
Tifinagh is a script used to write the Berber languages. Tifinagh is descended from the ancient Libyco-Berber alphabet. The traditional Tifinagh, sometimes called Tuareg Tifinagh, is still favored by the Tuareg people of the Sahara desert in southern Algeria, northeastern Mali, northern Niger, and northern Burkina Faso for writing the Tuareg languages. Neo-Tifinagh is an alphabet developed by the Berber Academy by adopting Tuareg Tifinagh for use for Kabyle; it has been since modified for use across North Africa.

Numidia was the ancient kingdom of the Numidians in northwest Africa, initially comprising the territory that now makes up Algeria, but later expanding across what is today known as Tunisia and Libya. The polity was originally divided between the Massylii state in the east and the Masaesyli state in the west. During the Second Punic War, Masinissa, king of the Massylii, defeated Syphax of the Masaesyli to unify Numidia into the first unified Berber state for Numidians in present-day Algeria. The kingdom began as a sovereign state and an ally of Rome and later alternated between being a Roman province and a Roman client state.

Baal Hammon, properly Baʿal Ḥamon, meaning "Lord Hammon", was the chief god of ancient Carthage. He was a weather god considered responsible for the fertility of vegetation and esteemed as king of the gods. He was depicted as a bearded older man with curling ram's horns. Baʿal Ḥammon's female cult partner was Tanit. Baal Hammon was worshipped only in North Africa and Carthagenian colonies of the western mediterranean including Iberia, Sicily, Sardinia and the Balearic Islands.

Tanit or Tinnit was a chief deity of Ancient Carthage; she derives from a local Berber deity and the consort of Baal Hammon. As Ammon is a local Libyan deity, so is Tannit, who represents the matriarchal aspect of Numidian society, whom the Egyptians identify as Neith and the Greeks identify as Athena. She was the goddess of wisdom, civilization and the crafts; she is the defender of towns and homes where she is worshipped. Ancient North Africans used to put her sign on tombstones and homes to ask for protection her main temples in Thinissut, Cirta, Lambaesis and Theveste. She had a yearly festival in Antiquity which persists to this day in many parts of North Africa but was banned by Muammar Gaddafi in Libya, who called it a pagan festival.

Dougga or Thugga or TBGG was a Berber, Punic and Roman settlement near present-day Téboursouk in northern Tunisia. The current archaeological site covers 65 hectares. UNESCO qualified Dougga as a World Heritage Site in 1997, believing that it represents "the best-preserved Roman small town in North Africa". The site, which lies in the middle of the countryside, has been protected from the encroachment of modern urbanization, in contrast, for example, to Carthage, which has been pillaged and rebuilt on numerous occasions. Dougga's size, its well-preserved monuments and its rich Numidian-Berber, Punic, ancient Roman, and Byzantine history make it exceptional. Amongst the most famous monuments at the site are a Libyco-Punic Mausoleum, the Capitol, the Roman theatre, and the temples of Saturn and of Juno Caelestis.

The Punic religion, Carthaginian religion, or Western Phoenician religion in the western Mediterranean was a direct continuation of the Phoenician variety of the polytheistic ancient Canaanite religion. However, significant local differences developed over the centuries following the foundation of Carthage and other Punic communities elsewhere in North Africa, southern Spain, Sardinia, western Sicily, and Malta from the ninth century BC onward. After the conquest of these regions by the Roman Republic in the third and second centuries BC, Punic religious practices continued, surviving until the fourth century AD in some cases. As with most cultures of the ancient Mediterranean, Punic religion suffused their society and there was no stark distinction between religious and secular spheres. Sources on Punic religion are poor. There are no surviving literary sources and Punic religion is primarily reconstructed from inscriptions and archaeological evidence. An important sacred space in Punic religion appears to have been the large open air sanctuaries known as tophets in modern scholarship, in which urns containing the cremated bones of infants and animals were buried. There is a long-running scholarly debate about whether child sacrifice occurred at these locations, as suggested by Greco-Roman and biblical sources.

