
SM U-19 was a German Type U 19 U-boat built for the Imperial German Navy. Her construction was ordered on 25 November 1910, and her keel was laid down on 20 October 1911, at the Kaiserliche Werft Danzig. She was launched on 10 October 1912, and commissioned into the Imperial German Navy on 6 July 1913.
Seven ships of the Royal Navy have borne the name HMS Niger after the Niger River, whilst another was planned.
Blücher was a wolfpack of German U-boats that operated during the World War II Battle of the Atlantic from 14 to 28 August 1942. They attacked the Freetown, Sierra Leone to Liverpool convoys SL-118 and SL-119, and sank six ships for a total of 41,984 gross register tons (GRT), and damaged one (10,552 GRT). The group was named after Gebhard Leberecht von Blücher (1742–1819), a Prussian Generalfeldmarschall in the Napoleonic Wars.
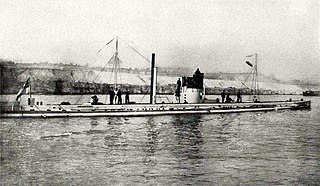
SM U-9 was a German Type U 9 U-boat. She was one of 329 submarines serving in the Imperial German Navy, and engaged in commerce raiding (Handelskrieg) during World War I.
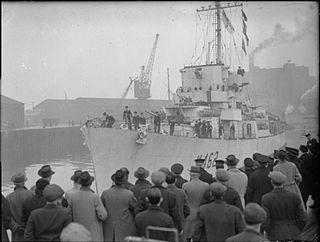
HMS Affleck was a Captain class frigate which served during World War II. The ship was named after Sir Edmund Affleck, commander of HMS Bedford at the Moonlight Battle in 1780 during the American Revolutionary War.

German submarine U-74 was a Type VIIB U-boat of Nazi Germany's Kriegsmarine during World War II.
HMS Heartsease was a Flower-class corvette of the Royal Navy. She served with both the Royal Navy and the United States Navy during the Second World War, with the latter navy as USS Courage. She then spent several years under a succession of names in civilian service. In 1957 she was chartered on behalf of Indonesian rebels to smuggle rubber, copra and matériel. The Indonesian Air Force intercepted and sank her off the coast of Minahasa in North Sulawesi in December 1958.

HMS Peony was a Flower-class corvette of the Royal Navy. In 1943 she was transferred to the Royal Hellenic Navy as ΒΠ Σαχτούρης, serving throughout World War II and the Greek Civil War. She was returned to the Royal Navy in 1951 and scrapped in April 1952.

German submarine U-510 was a Type IXC U-boat of Nazi Germany's Kriegsmarine during World War II, which later served in the French Navy. The submarine was laid down on 1 November 1940 at the Deutsche Werft yard at Hamburg as yard number 306, launched on 4 September 1941, and commissioned on 25 November 1941 under the command of Korvettenkapitän Karl Neitzel.
The Type U 66 was a class of five submarines or U-boats operated by the German Imperial Navy during World War I. The class is alternately referred to as the U-66-class or the Type UD. The class was built by Germaniawerft of Kiel to their 506d design as the U-7-class for the Austro-Hungarian Navy. The five boats were sold to the Imperial Germany Navy at the beginning of World War I when it was thought impossible for the submarines to reach the Mediterranean for delivery to Austria-Hungary.
German submarine U-652 was a Type VIIC U-boat of Nazi Germany's Kriegsmarine during World War II. The submarine was laid down on 5 February 1940 at the Howaldtswerke yard at Hamburg, launched on 7 February 1941, and commissioned on 3 April 1941 under the command of Oberleutnant zur See Georg-Werner Fraatz.
HMIS Cornwallis (L09) was an Aubrietia-class sloop, originally built during World War I and commissioned as HMS Lychnis in the Royal Navy (RN) in 1917. She was transferred to the Royal Indian Marine (RIM) and commissioned as Cornwallis in 1921.

HMS Anguilla (K500) was a Colony-class frigate of the United Kingdom in commission from 1943 to 1946 that served during World War II. She originally was ordered by the United States Navy as the Tacoma-class patrol frigateUSS Hallowell (PF-72), later renamed USS Machias (PF-72), and was transferred prior to completion.
HMS Papua (K588) was a Colony-class frigate of the United Kingdom that served during World War II. She originally was ordered by the United States Navy as the Tacoma-class patrol frigateUSS Howett (PF-84) and was transferred to the Royal Navy prior to completion.
HMS Goodall (K479) was a British Captain-class frigate of the Royal Navy in commission during World War II. Originally constructed as the United States Navy Evarts-class destroyer escort USS Reybold (DE-275), she served in the Royal Navy from 1943 until her sinking in 1945.
HMS Gould (K476) was a British Captain-class frigate of the Royal Navy in commission during World War II. Originally constructed as the United States Navy Evarts-class destroyer escort USS Lovering (DE-272), she served in the Royal Navy from 1943 until her sinking in 1944.

MV Southern Prince was a cargo liner launched in 1929 for the Prince Line between New York City and Argentina. She was requisitioned by the Royal Navy for conversion to the auxiliary minelayer HMS Southern Prince. She joined the 1st Minelaying Squadron based at Kyle of Lochalsh laying mines for the World War II Northern Barrage. She was the largest of five ships requisitioned for this minelaying operation. She was torpedoed by German submarine U-652 shortly after midnight on 26 August 1941 while returning from laying minefield SN-70A; but was escorted to Belfast for repair. After minelaying was completed in October 1943, she became the flagship of Rear Admiral Rivett-Carnac for Operation Neptune; and anchored off Juno Beach on 8 June 1944. She was used as an accommodation ship from October 1944 until returned to the Prince Line in 1946.

HMS Loosestrife (K105) was a Flower-class corvette of the British Royal Navy which sailed with the North Atlantic convoys of the Second World War.

Alysse was one of the nine Flower-class corvettes lent by the Royal Navy to the Free French Naval Forces.













