Klez is a computer worm that propagates via e-mail. It first appeared in October 2001 and was originated in China. A number of variants of the worm exist.
Sircam is a computer worm that first propagated in 2001 by e-mail in Microsoft Windows systems. It affected computers running Windows 95, Windows 98, and Windows Me (Millennium). It began with one of the following lines of text and had an attachment consisting of the worm's executable with some file from the infected computer appended:

This timeline of computer viruses and worms presents a chronological timeline of noteworthy computer viruses, computer worms, Trojan horses, similar malware, related research and events.
The Melissa virus is a mass-mailing macro virus released on or around March 26, 1999. It targets Microsoft Word and Outlook-based systems and created considerable network traffic. The virus infects computers via email; the email is titled "Important Message From," followed by the current username. Upon clicking the message, the body reads, "Here's that document you asked for. Don't show anyone else ;)." Attached is a Word document titled "list.doc," containing a list of pornographic sites and accompanying logins for each. It then mass-mails itself to the first fifty people in the user's contact list and disables multiple safeguard features on Microsoft Word and Microsoft Outlook.

Blaster was a computer worm that spread on computers running operating systems Windows XP and Windows 2000 during August 2003.

Mydoom was a computer worm that targeted computers running Microsoft Windows. It was first sighted on January 26, 2004. It became the fastest-spreading e-mail worm ever, exceeding previous records set by the Sobig worm and ILOVEYOU, a record which as of 2024 has yet to be surpassed.

WinFixer was a family of scareware rogue security programs developed by Winsoftware which claimed to repair computer system problems on Microsoft Windows computers if a user purchased the full version of the software. The software was mainly installed without the user's consent. McAfee claimed that "the primary function of the free version appears to be to alarm the user into paying for registration, at least partially based on false or erroneous detections." The program prompted the user to purchase a paid copy of the program.
Blackworm is an Internet worm discovered on January 20, 2006 that infects several versions of Microsoft Windows. It is also known as Grew.a, Grew.b, Blackmal.e, Nyxem.e, Nyxem.d, Mywife.d, Tearec.a, CME-24, and Kama Sutra.
CTX is a computer virus created in Spain in 1999. CTX was initially discovered as part of the Cholera worm, with which the author intentionally infected with CTX. Although the Cholera worm had the capability to send itself via email, the CTX worm quickly surpassed it in prevalence. Cholera is now considered obsolete, while CTX remains in the field, albeit with only rare discoveries.
A computer virus hoax is a message warning the recipients of a non-existent computer virus threat. The message is usually a chain e-mail that tells the recipients to forward it to everyone they know, but it can also be in the form of a pop-up window.
W32.Navidad is a mass-mailing worm program or virus, discovered in December 2000 that ran on Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows NT, and Windows 2000 systems. It was designed to spread through email clients such as Microsoft Outlook while masquerading as an executable electronic Christmas card. Infected computers can be identified by blue eye icons which appear in the Windows system tray.
Brontok is a computer worm running on Microsoft Windows. It is able to disperse by e-mail. Variants include:
RavMonE, also known as RJump, is a Trojan that opens a backdoor on computers running Microsoft Windows. Once a computer is infected, the virus allows unauthorized users to gain access to the computer's contents. This poses a security risk for the infected machine's user, as the attacker can steal personal information, and use the computer as an access point into an internal network.
ExploreZip is a destructive computer worm that attacks machines running Microsoft Windows. It was first discovered in Israel on June 6, 1999. The worm contains a malicious payload, and utilizes Microsoft Outlook, Outlook Express, or Exchange to mail itself out by replying to unread messages in the user's inbox. The worm also searches mapped drives and networked computers for Windows installations. If found, it copies itself to the Windows folder of the remote computer and then modifies the Win.ini file of the infected computer. On January 8, 2003, Symantec discovered a packed variant of this threat which exhibits the same characteristics.
Stration is a family of computer worms that can affect computers running Microsoft Windows, disabling security features and propagating itself to other computers via e-mail attachments. This family of worms is unusual in that new variants are being produced at an unprecedented rate, estimated to be up to one every 30 minutes at its peak, and downloaded from remote servers by infected machines to speed propagation. This makes detection and removal a particular challenge for anti-virus software vendors, because new signature files for each variant need to be issued to allow their software to detect them.

The Storm Worm is a phishing backdoor Trojan horse that affects computers using Microsoft operating systems, discovered on January 17, 2007. The worm is also known as:
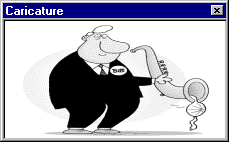
MyLife, discovered by MessageLabs in 2002, is a computer worm that spreads itself by sending email to the addresses found in Microsoft Outlook's contacts list. Written in Visual Basic, it displays an image of a girl holding a flower while it attempts to delete files with certain filename extensions. It is named for a phrase appearing in the subject lines of the emails it sends. A variant, MyLife.B, also called the Bill Clinton worm, instead uses a subject line "bill caricature" and displays a cartoon image of Bill Clinton playing a saxophone. Many additional variants have been reported. When the infected file is run, and the picture is closed, the worm runs its payload. MyLife checks the current date. If the minute value is higher or at 45, the worm searches the C:\ directory and deletes .SYS files, .COM files and the same in D:\ Drives.
Koobface is a network worm that attacks Microsoft Windows, Mac OS X, and Linux platforms. This worm originally targeted users of networking websites such as Facebook, Skype, Yahoo Messenger, and email websites such as GMail, Yahoo Mail, and AOL Mail. It also targets other networking websites, such as MySpace, Twitter, and it can infect other devices on the same local network. Technical support scammers also fraudulently claim to their intended victims that they have a Koobface infection on their computer by using fake popups and using built-in Windows programs.

Conficker, also known as Downup, Downadup and Kido, is a computer worm targeting the Microsoft Windows operating system that was first detected in November 2008. It uses flaws in Windows OS software and dictionary attacks on administrator passwords to propagate while forming a botnet, and has been unusually difficult to counter because of its combined use of many advanced malware techniques. The Conficker worm infected millions of computers including government, business and home computers in over 190 countries, making it the largest known computer worm infection since the 2003 SQL Slammer worm.
The Pikachu virus, also referred to as Pokey or the Pokémon virus, was a computer worm believed to be the first malware geared at children, due to its incorporation of Pikachu, the mascot species of the Pokémon media franchise. It was considered similar to the Love Bug, albeit slower in its spread and less dangerous.