During the Iron Age and Classical antiquity, Libya referred to the area of North Africa directly west of the Nile river, not to be confused with modern country Libya which only represents the eastern part of the territory at the time. Ancient Libya was one of the three parts of the world of the ancients the territory also had part of the Mediterranean Sea named after it called the Libyan Sea or Mare Libycum which was the part of the Mediterranean south of Crete, between Cyrene and Alexandria.
The traditional Berber religion is the sum of ancient and native set of beliefs and deities adhered to by the Berbers. Originally, the Berbers seem to have believed in worship of the sun and moon, animism and in the afterlife, but interactions with the Phoenicians, Greeks and Romans influenced religious practice and melted traditional faiths with new ones.
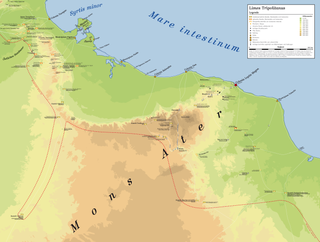
The Limes Tripolitanus was a frontier zone of defence of the Roman Empire, built in the south of what is now Tunisia and the northwest of Libya. It was primarily intended as a protection for the tripolitanian cities of Leptis Magna, Sabratha and Oea in Roman Libya.
John Troglita was a 6th-century Byzantine general. He participated in the Vandalic War and served in North Africa as a regional military governor during the years 533–538, before being sent east to the wars with the Sassanid Persians. As dux Mesopotamiae, Troglita distinguished himself in several battles, and was noticed by agents of the Byzantine emperor, Justinian I. In summer 546, Justinian chose John Troglita to assume overall command of Byzantine forces in Africa, where a succession of revolts by the indigenous Moorish tribes and within the imperial army itself had seriously reduced the Byzantine position. Troglita quickly secured an initial victory in the winter of 546/547 against the Moors of Byzacena, but was defeated in summer 547 by the tribes of Tripolitania, and Africa was once again laid open to destructive raids. Troglita reorganized his army and secured the assistance of some tribal leaders, and confronted and decisively defeated the tribal coalition at the Fields of Cato in summer 548. This victory spelled the end of the Moorish revolt and heralded an era of peace for Africa. Troglita was also involved in the Gothic War, twice sending some of his troops to Italy to assist against the Ostrogoths.
Amun was a major ancient Egyptian deity who appears as a member of the Hermopolitan Ogdoad. Amun was attested from the Old Kingdom together with his wife Amunet. His oracle in Siwa Oasis, located in Western Egypt near the Libyan Desert, remained the only oracle of Amun throughout. With the 11th Dynasty, Amun rose to the position of patron deity of Thebes by replacing Montu.

Deities depicted with horns or antlers are found in numerous religions across the world. Horned animals, such as bulls, goats, and rams, may be worshiped as deities or serve as inspiration for a deity's appearance in religions that venerate animal gods. Many pagan religions include horned gods in their pantheons, such as Pan in Greek mythology and Ikenga in Odinala. Some neopagan religions have reconstructed these deities into the concept of the Horned God, representing the male aspect of divinity in Wiccan belief.

Gerisa, also called Ghirza, was an ancient city of Roman Libya near the Limes Tripolitanus. It was a small village of 300 inhabitants on the pre-desert zone of Tripolitania.

The area of North Africa which has been known as Libya since 1911 was under Roman domination between 146 BC and 672 AD. The Latin name Libya at the time referred to the continent of Africa in general. What is now coastal Libya was known as Tripolitania and Pentapolis, divided between the Africa province in the west, and Crete and Cyrenaica in the east. In 296 AD, the Emperor Diocletian separated the administration of Crete from Cyrenaica and in the latter formed the new provinces of "Upper Libya" and "Lower Libya", using the term Libya as a political state for the first time in history.

Human habitation in the North African region began over one million years ago. Remains of Homo erectus during the Middle Pleistocene period, has been found in North Africa. The Berbers, who generally antedate by many millennia the Phoenicians and the establishment of Carthage, are understood to have arisen out of social events shaped by the confluence of several earlier peoples, i.e., the Capsian culture, events which eventually constituted their ethnogenesis. Thereafter Berbers lived as an independent people in North Africa, including the Tunisian region.
The Laguatan was a Berber clan that inhabited the Cyrenaica area during the Roman period. They have been described as primarily raiders and nomadic as their ancestors the Nasamones, but others consider them a settled group who also raided.
The Nasamones were a nomadic Berber tribe inhabiting southeast Libya. They were believed to be a Numidian people, along with the Garamantes they hunted Troglodytae referred to as Arabs of south. They had established their tribe with their important leaders as rulers and they had a sphere of influence from Siwa Oasis to the Gulf of Sitre.
Ierna was a Berber tribal leader of the Laguatan and also high priest of the god Gurzil who was active in the praetorian prefecture of Africa during the Moorish Wars of the mid-sixth century. Apparently he led the Laguatan at the Battle of Cilium in 544, when the Byzantine governor Solomon was killed and many Byzantine soldiers were captured.
The Battle of Sufetula took place in either late 546 or early 547, at Sufetula in Byzacena, a province of Byzantine Empire, in what is now Tunisia during the Moorish uprisings against the Byzantines. It was fought by Byzantine forces led by John Troglita, against Moorish rebels led by Antalas. The battle resulted in a crushing Byzantine victory: the Berbers suffered heavy losses, and the battle-standards lost at the battle of Cillium in 544 were recovered by the Byzantines.
The Austuriani or Austoriani were a Berber people who lived along the frontier of the Roman Empire in Africa in the desert region south of the Gaetulii in the border of modern day Algeria and Libya. They appear as raiders and enemies of the Romans from Roman sources between the fourth and sixth centuries. These polytheistic nomads worshipped Agurzil, the bull-god of war, emblem of the Laguatans, "son of the god Ammon and a fierce heifer". He was worshipped by all the berber peoples of Libya. Ghirza seems to be his main place of worship.












