Related Research Articles

Dietary fiber or roughage is the portion of plant-derived food that cannot be completely broken down by human digestive enzymes. Dietary fibers are diverse in chemical composition, and can be grouped generally by their solubility, viscosity, and fermentability, which affect how fibers are processed in the body. Dietary fiber has two main components: soluble fiber and insoluble fiber, which are components of plant-based foods, such as legumes, whole grains and cereals, vegetables, fruits, and nuts or seeds. A diet high in regular fiber consumption is generally associated with supporting health and lowering the risk of several diseases. Dietary fiber consists of non-starch polysaccharides and other plant components such as cellulose, resistant starch, resistant dextrins, inulin, lignins, chitins, pectins, beta-glucans, and oligosaccharides.

A dietary supplement is a manufactured product intended to supplement a person's diet by taking a pill, capsule, tablet, powder, or liquid. A supplement can provide nutrients either extracted from food sources, or that are synthetic. The classes of nutrient compounds in supplements include vitamins, minerals, fiber, fatty acids, and amino acids. Dietary supplements can also contain substances that have not been confirmed as being essential to life, and so are not nutrients per se, but are marketed as having a beneficial biological effect, such as plant pigments or polyphenols. Animals can also be a source of supplement ingredients, such as collagen from chickens or fish for example. These are also sold individually and in combination, and may be combined with nutrient ingredients. The European Commission has also established harmonized rules to help insure that food supplements are safe and appropriately labeled.

Fenugreek is an annual plant in the family Fabaceae, with leaves consisting of three small obovate to oblong leaflets. It is cultivated worldwide as a semiarid crop. Its seeds and leaves are common ingredients in dishes from the Indian subcontinent, and have been used as a culinary ingredient since ancient times. Its use as a food ingredient in small quantities is safe.

The beetroot is the taproot portion of a beet plant, usually known in North America as beets while the vegetable is referred to as beetroot in British English, and also known as the table beet, garden beet, red beet, dinner beet or golden beet.

Vegetarian nutrition is the set of health-related challenges and advantages of vegetarian diets.
Nutraceutical is a marketing term used to imply a pharmaceutical effect from a compound or food product that has not been scientifically confirmed or approved to have clinical benefits. In the United States, nutraceuticals are unregulated, existing in the same category as dietary supplements and food additives by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), under the authority of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act.

A healthy diet is a diet that maintains or improves overall health. A healthy diet provides the body with essential nutrition: fluid, macronutrients such as protein, micronutrients such as vitamins, and adequate fibre and food energy.

Leaf vegetables, also called leafy greens, pot herbs, vegetable greens, or simply greens, are plant leaves eaten as a vegetable, sometimes accompanied by tender petioles and shoots. Leaf vegetables eaten raw in a salad can be called salad greens.

Wheatgrass is the freshly sprouted first leaves of the common wheat plant, used as a food, drink, or dietary supplement. Wheatgrass is served freeze dried or fresh, and so it differs from wheat malt, which is convectively dried. Wheatgrass is allowed to grow longer and taller than wheat malt.
Bodybuilding supplements are dietary supplements commonly used by those involved in bodybuilding, weightlifting, mixed martial arts, and athletics for the purpose of facilitating an increase in lean body mass. Bodybuilding supplements may contain ingredients that are advertised to increase a person's muscle, body weight, athletic performance, and decrease a person's percent body fat for desired muscle definition. Among the most widely used are high protein drinks, pre-workout blends, branched-chain amino acids (BCAA), glutamine, arginine, essential fatty acids, creatine, HMB, whey protein, ZMA, and weight loss products. Supplements are sold either as single ingredient preparations or in the form of "stacks" – proprietary blends of various supplements marketed as offering synergistic advantages.
Superfood is a marketing term for food claimed to confer health benefits resulting from an exceptional nutrient density. The term is not commonly used by experts, dietitians and nutrition scientists, most of whom dispute that particular foods have the health benefits claimed by their advocates. Even without scientific evidence of exceptional nutrient content, many new, exotic, and foreign fruits or ancient grains are marketed under the term – or superfruit or supergrain respectively – after being introduced or re-introduced to Western markets.

Juice Plus is a branded line of dietary supplements. It is produced by Natural Alternatives International of San Marcos, California, for National Safety Associates. Introduced in 1993, the supplements are distributed by NSA via multi-level marketing. Juice Plus supplements contain fruit and vegetable juice extracts with added vitamins and nutrients.

