

Infrastructure is the set of facilities and systems that serve a country, city, or other area, and encompasses the services and facilities necessary for its economy, households and firms to function. Infrastructure is composed of public and private physical structures such as roads, railways, bridges, tunnels, water supply, sewers, electrical grids, and telecommunications. In general, infrastructure has been defined as "the physical components of interrelated systems providing commodities and services essential to enable, sustain, or enhance societal living conditions" and maintain the surrounding environment.
Industrial ecology (IE) is the study of material and energy flows through industrial systems. The global industrial economy can be modelled as a network of industrial processes that extract resources from the Earth and transform those resources into by-products, products and services which can be bought and sold to meet the needs of humanity. Industrial ecology seeks to quantify the material flows and document the industrial processes that make modern society function. Industrial ecologists are often concerned with the impacts that industrial activities have on the environment, with use of the planet's supply of natural resources, and with problems of waste disposal. Industrial ecology is a young but growing multidisciplinary field of research which combines aspects of engineering, economics, sociology, toxicology and the natural sciences.

An eco-industrial park (EIP) is an industrial park in which businesses cooperate with each other and with the local community in an attempt to reduce waste and pollution, efficiently share resources, and help achieve sustainable development, with the intention of increasing economic gains and improving environmental quality. An EIP may also be planned, designed, and built in such a way that it makes it easier for businesses to co-operate, and that results in a more financially sound, environmentally friendly project for the developer.

Environment friendly processes, or environmental-friendly processes, are sustainability and marketing terms referring to goods and services, laws, guidelines and policies that claim reduced, minimal, or no harm upon ecosystems or the environment.
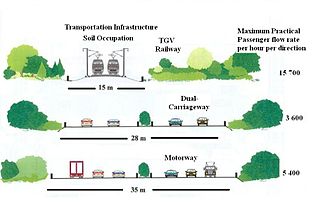
Sustainable urban infrastructure expands on the concept of urban infrastructure by adding the sustainability element with the expectation of improved and more resilient urban development. In the construction and physical and organizational structures that enable cities to function, sustainability also aims to meet the needs of the present generation without compromising the capabilities of the future generations.

The Center for Neighborhood Technology (CNT) is a non-profit organization, headquartered in Chicago, Illinois, which is committed to sustainable development and urban communities.

A sustainable city, eco-city, or green city is a city designed with consideration for social, economic, environmental impact, and resilient habitat for existing populations, without compromising the ability of future generations to experience the same. The UN Sustainable Development Goal 11 defines sustainable cities as those that are dedicated to achieving green sustainability, social sustainability and economic sustainability. They are committed to doing so by enabling opportunities for all through a design focused on inclusivity as well as maintaining a sustainable economic growth. The focus will also includes minimizing required inputs of energy, water, and food, and drastically reducing waste, output of heat, air pollution – CO2, methane, and water pollution. Richard Register, a visual artist, first coined the term ecocity in his 1987 book Ecocity Berkeley: Building Cities for a Healthy Future, where he offers innovative city planning solutions that would work anywhere. Other leading figures who envisioned sustainable cities are architect Paul F Downton, who later founded the company Ecopolis Pty Ltd, as well as authors Timothy Beatley and Steffen Lehmann, who have written extensively on the subject. The field of industrial ecology is sometimes used in planning these cities.

Green infrastructure or blue-green infrastructure refers to a network that provides the “ingredients” for solving urban and climatic challenges by building with nature. The main components of this approach include stormwater management, climate adaptation, the reduction of heat stress, increasing biodiversity, food production, better air quality, sustainable energy production, clean water, and healthy soils, as well as more anthropocentric functions, such as increased quality of life through recreation and the provision of shade and shelter in and around towns and cities. Green infrastructure also serves to provide an ecological framework for social, economic, and environmental health of the surroundings. More recently scholars and activists have also called for green infrastructure that promotes social inclusion and equity rather than reinforcing pre-existing structures of unequal access to nature-based services.
A green highway is a roadway constructed per a relatively new concept for roadway design that integrates transportation functionality and ecological sustainability. An environmental approach is used throughout the planning, design, and the construction. The result is a highway that will benefit transportation, the ecosystem, urban growth, public health and surrounding communities.
The Joint Ocean Commission Initiative is a bipartisan, collaborative group in the United States that aims to "accelerate the pace of change that results in meaningful ocean policy reform." The Joint Initiative was established by the members of two major U.S.-based oceans commissions: the Pew Oceans Commission and the United States Commission on Ocean Policy. It was originally co-chaired by former White House Chief of Staff Leon Panetta and former Chief of Naval Operations Admiral James D. Watkins, chairs of the Pew and U.S. Ocean Commissions, respectively. Currently, the Joint Initiative is led by a Leadership Council, which is co-chaired by Christine Todd Whitman, former EPA Administrator under President George W. Bush and former governor of New Jersey, and Norman Y. Mineta, Secretary of Commerce under President Bill Clinton and Secretary of Transportation under President George W. Bush.

