Related Research Articles
The history of Brunei concerns the settlements and societies located on the north coast of the island of Borneo, which has been under the influence of Indianised kingdoms and empires for much of its history. Local scholars assume that the Islamisation of Brunei started in the fifteenth century with the formation of the Bruneian Empire, a thalassocracy that covered the northern part of Borneo and the southern Philippines. At the end of the 17th century, Brunei subsequently entered a period of decline brought on by Brunei Civil War, piracy, and European colonial expansion. Later, there was a brief war with Spain, in which Brunei lost Manila and evacuated their capital for a brief period until the Spanish withdrew. The empire lost much of its territory with the arrival of the Western powers, such as the Spanish in the Philippines and the British in Labuan, Sarawak, and North Borneo. The decline of the Bruneian Empire accelerated in the nineteenth century when Brunei gave much of its territory to the White Rajahs of Sarawak, resulting in its current small landmass and separation into two parts. Sultan Hashim Jalilul Alam Aqamaddin later appealed to the British to stop further annexation in 1888. In the same year, the British signed a "Treaty of Protection" and made Brunei a British protectorate until 1984 when it gained independence and prospered due to the discovery of oil.

The Sultanate of Sulu was a Muslim state that ruled the Sulu Archipelago, costal areas of Zamboanga City and certain portions of Palawan in the today's Philippines, alongside parts of present-day Sabah, North and East Kalimantan in north-eastern Borneo.

The Tausūg, are an ethnic group of the Philippines and Malaysia. A small population can also be found in the northern part of North Kalimantan, Indonesia. The Tausūg are part of the wider political identity of Muslim Filipinos of western Mindanao, the Sulu archipelago, and southern Palawan, collectively referred to as the Moro people. The Tausugs originally had an independent state known as the Sultanate of Sulu, which once exercised sovereignty over the present day provinces of Basilan, Palawan, Sulu, Tawi-Tawi, Zamboanga City, North Kalimantan and the eastern part of the Malaysian state of Sabah. They are also known in the Malay language as Suluk.
Omar Ali Saifuddin I ibni Muhammad Alauddin, also known as Al-Marhum Makam Besar, was the 18th Sultan of Brunei and the second son of Sultan Muhammad Alauddin. He was regarded as one of the longest-serving sultans and was renowned for his wise leadership and just rule, merely following his father-in-law, Sultan Hussin Kamaluddin. In fact, he received helpful knowledge, counsel, and experience from his father-in-law when he was still alive during his reigning period.

Islam in the Philippines is the second largest religion in the country, and the faith was the first-recorded monotheistic religion in the Philippines. Historically, Islam reached the Philippine archipelago in the 14th century, through contact with Muslim Malay and Arab merchants along Southeast Asian trade networks, in addition to Yemeni missionaries from the tribe of Alawi of Yemen from the Persian Gulf, southern India, and their followers from several sultanates in the wider Malay Archipelago. The first missionaries then followed in the late 14th and early 15th centuries. They facilitated the formation of sultanates and conquests in mainland Mindanao and Sulu. Those who converted to Islam came to be known as the Moros, with Muslim conquest reaching as far as Tondo that was later supplanted by Bruneian Empire vassal-state of Maynila.

The Moro people or Bangsamoro people are the 13 Muslim-majority ethnolinguistic Austronesian groups of Mindanao, Sulu, and Palawan, native to the region known as the Bangsamoro. As Muslim-majority ethnic groups, they form the largest non-Christian population in the Philippines, and comprise about 5% of the country's total population, or 5 million people.

The Iranun are an Austronesian ethnic group native to southwestern Mindanao, Philippines. They are ethnically and culturally closely related to the Maranao, and Maguindanaon, all three groups being denoted as speaking Danao languages and giving name to the island of Mindanao. The Iranun were traditionally sailors and were renowned for their ship-building skills. Iranun communities can also be found in Malaysia and Philippines.

The Maguindanaon people are an Austronesian ethnic group from the Philippines. The Maguindanaon are part of wider political identity of Muslims known as Moro, who constitute the third largest ethnic group of Mindanao, Sulu and Palawan. The Maguindanaons constitute the ninth largest Filipino ethnic group and are known for being distinguished in the realm of visual art. They have been renowned as metalworkers, producing the wavy-bladed keris ceremonial swords and other weapons, as well as gongs. The Maguindanaons historically had an independent sultanate known as the Sultanate of Maguindanao which comprises modern day Maguindanao del Norte, Maguindanao del Sur, Zamboanga Peninsula, Davao Region and Soccsksargen. The name "Maguindanao/Magindanaw" itself was corrupted by Spanish sources into "Mindanao", which became the name for the entire island of Mindanao.