Glebionis coronaria, formerly called Chrysanthemum coronarium, is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae. It is native to the Mediterranean region. It is cultivated and naturalized in East Asia and in scattered locations in North America.

A smoothie is a beverage made by puréeing ingredients in a blender. A smoothie commonly has a liquid base, such as fruit juice or milk, yogurt or ice cream. Other ingredients may be added, including fruits, vegetables, non-dairy milk, crushed ice, whey powder or nutritional supplements.

Sustainable diets are "dietary patterns that promote all dimensions of individuals’ health and wellbeing; have low environmental pressure and impact; are accessible, affordable, safe and equitable; and are culturally acceptable". These diets are nutritious, eco-friendly, economically sustainable, and accessible to people of various socioeconomic backgrounds. Sustainable diets attempt to address nutrient deficiencies and excesses, while accounting for ecological phenomena such as climate change, loss of biodiversity and land degradation. These diets are comparable to the climatarian diet, with the added domains of economic sustainability and accessiblity.
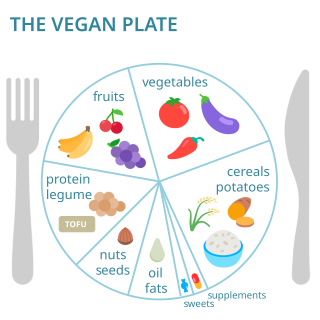
Vegan nutrition refers to the nutritional and human health aspects of vegan diets. A well-planned vegan diet is suitable to meet all recommendations for nutrients in every stage of human life. Vegan diets tend to be higher in dietary fiber, magnesium, folic acid, vitamin C, vitamin E, and phytochemicals; and lower in calories, saturated fat, iron, cholesterol, long-chain omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, calcium, zinc, and vitamin B12.

MyPlate is the current nutrition guide published by the United States Department of Agriculture's Center for Nutrition Policy and Promotion, and serves as a recommendation based on the Dietary Guidelines for Americans. It replaced the USDA's MyPyramid guide on June 2, 2011, ending 19 years of USDA food pyramid diagrams. MyPlate is displayed on food packaging and used in nutrition education in the United States. The graphic depicts a place setting with a plate and glass divided into five food groups that are recommended parts of a healthy diet. This dietary recommendation combines an organized amount of fruits, vegetables, grains, protein, and dairy. It is designed as a guideline for Americans to base their plate around in order to make educated food choices. ChooseMyPlate.gov shows individuals the variety of these 5 subgroups based on their activity levels and personal characteristics.

Huel Ltd. is a company that makes plant-based meals, snacks, drinks, and food supplements. Its products are made from oats, rice protein, pea protein, sunflower, flaxseed, coconut oil MCTs, and several dietary supplements. Most products are sweetened with sucralose or stevia. The product's name is a portmanteau of human fuel.

As in the human practice of veganism, vegan dog foods are those formulated with the exclusion of ingredients that contain or were processed with any part of an animal, or any animal byproduct. Vegan dog food may incorporate the use of fruits, vegetables, cereals, legumes including soya, nuts, vegetable oils, as well as any other non-animal based foods.

The Lectin-free diet is a fad diet promoted with the false claim that avoiding all foods that contain high amounts of lectins will prevent and cure disease. There is no clinical evidence the lectin-free diet is effective to treat any disease and its claims have been criticized as pseudoscientific.
References
- ↑ 9 Best Greens Powders Of 2024, According To Experts. Forbes Health. 3 April 2024. Retrieved 30 April 2024.
- ↑ Greens Powder: Are there Health Benefits?. WebMD. 14 September 2022. Retrieved 30 April 2024.
- ↑ Best greens powder to add essential nutrients to your diet. The Standard. 5 April 2024. Retrieved 30 April 2024.
- ↑ Can bright green 'super powders' really make you healthy?. BBC News. 3 March 2024. Retrieved 30 April 2024.
- ↑ Greens Powders: Benefits, Dangers and Dietitian Recommendations. U.S. News. 28 March 2024. Retrieved 30 April 2024.
- ↑ Will ‘Superfood Powders’ Actually Make You Healthier?. The New York Times. Retrieved 30 April 2024.
- ↑ Greens Powders are Popular, but Are They Worth It? Dietitians Weigh In. health.com. 8 May 2023. Retrieved 30 April 2024.