
Transylvania is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains and to the west the Apuseni Mountains. Broader definitions of Transylvania also include the western and northwestern Romanian regions of Crișana and Maramureș, and occasionally Banat. Historical Transylvania also includes small parts of neighbouring Western Moldavia and even a small part of south-western neighbouring Bukovina to its north east. The capital of the region is Cluj-Napoca.

Stephen V was King of Hungary and Croatia between 1270 and 1272, and Duke of Styria from 1258 to 1260. He was the oldest son of King Béla IV and Maria Laskarina. King Béla had his son crowned king at the age of six and appointed him Duke of Slavonia. Still a child, Stephen married Elizabeth, a daughter of a chieftain of the Cumans whom his father settled in the Great Hungarian Plain.
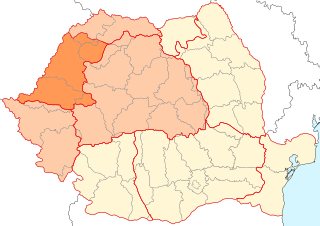
Crișana is a geographical and historical region in north-western Romania, named after the Criș (Körös) River and its three tributaries: the Crișul Alb, Crișul Negru, and Crișul Repede. In Romania, the term is sometimes extended to include areas beyond the border, in Hungary; in this interpretation, the region is bounded to the east by the Apuseni Mountains, to the south by the Mureș River, to the north by the Someș River, and to the west by the Tisza River, the Romanian-Hungarian border cutting it in two. However, in Hungary, the area between the Tisza River and the Romanian border is usually known as Tiszántúl.

Árpád was the head of the confederation of the Magyar tribes at the turn of the 9th and 10th centuries. He might have been either the sacred ruler or kende of the Hungarians, or their military leader or gyula, although most details of his life are debated by historians, because different sources contain contradictory information. Despite this, many Hungarians refer to him as the "founder of our country", and Árpád's preeminent role in the Hungarian conquest of the Carpathian Basin has been emphasized by some later chronicles. The dynasty descending from Árpád ruled the Kingdom of Hungary until 1301.

The Turul is a mythological bird of prey, mostly depicted as a falcon, in Hungarian tradition and Turkic tradition, and a national symbol of Hungarians.

Alba Iulia is a city that serves as the seat of Alba County in the west-central part of Romania. Located on the river Mureș in the historical region of Transylvania, it has a population of 63,536.

These are lists of political office-holders in Transylvania, from the 10th century, until 1867.

Bihar was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary and a county of the Eastern Hungarian Kingdom and Principality of Transylvania. Most of its territory is now part of Romania, while a smaller western part belongs to Hungary. The capital of the county was Nagyvárad. Albrecht Dürer's father was from this county.
Menumorut or Menumorout was the ruler of the lands between the rivers Mureș, Someș and Tisza at the time of the Hungarian conquest of the Carpathian Basin around 900, according to the Gesta Hungarorum, a Hungarian chronicle written after 1150 by an unidentified author, referred to as Anonymus. Historians debate whether Menumorut was an actual ruler or a fictional character created by the author, since the Gesta tells of multiple figures, including Menumorut, who are not identified in any other primary sources, and does not name any of the enemies of the invading Hungarians written of in other contemporary accounts of the invasion. According to Anonymus, Menumorut's duchy was populated primarily with Khazars and Székelys, and he acknowledged the suzerainty of the (unnamed) ruling Byzantine Emperor at the time.

Gelou was the Vlach ruler of Transylvania at the time of the Hungarian conquest of the Carpathian Basin around 900 AD, according to the Gesta Hungarorum. Although the Gesta Hungarorum, which was written after 1150, does not indicate the enemies of the conquering Hungarians (Magyars) known from earlier annals and chronicles, it refers to local rulers—including Gelou—who are not mentioned in other primary sources. Consequently, historians debate whether Gelou was a historical person or an imaginary figure created by the unidentified author of the Gesta Hungarorum. In Romanian historiography, based on the mention of him by Anonymus some 300 years later, Gelou is considered one of three early-10th-century Romanian dukes with lands in the intra-Carpathian region of present-day Romania.

Gyula was, according to Muslim and Byzantine sources, the title of one of the leaders, the second in rank, of the Hungarian tribal federation in the 9th–10th centuries. In the earliest Hungarian sources, the title name is only recorded as a personal name.

