Related Research Articles

Greyfriars is a Roman Catholic friary and parish located in East Oxford, which until 2008 was also a Permanent Private Hall of the University of Oxford. Situated on the Iffley Road in East Oxford, it was one of the smallest constituent halls of the university. Its status as a Permanent Private Hall (PPH) referred to the fact that it was governed by an outside institution, rather than by its fellows as is a College.
Greyfriars, Grayfriars or Gray Friars is a term for Franciscan Order of Friars Minor, in particular, the Conventual Franciscans. The term often refers to buildings or districts formerly associated with the order.

Greyfriars Church is an evangelical Anglican church, and former Franciscan friary, in the town centre of Reading in the English county of Berkshire. The church forms part of the Church of England's Diocese of Oxford.
Greyfriars was a monastic house in Bedford, England. The house of the Grey Friars was founded either by Mabilea de Plateshull or John St. John during the reign of King Edward II, and their church was dedicated on 3 November 1295. The date of the arrival of the Franciscans in the town is not known.
The Franciscan Friary of Southampton was founded c. 1233. It occupied a south-eastern area of the city, within the walls and adjacent to God's House Tower. The friary was notable for its water supply system, which supplied water for use by the friars themselves and by the other inhabitants of Southampton. The friary was dissolved in 1538 and the last remains were swept away in the 1940s. The site is now occupied by Friary House. Elsewhere, remnants of the extensive water supply system still survive today.
Greyfriars, in Bristol, England, was a Franciscan friary. The name Greyfriars derived from the grey robes worn by the friars. It was founded at some time before 1234, within the town walls and then moved to Lewin's Mead in 1250. The site included extensive gardens surrounded by a stone wall. Following the Dissolution of the Monasteries in the sixteenth century, the premises were leased to the town council in 1541, who desired to use the stone to make repairs to the town walls, and the harbour facilities. In succeeding centuries many different uses have been made of the site, which is currently occupied by an office block and part of Bristol Dental School.
Dorchester Friary, also known as Dorchester Priory, was a Franciscan friary formerly located in Dorchester, Dorset, England.
Colchester Greyfriars, otherwise the Franciscan Friary, Colchester, was a Franciscan friary in Colchester, Essex, England, situated to the north of the town's east gate. It was founded sometime before 1237. In 1309 the friars received a grant of half an acre of land from Robert Fitzwalter, Lord Fitzwalter, on which he built their church. According to John Weever, the antiquarian, in his Ancient Funerall Monuments, Fitzwalter became a friar here himself in 1325, and was buried here.

Whitefriars, also known as the White Friars or The College of Carmelites, Gloucester, England, was a Carmelite friary of which nothing now survives.

The Greyfriars, Lincoln was a Franciscan friary in Lincolnshire, England. The surviving building is the remains of the infirmary of the friary, built of dressed stone and brick and dating from c.1230, with mid 19th century additions.

Boston Friary refers to any one of four friaries that existed in Boston, Lincolnshire, England.
Greyfriars Nottingham was a Franciscan friary in Nottinghamshire, England. It was founded c. 1224–1230, and dissolved in 1539 as part of King Henry VIII's Dissolution of the Monasteries. The site of the friary is now occupied by the Broadmarsh Shopping Centre.

In London, the Greyfriars was a Conventual Franciscan friary that existed from 1225 to 1538 on a site at the North-West of the City of London by Newgate in the parish of St Nicholas in the Shambles. It was the second Franciscan religious house to be founded in the country. The establishment included a conventual church that was one of the largest in London; a studium or regional university; and an extensive library of logical and theological texts. It was an important intellectual centre in the early fourteenth century, rivalled only by Oxford University in status. Members of the community at that time included William of Ockham, Walter Chatton and Adam Wodeham. It flourished in the fourteenth and fifteenth century but was dissolved in 1538 at the instigation of Henry VIII as part of the Dissolution of the Monasteries. Christ's Hospital was founded in the old conventual buildings, and the church was rebuilt completely by Sir Christopher Wren as Christ Church Greyfriars after the original church was almost completely destroyed in the Great Fire of London of 1666. The building now standing on the site, designed by Arup Group Limited, is currently occupied by Merrill Lynch.
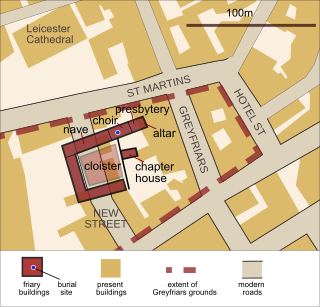
Greyfriars, Leicester, was a friary of the Order of Friars Minor, commonly known as the Franciscans, established on the west side of Leicester by 1250, and dissolved in 1538. Following dissolution the friary was demolished and the site levelled, subdivided, and developed over the following centuries. The locality has retained the name Greyfriars particularly in the streets named "Grey Friars", and the older "Friar Lane".
Newark Friary, also known as Newark Greyfriars, and Newark Observant Friary, was a friary of the reformed "Observant Friars" of the Franciscan Order, located in the town of Newark, Nottinghamshire, England. The friary as founded by Henry Tudor c. 1499, and dissolved by his son, Henry VIII, in 1539.
Greyfriars, Dumfries, was a friary of the Friars Minor, commonly known as the Franciscans, established in Dumfries, Scotland. Following dissolution the friary was demolished and the site levelled. The locality has retained a reference to the friary in the street named "Friars Vennel". The present neo-Gothic Greyfriars was built from 1868 and is located at the site of the former Maxwell's Castle at the top of High Street.

Ipswich Greyfriars was a mediaeval monastic house of Friars Minor (Franciscans) founded during the 13th century in Ipswich, Suffolk. It was said conventionally to have been founded by Sir Robert Tibetot of Nettlestead, Suffolk, but the foundation is accepted to be set back before 1236. This makes it the earliest house of mendicant friars in Suffolk, and established no more than ten years after the death of St Francis himself. It was within the Cambridge Custody. It remained active until dissolved in the late 1530s.
References
- 1 2 William Page, ed. (1974). "Friaries: Houses of grey friars". A History of the County of York. Vol. 3. London: Victoria County History. pp. 264–267.
- ↑ "Pamela Hopkins on Medieval Beverley" (PDF). 27 September 2017.
Coordinates: 53°50′13″N0°26′08″W / 53.837008°N 0.435626°W