HDMI is a proprietary audio/video interface for transmitting uncompressed video data and compressed or uncompressed digital audio data from an HDMI-compliant source device, such as a display controller, to a compatible computer monitor, video projector, digital television, or digital audio device. HDMI is a digital replacement for analog video standards.
16:9 (1.77:1 = 42:32) is an aspect ratio with a width of 16 units and height of 9. Since 2010 it has become the most common aspect ratio for televisions and computer monitors, and is also the international standard format of HDTV, Full HD, non-HD digital television and analog widescreen television. This has replaced the old 4:3 aspect ratio.
1080i is an abbreviation referring to a combination of frame resolution and scan type, used in high-definition television (HDTV) and high-definition video. The number "1080" refers to the number of horizontal lines on the screen. The "i" is an abbreviation for "interlaced"; this indicates that only the odd lines, then the even lines of each frame are drawn alternately, so that only half the number of actual image frames are used to produce video. A related display resolution is 1080p, which also has 1080 lines of resolution; the "p" refers to progressive scan, which indicates that the lines of resolution for each frame are "drawn" in on the screen sequence.
High-definition video is video of higher resolution and quality than standard-definition. While there is no standardized meaning for high-definition, generally any video image with considerably more than 480 vertical lines or 576 vertical lines (Europe) is considered high-definition. 480 scan lines is generally the minimum even though the majority of systems greatly exceed that. Images of standard resolution captured at rates faster than normal, by a high-speed camera may be considered high-definition in some contexts. Some television series shot on high-definition video are made to look as if they have been shot on film, a technique which is often known as filmizing.

1080p is a set of HDTV high-definition video modes characterized by 1,920 pixels displayed across the screen horizontally and 1,080 pixels down the screen vertically; the p stands for progressive scan, i.e. non-interlaced. The term usually assumes a widescreen aspect ratio of 16:9, implying a resolution of 2.1 megapixels. It is often marketed as full HD, to contrast 1080p with 720p resolution screens.

The HD ready is a certification program introduced in 2005 by EICTA, now DIGITALEUROPE. HD ready minimum native resolution is 720 rows in widescreen ratio.

Windows Photo Viewer is an image viewer included with the Windows NT family of operating systems. It was first included with Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 under its former name. It was temporarily replaced with Windows Photo Gallery in Windows Vista, but has been reinstated in Windows 7. This program succeeds Imaging for Windows. In Windows 10, it is deprecated in favor of a Universal Windows Platform app called Photos, although it can be brought back with a registry tweak.

NRK1 is the Norwegian Broadcasting Corporation's (NRK) main television channel. Test broadcasts started on 12 January 1954, regular test broadcasts started on 13 April 1958 and regular broadcasts started on 20 August 1960. It is Norway's oldest and largest television channel. Previously known simply as "NRK", the channel is now known as "NRK1", to distinguish itself from sister channel "NRK2", which started broadcasting in 1996.
The Radeon R700 is the engineering codename for a graphics processing unit series developed by Advanced Micro Devices under the ATI brand name. The foundation chip, codenamed RV770, was announced and demonstrated on June 16, 2008 as part of the FireStream 9250 and Cinema 2.0 initiative launch media event, with official release of the Radeon HD 4800 series on June 25, 2008. Other variants include enthusiast-oriented RV790, mainstream product RV730, RV740 and entry-level RV710.
The Evergreen series is a family of GPUs developed by Advanced Micro Devices for its Radeon line under the ATI brand name. It was employed in Radeon HD 5000 graphics card series and competed directly with Nvidia's GeForce 400 Series.

Intel Graphics Technology (GT) is the collective name for a series of integrated graphics processors (IGPs) produced by Intel that are manufactured on the same package or die as the central processing unit (CPU). It was first introduced in 2010 as Intel HD Graphics.

4K resolution, also called 4K, refers to a horizontal display resolution of approximately 4,000 pixels. Digital television and digital cinematography commonly use several different 4K resolutions. In television and consumer media, 3840 × 2160 is the dominant 4K standard, whereas the movie projection industry uses 4096 × 2160.
The Story is an e-book reader manufactured and marketed by iriver and employing a Linux operating system. The device uses code licensed under the GPL, but iriver did not make the sources available immediately; this issue has since been addressed. The reader was updated in July 2010, and supports Wi-Fi. A July 2011 update integrated the device with the Google eBooks store. The product was a Target exclusive release.
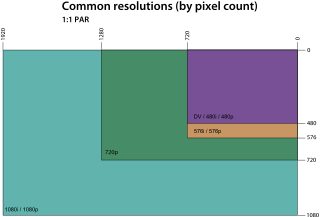
The graphics display resolution is the width and height dimension of an electronic visual display device, such as a computer monitor, in pixels. Certain combinations of width and height are standardized and typically given a name and an initialism that is descriptive of its dimensions. A higher display resolution in a display of the same size means that displayed photo or video content appears sharper, and pixel art appears smaller.

HD3D is AMD's stereoscopic 3D API.

Wireless Display (WiDi) was technology developed by Intel that enabled users to stream music, movies, photos, videos and apps without wires from a compatible computer to a compatible HDTV or through the use of an adapter with other HDTVs or monitors. Intel WiDi supported HD 1080p video quality, 5.1 surround sound, and low latency for interacting with applications sent to the TV from a PC.
Miracast is a standard for wireless connections from devices to displays, introduced in 2012 by the Wi-Fi Alliance. It can roughly be described as "HDMI over Wi-Fi", replacing the cable from the device to the display.

The Droid Razr HD and Droid Razr Maxx HD are Android-based, 4G LTE-capable smartphones designed by Motorola as the successor to the Droid Razr series released nearly a year prior. Notable changes from their predecessors include 720p resolution displays and increased display size while maintaining similar overall dimensions. Additionally, the battery capacity on the standard Razr HD is 42% larger than its predecessor. Both go by the model number XT926. These phones were released on October 18, 2012 exclusively on Verizon Wireless in the United States. The Motorola Razr HD were available as international or global phones in Europe, Latin America, Australia and Canada as early as October 2, 2012. In the summer of 2013, storyboards surfaced of television commercials that have not yet aired. These commercials will feature the Droid Maxx and Droid Ultra, the apparent successors to the Droid Razr Maxx HD and Droid Razr HD, respectively.

The Samsung Galaxy J is a smartphone developed and manufactured by Samsung which works on the Android platform. This phone was originally developed for Japanese cellular carrier NTT DoCoMo in fall 2013, and the overseas version initially released in Taiwan in December 2013. The device features a Qualcomm Snapdragon 800 quad-core 2.3 GHz processor with 3GB of RAM and a Full HD Super AMOLED display.

Ultra-high-definition television today includes 4K UHD and 8K UHD, which are two digital video formats with an aspect ratio of 16:9. These were first proposed by NHK Science & Technology Research Laboratories and later defined and approved by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU).