
Grande Prairie is a city in northwest Alberta, Canada within the southern portion of an area known as Peace River Country. It is located at the intersection of Highway 43 and Highway 40, approximately 456 km (283 mi) northwest of Edmonton. The city is surrounded by the County of Grande Prairie No. 1.

Dawson Creek is a city in northeastern British Columbia, Canada. The municipality of 24.37 square kilometres (9.41 sq mi) had a population of 12,978 in 2016. Dawson Creek derives its name from the creek of the same name that runs through the community. The creek was named after George Mercer Dawson by a member of his land survey team when they passed through the area in August 1879. Once a small farming community, Dawson Creek became a regional centre after the western terminus of the Northern Alberta Railways was extended there in 1932. The community grew rapidly in 1942 as the US Army used the rail terminus as a transshipment point during construction of the Alaska Highway. In the 1950s, the city was connected to the interior of British Columbia via a highway and a railway through the Rocky Mountains. Since the 1960s, growth has slowed, but the area population has increased.

The Village of Pouce Coupe is a small town in northeastern British Columbia, Canada, and a member municipality of the Peace River Regional District. It was originally named 'Pouskapie's Prairie', after the name of the local native band chief. The 2.06-square-kilometre (0.80 sq mi) municipality is home to 792 residents.

The Peace River is a 1,923-kilometre-long (1,195 mi) river in Canada that originates in the Rocky Mountains of northern British Columbia and flows to the northeast through northern Alberta. The Peace River joins the Athabasca River in the Peace-Athabasca Delta to form the Slave River, a tributary of the Mackenzie River. The Finlay River, the main headwater of the Peace River, is regarded as the ultimate source of the Mackenzie River. The combined Finlay–Peace–Slave–Mackenzie river system is the 13th longest river system in the world.

Northern Alberta Railways was a Canadian railway which served northern Alberta and northeastern British Columbia. Jointly owned by both Canadian National Railway and Canadian Pacific Railway, NAR existed as a separate company from 1929 until 1981.

Sexsmith is a town in northern Alberta, it is on Highway 2, 20 kilometres (12 mi) north of Grande Prairie.

The Peace River Regional District is a regional district in northeastern British Columbia, Canada. The regional district comprises seven municipalities and four electoral areas. Its member municipalities are the cities of Fort St. John and Dawson Creek, the district municipalities of Tumbler Ridge, Chetwynd, Taylor, and Hudson's Hope, and the village of Pouce Coupe. The district's administrative offices are in Dawson Creek.

The Peace River Country is an aspen parkland region centring on the Peace River in Canada. It extends from northwestern Alberta to the Rocky Mountains in northeastern British Columbia, where a certain portion of the region is also referred to as the Peace River Block.
The Peace River Block is an 3,500,000-acre (14,000 km2) area of land in northeastern British Columbia, in the Peace River Country. In exchange for building a rail line across Canada to British Columbia, the Canadian Pacific Railway was given the Railway Belt, 20 miles (32 km) of land on each side of the railway. To compensate the CPR for alienated or non-arable land in the 40-mile-wide (64 km) strip, the province allowed the Government of Canada to take control of 3,500,000 acres within B.C., northeast of the Rocky Mountains. This arrangement passed the provincial Legislature on December 19, 1883, and passed the Parliament of Canada on March 21, 1884, as the Settlement Act. All the land northeast of the Rocky Mountains became a provincial reserve pending the government of Canada's decision on what land to select, which prevented homesteading and land claims. After several surveys of the land the government took possession in 1907. The land the government chose was an approximately square-shaped block of land 72.4 miles (116.5 km) north-south and 75.7 miles (121.8 km) east-west. The south boundary begins at the intersection of the Alberta-British Columbia border and the Twentieth Baseline of the Dominion Land Survey, and the north boundary begins at the Twenty-third Baseline; however, both boundaries are run at right angles to the Alberta-British Columbia Border without accounting for meridian convergence and thus deviate south of each baseline. Land within the block was initially surveyed using the 3rd and 4th Systems of the Dominion Land Survey; however, much of the south and west parts of the block were eventually surveyed into district lots similar to other parts of British Columbia.

