Atmospheric pressure, sometimes also called barometric pressure, is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere is a unit of pressure defined as 1013.25 mbar (101325 Pa), equivalent to 760 mmHg (torr), 29.9212 inches Hg, or 14.696 psi. The atm unit is roughly equivalent to the mean sea-level atmospheric pressure on Earth, that is, the Earth's atmospheric pressure at sea level is approximately 1 atm.

Bavarian Alps is a summarizing term of several mountain ranges of the Northern Limestone Alps in the German state of Bavaria.

Krün is a municipality in the Upper Bavarian district of Garmisch-Partenkirchen. It belongs with Garmisch-Partenkirchen as district capital and cultural center as well as other municipalities to the region Werdenfelser Land. A few kilometers south runs the German-Austrian border.
The Finne is a ridge of hills in the German states of Saxony-Anhalt and Thuringia up to 370.1 m above sea level (NHN) and 23 km long.
The Zitter Forest is located in the Eifel region in the German district of Euskirchen and in the Belgian province of Liège (Wallonia). Its highest point is 692 m above sea level (NN).

The Ebbe Mountains or Ebbe form a range of uplands up to 663.3 m above sea level (NN) high in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. They have given their name to the Ebbe Mountain Nature Park and are part of the Süder Uplands within the Rhine Massif.

The Lenne Mountains, or Lenne Uplands (Lennebergland), is a range of hills up to 656 m above sea level (NN) high in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. It is part of the Süder Uplands within the Rhine Massif.

The Arnsberg Forest Nature Park is a nature park in the districts of Hochsauerlandkreis and Soest within the administrictive region of Arnsberg in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. The park has an area of 482 km² and its wooded hills are up to 581.5 m above sea level (NN).
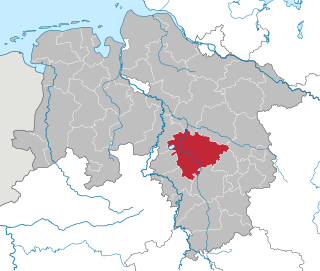
The Calenberg Uplands are a landscape unit in the Weser-Leine Uplands in Lower Saxony, Germany. They border on the Calenberg Land to the north and merge into the Weser Uplands in the west and the Leine Uplands in the east. They are dissected by the Deister-Süntel and Aue valleys.

Lenne is river of Lower Saxony, Germany. It is a 24 km (15 mi) long, right-hand, eastern tributary of the river Weser in the district of Holzminden in the Weser Uplands.

The Alter Stolberg is a wooded karst plateau, up to 357.7 m above sea level (NN), in the South Harz in Central Germany. It lies in the districts of Nordhausen in the state of Thuringia and Mansfeld-Südharz in the state of Saxony-Anhalt.

The Großer Krottenkopf is the highest mountain in the Allgäu Alps of Austria. It is 2,656 m (AA) and is part of a side branch of the Hornbach chain, which branches off the main chain of the Allgäu Alps and runs for about 15 km eastwards.

The Thuringian Forest Nature Park is one of the two nature parks in the state of Thuringia, Germany.

The Ardey Hills are a range of wooded hills, up to 273.8 m above sea level (NN), in the territory of the city of Dortmund and the districts of Ennepe-Ruhr-Kreis and Unna in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. The hills form part of the eastern Rhenish Massif and, to a lesser extent, to the Berg-Mark Hills.
The Allerbach is a left tributary of the Warme Bode, just under 5 kilometres (3 mi) long, in the Harz Mountains of central Germany.

The Hüggel is a ridge, up to 225.6 m above sea level (NN), about 5 kilometres long and 1 kilometre wide, near Hasbergen in the Lower Saxon district of Osnabrück in central Germany. It is the highest point of the Osnabrück Uplands. This Upper Carboniferous outcrop is part of the Ibbenbüren Coalfield.

The Ackeburg, also called the Ackenburg, in the Harz Mountains of central Germany, is the site of a high medieval hill castle, 333.2 m above sea level (NN), in the borough of Falkenstein/Harz in Harz district in the state of Saxony-Anhalt. It was first mentioned in 1216 and was abandoned or destroyed in 1400. There was also a village associated with it, known as Akkeburg.

The Steina Dam in the Harz Mountains of central Germany is a dam system comprising a dam, reservoir and waterworks near the village of Steina and belongs to the unincorporated area of Harz in the county of Osterode am Harz in Lower Saxony.
The Alzey Hills form a region of low, rolling hills, or Hügelland, 275 km² in area and up to 337 m above sea level (NHN), in Rhenish Hesse in the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate. From a natural region perspective they are part of the Upper Rhine Plain and classed as major unit no. 227.

The Lange Berge are a small range of the German Central Uplands, up to 527.2 m above sea level (NN), which lie mainly in the Bavarian provinces of Upper Franconia with northwestern foothills in Thuringia.