Related Research Articles

A stream cipher is a symmetric key cipher where plaintext digits are combined with a pseudorandom cipher digit stream (keystream). In a stream cipher, each plaintext digit is encrypted one at a time with the corresponding digit of the keystream, to give a digit of the ciphertext stream. Since encryption of each digit is dependent on the current state of the cipher, it is also known as state cipher. In practice, a digit is typically a bit and the combining operation is an exclusive-or (XOR).

In statistics, correlation or dependence is any statistical relationship, whether causal or not, between two random variables or bivariate data. Although in the broadest sense, "correlation" may indicate any type of association, in statistics it normally refers to the degree to which a pair of variables are linearly related. Familiar examples of dependent phenomena include the correlation between the height of parents and their offspring, and the correlation between the price of a good and the quantity the consumers are willing to purchase, as it is depicted in the so-called demand curve.

In computing, a hardware random number generator (HRNG) or true random number generator (TRNG) is a device that generates random numbers from a physical process, rather than by means of an algorithm. Such devices are often based on microscopic phenomena that generate low-level, statistically random "noise" signals, such as thermal noise, the photoelectric effect, involving a beam splitter, and other quantum phenomena. These stochastic processes are, in theory, completely unpredictable for as long as an equation governing such phenomena is unknown or uncomputable. This is in contrast to the paradigm of pseudo-random number generation commonly implemented in computer programs.
A cryptographically secure pseudorandom number generator (CSPRNG) or cryptographic pseudorandom number generator (CPRNG) is a pseudorandom number generator (PRNG) with properties that make it suitable for use in cryptography. It is also loosely known as a cryptographic random number generator (CRNG).

A scatter plot is a type of plot or mathematical diagram using Cartesian coordinates to display values for typically two variables for a set of data. If the points are coded (color/shape/size), one additional variable can be displayed. The data are displayed as a collection of points, each having the value of one variable determining the position on the horizontal axis and the value of the other variable determining the position on the vertical axis.
In cryptography, padding is any of a number of distinct practices which all include adding data to the beginning, middle, or end of a message prior to encryption. In classical cryptography, padding may include adding nonsense phrases to a message to obscure the fact that many messages end in predictable ways, e.g. sincerely yours.
This glossary of statistics and probability is a list of definitions of terms and concepts used in the mathematical sciences of statistics and probability, their sub-disciplines, and related fields. For additional related terms, see Glossary of mathematics and Glossary of experimental design.

Zarch is a computer game developed by David Braben in 1987, for the release of the Acorn Archimedes computer. Zarch started off as a demo called Lander which was bundled with almost all releases of the Acorn Archimedes.

Twilight Zone is a widebody pinball machine, designed by Pat Lawlor and based on the TV series of the same name. It was first released in 1993 by Midway. This game is part of WMS' SuperPin line of widebody games alongside Star Trek: The Next Generation and Indiana Jones: The Pinball Adventure.

Google Image Labeler is a feature, in the form of a game, of Google Images that allows the user to label random images to help improve the quality of Google's image search results. It was online from 2006 to 2011 and relaunched in 2016.
In statistics, regression validation is the process of deciding whether the numerical results quantifying hypothesized relationships between variables, obtained from regression analysis, are acceptable as descriptions of the data. The validation process can involve analyzing the goodness of fit of the regression, analyzing whether the regression residuals are random, and checking whether the model's predictive performance deteriorates substantially when applied to data that were not used in model estimation.
In applied statistics, a partial regression plot attempts to show the effect of adding another variable to a model that already has one or more independent variables. Partial regression plots are also referred to as added variable plots, adjusted variable plots, and individual coefficient plots.
A human-based computation game or game with a purpose (GWAP) is a human-based computation technique of outsourcing steps within a computational process to humans in an entertaining way (gamification).
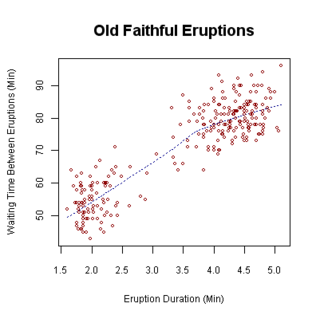
A plot is a graphical technique for representing a data set, usually as a graph showing the relationship between two or more variables. The plot can be drawn by hand or by a computer. In the past, sometimes mechanical or electronic plotters were used. Graphs are a visual representation of the relationship between variables, which are very useful for humans who can then quickly derive an understanding which may not have come from lists of values. Given a scale or ruler, graphs can also be used to read off the value of an unknown variable plotted as a function of a known one, but this can also be done with data presented in tabular form. Graphs of functions are used in mathematics, sciences, engineering, technology, finance, and other areas.
In cryptography, correlation attacks are a class of known plaintext attacks for breaking stream ciphers whose keystream is generated by combining the output of several linear-feedback shift registers (LFSRs) using a Boolean function. Correlation attacks exploit a statistical weakness that arises from certain choices of the Boolean function. The cipher is not inherently insecure if there is a choice of the Boolean function that avoids this weakness. As with all attack methods, this should be accounted for when designing an encryption system.
In statistics, bivariate data is data on each of two variables, where each value of one of the variables is paired with a value of the other variable. Typically it would be of interest to investigate the possible association between the two variables. The association can be studied via a tabular or graphical display, or via sample statistics which might be used for inference. The method used to investigate the association would depend on the level of measurement of the variable. This association that involves exactly two variables can be termed a bivariate correlation, or bivariate association.
In cryptography, Mutual Irregular Clocking KEYstream generator (MICKEY) is a stream cipher algorithm developed by Steve Babbage and Matthew Dodd. The cipher is designed to be used in hardware platforms with limited resources, and was one of the three ciphers accepted into Profile 2 of the eSTREAM portfolio. The algorithm is not patented and is free for any use.

Jackbox Games, Inc. is an American video game developer based in Chicago, Illinois, best known for the You Don't Know Jack series of quiz-based party video games and The Jackbox Party Pack series. Founded by Harry Gottlieb, the company operated as Jellyvision Games from 1995 until its closure in 2001. After seven years of dormancy, Jellyvision Games was revived in 2008, and the company rebranded as Jackbox Games in 2013.

The Jackbox Party Pack is a series of party video games developed by Jackbox Games for many different platforms on a near-annual release schedule since 2014. Each installation contains five games that are designed to be played in large groups, including in conjunction with streaming services like Twitch which provide means for audiences to participate.

Puzzle Link 2 is a 1999 Arcade-style puzzle video game for the Neo-Geo Pocket Color. Like 1998's Puzzle Link, to which it is the direct sequel, Puzzle Link 2 was developed by Yumekobo and published by SNK.
References
- 1 2 Ed Yong (30 March 2016). "The 8-Bit Game That Makes Statistics Addictive". The Atlantic . Retrieved 20 July 2017.
- 1 2 3 Omar Wagih (10 December 2015). "Guess the Correlation" . Retrieved 26 July 2017.
- 1 2 3 Brian Tarran (9 February 2016). "A game about correlations that's more than just fun". Significance . Retrieved 26 July 2017.
- ↑ Jamie Condliffe (1 February 2016). "This 8-Bit Guess-the-Correlation Game Is Way More Fun Than It Should Be". Gizmodo . Retrieved 20 July 2017.