Related Research Articles

Huntington's disease (HD), also known as Huntington's chorea, is an incurable neurodegenerative disease that is mostly inherited. The earliest symptoms are often subtle problems with mood or mental/psychiatric abilities. A general lack of coordination and an unsteady gait often follow. It is also a basal ganglia disease causing a hyperkinetic movement disorder known as chorea. As the disease advances, uncoordinated, involuntary body movements of chorea become more apparent. Physical abilities gradually worsen until coordinated movement becomes difficult and the person is unable to talk. Mental abilities generally decline into dementia, depression, apathy, and impulsivity at times. The specific symptoms vary somewhat between people. Symptoms usually begin between 30 and 50 years of age, and can start at any age but are usually seen around the age of 40. The disease may develop earlier in each successive generation. About eight percent of cases start before the age of 20 years, and are known as juvenile HD, which typically present with the slow movement symptoms of Parkinson's disease rather than those of chorea.
Trinucleotide repeat disorders, a subset of microsatellite expansion diseases, are a set of over 30 genetic disorders caused by trinucleotide repeat expansion, a kind of mutation in which repeats of three nucleotides increase in copy numbers until they cross a threshold above which they cause developmental, neurological or neuromuscular disorders. Depending on its location, the unstable trinucleotide repeat may cause defects in a protein encoded by a gene; change the regulation of gene expression; produce a toxic RNA, or lead to production of a toxic protein. In general, the larger the expansion the faster the onset of disease, and the more severe the disease becomes.

Huntingtin(Htt) is the protein coded for in humans by the HTT gene, also known as the IT15 ("interesting transcript 15") gene. Mutated HTT is the cause of Huntington's disease (HD), and has been investigated for this role and also for its involvement in long-term memory storage.
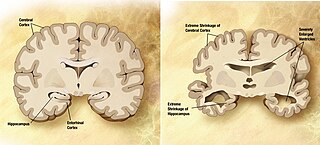
A neurodegenerative disease is caused by the progressive loss of structure or function of neurons, in the process known as neurodegeneration. Such neuronal damage may ultimately involve cell death. Neurodegenerative diseases include amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, Huntington's disease, multiple system atrophy, tauopathies, and prion diseases. Neurodegeneration can be found in the brain at many different levels of neuronal circuitry, ranging from molecular to systemic. Because there is no known way to reverse the progressive degeneration of neurons, these diseases are considered to be incurable; however research has shown that the two major contributing factors to neurodegeneration are oxidative stress and inflammation. Biomedical research has revealed many similarities between these diseases at the subcellular level, including atypical protein assemblies and induced cell death. These similarities suggest that therapeutic advances against one neurodegenerative disease might ameliorate other diseases as well.

Slipped strand mispairing is a mutation process which occurs during DNA replication. It involves denaturation and displacement of the DNA strands, resulting in mispairing of the complementary bases. Slipped strand mispairing is one explanation for the origin and evolution of repetitive DNA sequences.

Dentatorubral–pallidoluysian atrophy (DRPLA) is an autosomal dominant spinocerebellar degeneration caused by an expansion of a CAG repeat encoding a polyglutamine tract in the atrophin-1 protein. It is also known as Haw River Syndrome and Naito–Oyanagi disease. Although this condition was perhaps first described by Smith et al. in 1958, and several sporadic cases have been reported from Western countries, this disorder seems to be very rare except in Japan.

Neurogenetics studies the role of genetics in the development and function of the nervous system. It considers neural characteristics as phenotypes, and is mainly based on the observation that the nervous systems of individuals, even of those belonging to the same species, may not be identical. As the name implies, it draws aspects from both the studies of neuroscience and genetics, focusing in particular how the genetic code an organism carries affects its expressed traits. Mutations in this genetic sequence can have a wide range of effects on the quality of life of the individual. Neurological diseases, behavior and personality are all studied in the context of neurogenetics. The field of neurogenetics emerged in the mid to late 20th century with advances closely following advancements made in available technology. Currently, neurogenetics is the center of much research utilizing cutting edge techniques.
Nervous system diseases, also known as nervous system or neurological disorders, refers to a small class of medical conditions affecting the nervous system. This category encompasses over 600 different conditions, including genetic disorders, infections, cancer, seizure disorders, conditions with a cardiovascular origin, congenital and developmental disorders, and degenerative disorders.
A polyglutamine tract or polyQ tract is a portion of a protein consisting of a sequence of several glutamine units. A tract typically consists of about 10 to a few hundred such units.
Bagadilico, Basal Ganglia Disorders Linnaeus Consortium, is a research group in Lund, Sweden, and a Linnaeus environment, supported by the Swedish Research Council. The group comprises about 120 researchers at either Lund University or Lund University Hospital.
Pridopidine is an orally administrated small molecule investigational drug. Pridopidine is a selective and potent Sigma-1 Receptor agonist. It is being developed by Prilenia Therapeutics and is currently in late-stage clinical development for Huntington’s disease (HD) and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS).