Hythe is a hamlet in northwest Alberta, Canada within the County of Grande Prairie No. 1. It is located on Highway 43 approximately 58 km (36 mi) northwest of the City of Grande Prairie and 73 km (45 mi) southeast of the City of Dawson Creek, British Columbia. It held village status prior to July 2021.
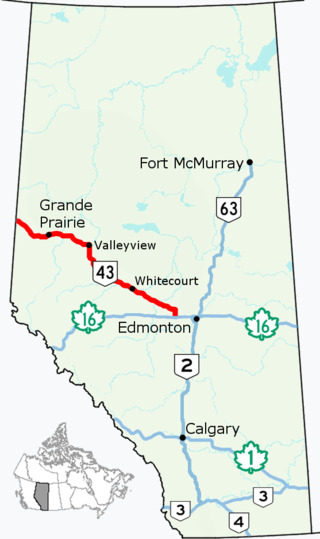
Alberta Provincial Highway No. 43, commonly referred to as Highway 43, is a major highway in northern and central Alberta, Canada that connects Edmonton to the British Columbia border via the Peace Country, forming the northernmost portion of the CANAMEX Corridor in Alberta. It stretches approximately 495 km (308 mi) from Highway 16 near Manly Corner west of Edmonton to the British Columbia border west of Demmitt. It is designated as a core route in Canada's National Highway System, comprising a portion of a key international corridor that stretches from Alaska into Mexico.

Patrick Burns was a Canadian rancher, meat packer, businessperson, senator, and philanthropist. A self-made man of wealth, he built one of the world's largest integrated meat-packing empires, P. Burns & Co., becoming one of the wealthiest Canadians of his time. He is honoured as one of the Big Four western cattle kings who started the Calgary Stampede in Alberta in 1912.

The Municipal District of Greenview No. 16 is a municipal district (MD) in northwest Alberta, Canada. It covers the full extent of Census Division 18, and with an area of 32,984 km2 (12,735 sq mi), it is the largest municipal district in Alberta. Its administrative office is located in the Town of Valleyview.
Monkman Pass, in the Canadian Rockies, is southwest of Tumbler Ridge and northeast of Hansard. Found in the Hart Ranges, some consider this mountain pass as the southern limit of the informal grouping known as the Northern Rockies, although those are occasionally reckoned as extending farther southeast to Mount Ovington or even to Mount Robson.

Elmworth is a hamlet in northern Alberta, Canada within the County of Grande Prairie No. 1. It is located on Highway 722 north of the Wapiti River and east of the British Columbia border. It has an elevation of 715 metres (2,346 ft). The Elmworth natural gas field stretches west and south of the hamlet.
The O'Keefe Ranch is a historic ranch in the Okanagan region of British Columbia, Canada on the Canadian National Railway, just northwest of Vernon. The ranch was founded in 1867 by Cornelius O'Keefe.
Homestead is a locality in northern Alberta, Canada within the County of Grande Prairie No. 1. It is approximately 48 km (30 mi) northwest of Grande Prairie and wa, formed around the Homestead post office that was established November 1, 1930. The post office was in the home of Christian & Caroline Nordhagen, who also operated a small store.

Hazelmere is a locality in northwest Alberta, Canada within the County of Grande Prairie No. 1. It is located between the Red Willow River and Diamond Dick Creek, approximately 75 km (47 mi) southwest of Grande Prairie.

Douglas Todd Loewen is a Canadian politician and the Member of the Legislative Assembly of Alberta for Central Peace-Notley. Loewen was first elected in 2015 as a member of the Wildrose Party for the electoral district of Grande Prairie-Smoky. He was afterward elected in Central Peace-Notley as a member of the United Conservative Party and briefly sat as an independent until being welcomed back by premier Danielle Smith.

Central Peace-Notley is a provincial electoral district in Alberta, Canada. The district was one of 87 districts mandated to return a single member (MLA) to the Legislative Assembly of Alberta using the first past the post method of voting. It was contested for the first time in the 2019 Alberta election.

















