Related Research Articles

Conservation agriculture (CA) can be defined by a statement given by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations as "A farming system that promotes minimum soil disturbance, maintenance of a permanent soil cover, and diversification of plant species. It enhances biodiversity and natural biological processes above and below the ground surface, which contribute to increased water and nutrient use efficiency and to improved and sustained crop production."
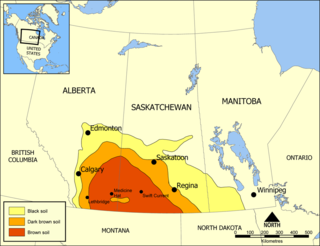
Palliser's Triangle, or the Palliser Triangle, is a semi-arid steppe occupying a substantial portion of the Western Canadian Prairie Provinces, Saskatchewan, Alberta and Manitoba, within the Great Plains region. While initially determined to be unsuitable for crops outside of the fertile belt due to arid conditions and dry climate, expansionists questioned this assessment, leading to homesteading in the Triangle. Agriculture in the region has since suffered from frequent droughts and other such hindrances.

The International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center is a non-profit research-for-development organization that develops improved varieties of wheat and maize with the aim of contributing to food security, and innovates agricultural practices to help boost production, prevent crop disease and improve smallholder farmers' livelihoods. CIMMYT is one of the 15 CGIAR centers. CIMMYT is known for hosting the world's largest maize and wheat genebank at its headquarters in Mexico.

No-till farming is an agricultural technique for growing crops or pasture without disturbing the soil through tillage. No-till farming decreases the amount of soil erosion tillage causes in certain soils, especially in sandy and dry soils on sloping terrain. Other possible benefits include an increase in the amount of water that infiltrates into the soil, soil retention of organic matter, and nutrient cycling. These methods may increase the amount and variety of life in and on the soil. While conventional no-tillage systems use herbicides to control weeds, organic systems use a combination of strategies, such as planting cover crops as mulch to suppress weeds.
Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada is the department of the Government of Canada responsible for the federal regulation of agriculture, including policies governing the production, processing, and marketing of all farm, food, and agri-based products. Agriculture in Canada is a shared jurisdiction and the department works with the provinces and territories in the development and delivery of policies and programs.

Contour bunding or contour farming or Contour ploughing is the farming practice of plowing and/or planting across a slope following its elevation contour lines. These contour lines create a water break which reduces the formation of rills and gullies during times of heavy precipitation, allowing more time for the water to settle into the soil. In contour plowing, the ruts made by the plow run perpendicular rather than parallel to the slopes, generally furrows that curve around the land and are level. This method is also known for preventing tillage erosion. Tillage erosion is the soil movement and erosion by tilling a given plot of land. A similar practice is contour bunding where stones are placed around the contours of slopes. Contour ploughing helps to reduce soil erosion.

Strip cropping is a method of farming which involves cultivating a field partitioned into long, narrow strips which are alternated in a crop rotation system. It is used when a slope is too steep or when there is no alternative method of preventing soil erosion. The most common crop choices for strip cropping are closely sown crops such as hay, wheat, or other forages which are alternated with strips of row crops, such as corn, soybeans, cotton, or sugar beets. The forages serve primarily as cover crops. In certain systems, strips in particularly eroded areas are used to grow permanent protective vegetation; in most systems, however, all strips are alternated on an annual basis.

Canada is one of the largest agricultural producers and exporters in the world. As with other developed nations, the proportion of the population agriculture employed and agricultural GDP as a percentage of the national GDP fell dramatically over the 20th century, but it remains an important element of the Canadian economy. A wide range of agriculture is practised in Canada, from sprawling wheat fields of the prairies to summer produce of the Okanagan valley. In the federal government, overview of Canadian agriculture is the responsibility of the Department of Agriculture and Agri-Food.

The Pembina Escarpment is a scarp that runs from South Dakota to Manitoba, and forms the western wall of the Red River Valley. The height of the escarpment above the river valley is 300–400 feet (91–122 m).

Agriculture in Saskatchewan is the production of various food, feed, or fiber commodities to fulfill domestic and international human and animal sustenance needs. The newest agricultural economy to be developed in renewable biofuel production or agricultural biomass which is marketed as ethanol or biodiesel. Plant cultivation and livestock production have abandoned subsistence agricultural practices in favor of intensive technological farming resulting in cash crops which contribute to the economy of Saskatchewan. The particular commodity produced is dependent upon its particular biogeography or ecozone of Geography of Saskatchewan. Agricultural techniques and activities have evolved over the years. The first nation nomadic hunter-gatherer lifestyle and the early immigrant ox and plow farmer proving up on his quarter section of land in no way resemble the present farmer operating huge amounts of land or livestock with their attendant technological mechanization. Challenges to the future of Saskatchewan agriculture include developing sustainable water management strategies for a cyclical drought prone climate in south western Saskatchewan, updating dryland farming techniques, stabilizing organic definitions or protocols and the decision to grow, or not to grow genetically modified foods. Domestically and internationally, some commodities have faced increased scrutiny from disease and the ensuing marketing issues.
Manitoba Agriculture—officially the Department of Agriculture and Resource Development —is the department of the Government of Manitoba responsible for the agriculture and natural resources sectors in Manitoba, including agrifood, agriproduct, and food safety, as well as animal health and welfare.

