The Royal Navy has used the name Comet no fewer than 18 times:
Nine ships of the Royal Navy have borne the name HMS Diana after the figure from Roman mythology, whilst another was planned but later cancelled:
Fifteen ships of the Royal Navy have borne the name HMS Ranger

HMS Plantagenet was a 74-gun third rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched on 22 October 1801 at Woolwich. She was designed by Sir William Rule as one of the 'large class' 74s, and was the only ship built to her draught. As a large 74, she carried 24-pounder guns on her upper gun deck instead of the 18-pounder guns found on the middling and common class 74s.
Two ships of the Royal Navy have borne the name Anna or HMS Anna:

HMS Severn was an Endymion-class frigate of the British Royal Navy, launched in 1813 as one of five heavy frigates built to match the powerful American frigates. The shortage of oak meant that she was built of "fir", which meant a considerably shortened lifespan. Nonetheless, the ship saw useful service, especially at the bombardment of Algiers in 1816, before being broken up in 1825.
Five vessels of the Royal Navy have been named HMS Harlequin.
Rolla may refer to a number of sailing ships;
A number of sailing vessels were named Alexander:
Nine ships of the Royal Navy have been named HMS Dove after the bird family Columbidae:
A number of ships of the Royal Navy have borne the name HMS Diligent.
HMS Express was the name-ship of a class of two schooner-rigged advice-boats of the Royal Navy. Express was launched in 1800 and served until she was sold in 1813. During her career she served in one action and one campaign that in 1847 qualified her surviving crew members for clasps to the Naval General Service Medal.
HMS Express was the American merchant vessel Achilles, launched in 1809 in America. Her owners in 1813 renamed her Anna Maria. In 1814 she served the British Royal Navy in North American waters as an advice boat. In 1815 the Royal Navy commissioned her as HMS Express, a ship's tender serving in the Mediterranean. In 1816 she was at the bombardment of Algiers. The Navy sold her at Malta in 1827.
HMS Nimrod was a brig-sloop of the British Royal Navy, launched in 1812. She spent her war years in north American waters where she captured one small privateer, assisted in the capture of another, and captured or destroyed some 50 American vessels. After the war she captured smugglers and assisted the civil authorities in maintaining order in Tyne. She was wrecked in 1827 and so damaged that the Navy decided she was not worth repairing. A private ship-owner purchased Nimrod and repaired her. She then went on to spend some 20 years trading between Britain and Charleston, the Mediterranean, Australia, and India. She was last listed in 1851.
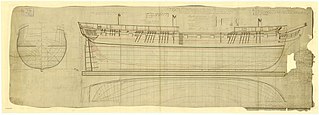
HMS Barrosa was launched in 1812 for the Royal Navy and served during the War of 1812 during which she captured several prices. After the war she spent a decade or so (1823–1833) on harbour duties. The navy sold Barrosa in 1841.
Dame Ernouf first appears under that name in 1807. Her origins are currently obscure. She served as a privateer first under that name, and then under the name Diligent. As Diligent she not only capture several merchantmen but also two British Royal Navy vessels: a schooner and a brig. She continued to capture prizes until the end of 1813 and then disappears from online records.

HMS Narcissus was the lead ship of the Royal Navy Narcissus-class 32-gun fifth-rate frigate, launched in 1801. She participated in the War of 1812.
HMS Cockchafer was a United States schooner, possibly Spence or Spencer, that the Royal Navy (RN) captured and employed as a ship's tender. She captured two American armed brigs, one in a single-ship action. The Navy sold her in 1815.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.