Anne Buckingham Young is an American physician and neuroscientist who has made major contributions to the study of neurodegenerative diseases, with a focus on movement disorders like Huntington's disease and Parkinson's disease. Young completed her undergraduate studies at Vassar College and earned a dual MD/PhD from Johns Hopkins Medical School. She has held faculty positions at University of Michigan and Harvard University. She became the first female chief of service at Massachusetts General Hospital when she was appointed Chief of Neurology in 1991. She retired from this role and from clinical service in 2012. She is a member of many academic societies and has won numerous awards. Young is also the only person to have been president of both the international Society for Neuroscience and the American Neurological Association.
The Hereditary Disease Foundation (HDF) aims to cure genetic disorders, notably Huntington's disease, by supporting basic biomedical research.

The UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology is an institute within the Faculty of Brain Sciences of University College London (UCL) and is located in London, United Kingdom. Together with the National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery, an adjacent facility with which it cooperates closely, the institute forms a major centre for teaching, training and research in neurology and allied clinical and basic neurosciences.
Cognitive genomics is the sub-field of genomics pertaining to cognitive function in which the genes and non-coding sequences of an organism's genome related to the health and activity of the brain are studied. By applying comparative genomics, the genomes of multiple species are compared in order to identify genetic and phenotypical differences between species. Observed phenotypical characteristics related to the neurological function include behavior, personality, neuroanatomy, and neuropathology. The theory behind cognitive genomics is based on elements of genetics, evolutionary biology, molecular biology, cognitive psychology, behavioral psychology, and neurophysiology.

Neurodegenerative diseases can disrupt the normal human homeostasis and result in abnormal estrogen levels. For example, neurodegenerative diseases can cause different physiological effects in males and females. In particular, estrogen studies have revealed complex interactions with neurodegenerative diseases. Estrogen was initially proposed to be a possible treatment for certain types of neurodegenerative diseases but a plethora of harmful side effects such as increased susceptibility to breast cancer and coronary heart disease overshadowed any beneficial outcomes. On the other hand, Estrogen Replacement Therapy has shown some positive effects with postmenopausal women. Estrogen and estrogen-like molecules form a large family of potentially beneficial alternatives that can have dramatic effects on human homeostasis and disease. Subsequently, large-scale efforts were initiated to screen for useful estrogen family molecules. Furthermore, scientists discovered new ways to synthesize estrogen-like compounds that can avoid many side effects.
Translational neuroscience is the field of study which applies neuroscience research to translate or develop into clinical applications and novel therapies for nervous system disorders. The field encompasses areas such as deep brain stimulation, brain machine interfaces, neurorehabilitation and the development of devices for the sensory nervous system such as the use of auditory implants, retinal implants, and electronic skins.
Huntington's disease-like syndromes are a family of inherited neurodegenerative diseases that closely resemble Huntington's disease (HD) in that they typically produce a combination of chorea, cognitive decline or dementia and behavioural or psychiatric problems.
Beverly L. Davidson is an American geneticist. She is the director of the Raymond G. Perelman Center for Cellular and Molecular Therapeutics at Children's Hospital of Philadelphia. In this role, she investigates gene therapy for neurodegenerative diseases, specifically Huntington's.

Bronwen Jane Connor is a New Zealand academic. She is a professor of pharmacology at the University of Auckland, where she is head of the Neural Reprogramming and Repair Lab.
References
- ↑ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: Huntington-like neurodegenerative disorder 2" . Retrieved 2017-09-25.