The Sultanate of Maguindanao was a sultanate that ruled parts of the island of Mindanao, in the southern Philippines, especially in modern-day Maguindanao provinces, Soccsksargen, Zamboanga Peninsula and Davao Region. Its known historical influence stretches from the peninsula of Zamboanga to bay of Sarangani until Davao Gulf. During the era of European colonization, the Sultanate maintained friendly relations with British and Dutch traders.

Muhammad Dipatuan Kudarat was the 7th Sultan of Maguindanao from 1619 to 1671.
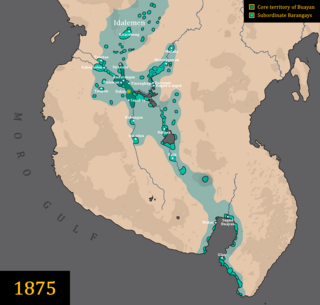
The Sultanate of Buayan, alternatively the Rajahnate of Buayan, was a Muslim state on the island of Mindanao in the southern Philippines from the mid-14th to the 20th century. Buayan was one of the four major sultanates in Mindanao, other sultanates being the Sultanate of Sulu, the Sultanate of Maguindanao, and the Confederacy of Lanao. Being the primary power in the upper Cotabato valley, it had access to an abundance of fertile land as well as raw materials, transforming into an agricultural powerhouse in contrast to Maguindanao. In addition, despite its status as an interior sultanate, Buayan was able to conduct maritime trade and diplomacy either through the Pulangi river mouth, or its port in Sarangani. At its maximum extent, its territory stretched from modern-day Kabuntalan to Sarangani Bay.
Muhammad Hasan ibni Saiful Rijal Nurul Alam, also known as Marhum di Tanjung, was the tenth Sultan of Brunei from 1582 to 1598. Under him, the Bruneian Empire had apparently full control of the island of Borneo and Northern Philippines, including Sulu.
Shariff Muhammed Kabungsuwan was the first Sultan of Maguindanao in the Philippines. A native of Johore in Maritime Southeast Asia, Kabungsuwan re-settled in Mindanao in the Philippines where he preached Islam to the native tribes around the region.
Kapitan Laut Buisan, also known as Datu Katchil or Sultan Laut Buisan, was the sixth Sultan of Maguindanao in the Philippines. He was a direct descendant of Shariff Kabungsuwan, a Muslim missionary who preached Islam in the Philippines and established the sultanate after marrying a Sulu princess in the 16th century.
Sultan Batara Shah Tengah was the 8th Sultan of Sulu. He reigned from 1596 to 1608. He was the son of the previous Sultan Muhammad ul-Halim, also known as Pangiran Buddiman.

Malays played a significant role in pre-Hispanic Philippine history. Malay involvement in Philippine history goes back to the Classical Era with the establishment of Rajahnates as well as the Islamic era, in which various sultanates and Islamic states were formed in Mindanao, the Sulu Archipelago, and around Manila.

Datu Uto, also known as Sultan Anwarud-din Utto or Sultan Utto Anwaruddin, alternatively spelled as Datu Utto, was the 18th Sultan of Buayan, one of the major sultanates of Mindanao. As a military leader he distinguished himself in many battles against the Spanish.
Sultan Dimasangcay Adel was the fourth sultan of Maguindanao in the Philippines. He was a direct descendant of Sharif Kabungsuwan, the first sultan of Maguindanao. He was the son of Sultan Bangkaya with his Maguindanao wife. Dimasangcay also had half brothers, Gugu Sarikula and Buisan, who also sequentially reigned as sultans of Maguindanao after him.

In the Philippine history, the Lupah Sug was a predecessor state before the establishment of Sultanate of Sulu.
References
- 1 2 Syed, Muzaffar Husain; Akhtar, Syed Saud; Usmani, B.D. (2011). Concise History of Islam. Vij Books India Pvt Ltd. p. 329. ISBN 978-93-82573-47-0.
- 1 2 3 "Dansalan Quarterly". Dansalan Quarterly. Vol. 1–4. Dansalan Research Center. 1979. p. 76.
- 1 2 Haerens, Margaret (2014). Mixed Marriage. Greenhaven Publishing LLC. p. 104. ISBN 978-0-7377-6266-2.
- 1 2 Daturaiz Mamadra. The Rise of the Maguindanao Sultanate.
- 1 2 Mastura, Michael O. (1984). Muslim Filipino Experience: A Collection of Essays. Ministry of Muslim Affairs. p. 21.