Related Research Articles

Borobudur, also transcribed Barabudur, is a 9th-century Mahayana Buddhist temple in Magelang Regency, near the city of Magelang and the town of Muntilan, in Central Java, Indonesia.

Prambanan is a 9th-century Hindu temple compound in the Special Region of Yogyakarta, in southern Java, Indonesia, dedicated to the Trimūrti, the expression of God as the Creator (Brahma), the Preserver (Vishnu) and the Destroyer (Shiva). The temple compound is located approximately 17 kilometres (11 mi) northeast of the city of Yogyakarta on the boundary between Central Java and Yogyakarta provinces.

Buddhist religious architecture developed in the Indian subcontinent. Three types of structures are associated with the religious architecture of early Buddhism: monasteries (viharas), places to venerate relics (stupas), and shrines or prayer halls, which later came to be called temples in some places.

Buddhism has a long history in Indonesia, and it is one of the six recognized religions in the country, along with Islam, Christianity, Hinduism and Confucianism. According to 2023 estimates roughly 0.71% of the total citizens of Indonesia were Buddhists, numbering around 2 million. Most Buddhists are concentrated in Jakarta, Riau, Riau Islands, Bangka Belitung, North Sumatra, and West Kalimantan. These totals, however, are probably inflated, as practitioners of Taoism and Chinese folk religion, which are not considered official religions of Indonesia, likely declared themselves as Buddhists on the most recent census. Today, the majority of Buddhists in Indonesia are Chinese and other East Asians, but small communities of native Buddhists also exist.

A candi is a Hindu or Buddhist temple in Indonesia, mostly built during the Zaman Hindu-Buddha or "Hindu-Buddhist period" between circa the 4th and 15th centuries.

Pawon is a Buddhist temple in Central Java, Indonesia.

Mendut is a ninth-century Buddhist temple, located in Mendut village, Mungkid sub-district, Magelang Regency, Central Java, Indonesia. The temple is located about three kilometres east of Borobudur. Mendut, Borobudur, and Pawon, all of which are Buddhist temples, are located in one straight line. There is a mutual religious relationship between the three temples, although the exact ritual process is unknown.

Borobudur Temple Compounds is the World Heritage designation of the area of three Buddhist temples in Central Java, Indonesia. It comprises Borobudur, Mendut, and Pawon. The temples were built during the Shailendra dynasty around the 8th and 9th centuries CE and fall on a straight line.

On large sailing ships a spritsail is a square-rigged sail carried on a yard below the bowsprit. One of the earliest depictions of a spritsail is carved on Borobudur ship carving in Borobudur temple, Indonesia.

A Borobudur ship is an 8th to 9th-century wooden double outrigger sailing vessel of Maritime Southeast Asia, depicted in some bas-reliefs of the Borobudur Buddhist monument in Central Java, Indonesia. It is a ship of the Javanese people, and derivative vessels of similar size continued to be used in East Java coastal trade at least until the 1940s.

Samudra Raksa Museum is a maritime museum that was built several hundred meters north of the 8th-century Borobudur Buddhist monument, within the Borobudur archaeological complex, Magelang, Central Java, Indonesia. The museum features and interprets the ancient maritime Indian Ocean trade among between ancient Indonesia, Madagascar, and East Africa, popularly dubbed as "the cinnamon route". The centerpiece of museum is the full-scale reconstruction of the 8th-century Borobudur ship. It was used in a successful expedition from Indonesia to Madagascar and Ghana in 2003—2004. The Borobudur Ship — a 25 meter-long wooden ship modeled after wall reliefs found on the 8th century Borobudur temple in Central Java.

Lake Borobudur is an ancient lake that has been suggested once existed surrounding Borobudur Buddhist monument in Kedu Plain, Central Java, Indonesia.

Cambodia and Indonesia established diplomatic relations in 1957. Cambodia has an embassy in Jakarta, while Indonesia has an embassy in Phnom Penh. Since diplomatic relations were established, Indonesia has been a strong supporter of peace and stability in Cambodia. In 1992, Indonesia provided troops for the United Nations Transitional Authority in Cambodia, and supported Cambodian membership to ASEAN in 1999. Cambodia appreciated that Indonesia has consistently helped Cambodia, especially in capacity building. Both nations are members of Non-Aligned Movement and ASEAN.

Nine bombs were detonated at the Borobudur Buddhist temple located in Magelang, Central Java, Indonesia on 21 January 1985. There were no human casualties in this attack; however, nine stupas on the upper rounded terraces of Arupadhatu were badly damaged by bombs.

Karmawibhangga Museum also known as Borobudur Museum, is an archaeology museum located just several hundred meters north of 8th century Borobudur Buddhist monument, within Borobudur Archaeological Park, Magelang Regency, Central Java, Indonesia. The museum featuring pictures of Karmawibhangga bas reliefs carved on the hidden foot of Borobudur, some disassembled Borobudur stones, archaeological artifacts found around Borobudur and Central Java. The museum also displays the Borobudur architecture and structure, also the documentation of restoration project conducted between 1975 and 1982 under UNESCO guidance. The museum was built in traditional Javanese architecture; the joglo house with pendopo pavilion. The museum is integrated within Borobudur Archaeological Park inaugurated in 1983.
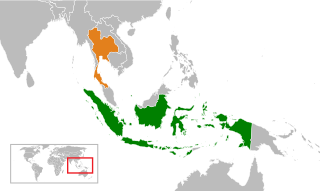
Indonesia and Thailand have officially established diplomatic ties on 7 March 1950. The two countries have since enjoyed a cordial bilateral relationship. Both countries have established embassies in each capitals, Indonesia has their embassy in Bangkok and a consulate in Songkhla, while Thailand has their embassy in Jakarta and honorary consulates in Denpasar, Medan and Surabaya. High rank stately visits has been conducted for years. Both nations are the founders of ASEAN and members of numerous organizations such as the Non-Aligned Movement, APEC, Cairns Group, G20 developing nations and the Indian-Ocean Rim Association. Indonesia and Thailand are viewed as natural allies. Indonesia is also appointed as observer in Cambodian–Thai border dispute.

Soekmono was an Indonesian archaeologist and historian.

Hotel Borobudur is a five star hotel and serviced apartment located in Central Jakarta, Indonesia. Conceived in the 1960s by President Sukarno, it was meant to be the second international-standard hotel to be built in the newly independent country. The hotel is located near Lapangan Banteng, which during the colonial times was the center of what was the military-European colonial neighborhood of Weltevreden. At its opening in 1974, as the Hotel Borobudur Inter-Continental, it was the largest hotel in Jakarta.

Leuit is a type of vernacular rice barn found in the Sundanese architecture of Western Java, Indonesia. It used to store rice after harvest for future and daily use. A leuit is an essential part of Sundanese agricultural tradition, especially during annual Seren Taun harvest ceremony. In Sundanese tradition, leuit symbolizes sustenance and livelihood.

Samudra Raksa is a replica ship built in 2003 based on the relief of ships in the Borobudur temple. In the late 20th century, Philip Beale, a British sailor, became interested in depictions of the ship at Borobudur and decided to reconstruct one. Aided by government and international bodies, he organized an expedition team that constructed the ship and, from 2003 to 2004, sailed it from Indonesia to Madagascar and to Ghana, proving that long-distance trade could have occurred. The Samudra Raksa Museum was constructed at Borobudur Archeological Park to house the ship, opening in 2005, and provides other displays to interpret the ancient maritime history of Indonesians.
References
- ↑ "Mark Long, "Architectural Survey of Borobudur's Summit"". Archived from the original on 2011-11-29. Retrieved 2008-08-20.