RML AgTech Pvt. Ltd., formerly known as Reuters Market Light was a business that provided Technology & Data Analytics Solutions to farmers and the agriculture value chain.

The Indian Institute of Soil Science is an autonomous institute for higher learning, established under the umbrella of Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) by the Ministry of Agriculture, Government of India for advanced research in the field of soil sciences.

Regenerative agriculture is a conservation and rehabilitation approach to food and farming systems. It focuses on topsoil regeneration, increasing biodiversity, improving the water cycle, enhancing ecosystem services, supporting biosequestration, increasing resilience to climate change, and strengthening the health and vitality of farm soil.
Heather McNairn, is a federal research scientist at the Ottawa Research and Development Centre, Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada. She specializes in remote sensing technology, and her research focuses on the use of Synthetic Aperture Radar satellites (SARs) to monitor the condition of crops and soils.
Cynthia Grant, Ph.D., is a former Canadian federal scientist who is internationally recognized as an expert in soil fertility and crop nutrition. A researcher with Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada (AAFC) (1986-2015), she is highly respected by industry, farmers, and public agencies alike. Her research provided the scientific foundation for the Made-in-Canada 4R nutrient stewardship framework that applies crop nutrients from the right source and at the right rate, time and place. Grant is now part of an elite group of ten women who have been inducted into the Canadian Agricultural Hall of Fame since 1960.
Barbara Cade-Menun is a research scientist with Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada at the Swift Current Research and Development Centre in Saskatchewan. Her research focuses on nutrient cycling and minimizing nutrient loss from agriculture and she is a world leader in studying phosphorus cycling in water, soils, and plants. She is recognized for her pioneering work in the use of 31P nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy to characterize phosphorus compounds in soil and other environmental samples. She has developed and refined investigative techniques in her field that have become the preferred standard.
Jennifer Mitchell Fetch is a Canadian research scientist with Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada (AAFC) with expertise in oat breeding. She is known for running the only organic oat breeding program in Canada and helping with the development of several oat milling quality cultivars, including the first organically developed cultivar, AAC Oravena. Canada is the largest exporter of oats in the world, emphasizing the importance of developing new and improved cultivars for farmers. Canada is responsible for producing approximately 3 million tonnes of quality oats every year, with 90% being from Western Canada, where Mitchell Fetch focused her research and was the only Agriculture Canada oat breeder for years. Mitchell Fetch was employed by AAFC in 1998 and spent 22 years as an oat breeder before her retirement in 2020.
Noura Ziadi is a Canadian research scientist with Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada (AAFC), at the Quebec Research and development centre, whose research focuses on soil fertility and plant nutrition. She has developed technologies, methods, and knowledge for better management of mineral fertilizers that increase their efficiency while reducing environmental impact. More specifically, Ziadi developed and validated models to diagnose nitrogen and phosphorus status for different crops, developed new technologies to ensure effective management of industrial wastes and biochar, and developed methods for soil analysis. Ziadi conducts her research on national and international scales in multidisciplinary teams that include government, university, and industry partners. Her research increases agricultural productivity and enhances environmental performance earning her recognition as an influential woman in agriculture.
Constantine Campbell is a Canadian scientist who is a researcher in soil organic matter and all features of nitrogen in soils and crops. Campbell is the leading authority on soil fertility and degradation of nitrogen in American prairie soil, which includes the amount of loss on the quality of organic matter. He was one of the first to radiocarbon date soil organic matter, and in 1967 published a paper which is cited as a landmark work. Majority of his career, he worked with Agriculture Canada in Swift Current, Saskatchewan, retiring in 1998.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 "Guy Lafond (2014)". SAHF. Retrieved Feb 17, 2021.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - 1 2 3 4 "Ag industry remembers researcher Guy Lafond". The Western Producer. 2013-05-03. Retrieved 2021-02-23.
- ↑ "Zero-Till Loses a Champion — A Tribute to Guy Lafond". RealAgriculture.com. Retrieved 2021-02-17.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - 1 2 3 "Guy LAFOND Obituary - (2013) - Indian Head, SK - Leader-Post". www.legacy.com. Retrieved 2021-02-17.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - 1 2 3 4 "No-till researcher nominated to Canadian Conservation Hall of Fame:Soil Conservation Council of Canada (SCCC)". www.soilcc.ca. Retrieved 2021-02-17.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - 1 2 3 politis (2011-09-03). "Farming from space". Canadian Geographic. Retrieved 2021-02-22.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ↑ "IHARF – Indian Head Agricultural Research Foundation" . Retrieved 2021-02-19.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link)