Sustainable engineering is the process of designing or operating systems such that they use energy and resources sustainably, in other words, at a rate that does not compromise the natural environment, or the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.

Land recycling is the reuse of abandoned, vacant, or underused properties for redevelopment or repurposing.

The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) was established in July 1970 when the White House and the United States Congress came together due to the public's demand for cleaner natural resources. The purpose of the EPA is to repair the damage done to the environment and to set up new criteria to allow Americans to make a clean environment a reality. The ultimate goal of the EPA is to protect human health and the environment.
Sustainable products are products who are either sustainability sourced, manufactured or processed that provide environmental, social and economic benefits while protecting public health and environment over their whole life cycle, from the extraction of raw materials until the final disposal.
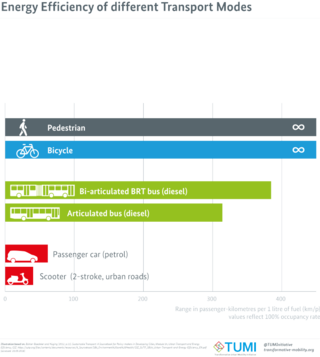
Sustainable urbanism is both the study of cities and the practices to build them (urbanism), that focuses on promoting their long term viability by reducing consumption, waste and harmful impacts on people and place while enhancing the overall well-being of both people and place. Well-being includes the physical, ecological, economic, social, health and equity factors, among others, that comprise cities and their populations. In the context of contemporary urbanism, the term cities refers to several scales of human settlements from towns to cities, metropolises and mega-city regions that includes their peripheries / suburbs / exurbs. Sustainability is a key component to professional practice in urban planning and urban design along with its related disciplines landscape architecture, architecture, and civil and environmental engineering. Green urbanism and ecological urbanism are other common terms that are similar to sustainable urbanism, however they can be construed as focusing more on the natural environment and ecosystems and less on economic and social aspects. Also related to sustainable urbanism are the practices of land development called Sustainable development, which is the process of physically constructing sustainable buildings, as well as the practices of urban planning called smart growth or growth management, which denote the processes of planning, designing, and building urban settlements that are more sustainable than if they were not planned according to sustainability criteria and principles.
Environmental stewardship refers to the responsible use and protection of the natural environment through active participation in conservation efforts and sustainable practices by individuals, small groups, nonprofit organizations, federal agencies, and other collective networks. Aldo Leopold (1887–1949) championed environmental stewardship in land ethics, exploring the ethical implications of "dealing with man's relation to land and to the animals and plants which grow upon it."

Low-impact development (LID) is a term used in Canada and the United States to describe a land planning and engineering design approach to manage stormwater runoff as part of green infrastructure. LID emphasizes conservation and use of on-site natural features to protect water quality. This approach implements engineered small-scale hydrologic controls to replicate the pre-development hydrologic regime of watersheds through infiltrating, filtering, storing, evaporating, and detaining runoff close to its source. Green infrastructure investments are one approach that often yields multiple benefits and builds city resilience.
Sustainable Materials Management is a systemic approach to using and reusing materials more productively over their entire lifecycles. It represents a change in how a society thinks about the use of natural resources and environmental protection. By looking at a product's entire lifecycle new opportunities can be found to reduce environmental impacts, conserve resources, and reduce costs.
E-highways, short for electric highways, are a new transportation infrastructure initiative aimed at electrifying heavy-duty vehicles to reduce carbon emissions and enhance sustainable mobility.