Ajtony, Ahtum or Achtum was an early-11th-century ruler in the territory now known as Banat in present Romania and Serbia. His primary source is the Long Life of Saint Gerard, a 14th-century hagiography. Ajtony was a powerful ruler who owned many horses, cattle and sheep and was baptised according to the Orthodox rite in Vidin. He taxed salt which was transferred to King Stephen I of Hungary on the Mureș River. The king sent Csanád, Ajtony's former commander-in-chief, against him at the head of a large army. Csanád defeated and killed Ajtony, occupying his realm. In the territory, at least one county and a Roman Catholic diocese were established.

Glad was the ruler of Banat at the time of the Hungarian conquest of the Carpathian Basin around 900 AD, according to the Gesta Hungarorum. The Gesta, which was written by an author known in modern scholarship as Anonymus in the second half of the 12th century or in the early 13th century, is the earliest extant Hungarian chronicle. The Gesta did not refer to the enemies of the conquering Hungarians, who had been mentioned in earlier annals and chronicles, but wrote of a dozen persons, including Glad, who are unknown from other primary sources of the Hungarian Conquest. Therefore, modern historians debate whether Glad was an actual enemy of the conquerors or only a "fictitious person" made up by Anonymus. In Romanian historiography, based on the mention by Anonymus some 300 years later, Glad is described as one of the three Romanian dukes who ruled a historical region of present-day Romania in the early 10th century.
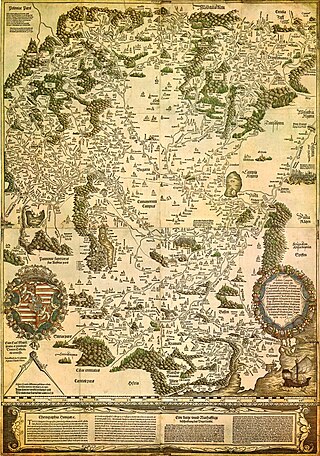
Transylvania is a historical region in central and northwestern Romania. It was under the rule of the Agathyrsi, part of the Dacian Kingdom, Roman Dacia (106–271), the Goths, the Hunnic Empire, the Kingdom of the Gepids, the Avar Khaganate, the Slavs, and the 9th century First Bulgarian Empire. During the late 9th century, Transylvania was part of the Hungarian conquest, and the family of Gyula II of the seven chieftains of the Hungarians ruled Transylvania in the 10th century. King Stephen I of Hungary asserted his claim to rule all lands dominated by Hungarian lords, and he personally led his army against his maternal uncle Gyula III. Transylvania became part of the Kingdom of Hungary in 1002, and it belonged to the Lands of the Hungarian Crown until 1920.

The Grand Principality of Hungary or Duchy of Hungary was the earliest documented Hungarian state in the Carpathian Basin, established in 895 or 896, following the 9th century Magyar invasion of the Carpathian Basin.
Grand Prince was the title used by contemporary sources to name the leader of the federation of the Hungarian tribes in the tenth century.

The Bulgarian–Hungarian wars were a series of conflicts that occurred during the 9th–14th centuries between the First and Second Bulgarian Empires and the Magyar tribes, the Principality of Hungary and later the Kingdom of Hungary. The nearly 500-year conflict encompassed the region of Southeast Europe, or what is known today as north-western Serbia, Romania, Moldavia and northwestern Bulgaria and southwestern Ukraine.
Gyula III, also Iula or Gyula the Younger, Geula or Gyla, was an early medieval ruler in Transylvania. Around 1003, he and his family were attacked, dispossessed and captured by King Stephen I of Hungary (1000/1001-1038). The name "Gyula" was also a title, the second highest rank in Hungarian tribal confederation.
Zombor, also referred to as Gyula II or Gylas, was a Hungarian tribal leader in the middle of the 10th century. He visited Constantinople, where he was baptized in 952 with the baptismal name of Stephen.

Álmos, also Almos or Almus, was—according to the uniform account of Hungarian chronicles—the first head of the "loose federation" of the Hungarian tribes from around 850. Whether he was the sacred ruler (kende) of the Hungarians or their military leader (gyula) is subject to scholarly debate. According to Constantine Porphyrogenitus, he accepted the Khazar khagan's suzerainty in the first decade of his reign, but the Hungarians acted independently of the Khazars from around 860. The 14th-century Illuminated Chronicle narrates that he was murdered in Transylvania at the beginning of the Hungarian conquest of the Carpathian Basin around 895.













