Related Research Articles

HMS Indefatigable was one of the Ardent-class 64-gun third-rate ships-of-the-line designed by Sir Thomas Slade in 1761 for the Royal Navy. She was built as a ship-of-the-line, but most of her active service took place after her conversion to a 44-gun razee frigate. She had a long career under several distinguished commanders, serving throughout the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars. She took some 27 prizes, alone or in company, and the Admiralty authorised the issue of four clasps to the Naval General Service Medal in 1847 to any surviving members of her crews from the respective actions. She was broken up in 1816.

HMS Sirius was a 36-gun fifth-rate frigate of the Royal Navy. Between 1797 and 1805, the Sirius was engaged in maintaining the blockade of Napoleonic Europe. She was lost in 1810 when her crew scuttled her after she grounded during the Battle of Grand Port.

HMS Phoenix was a 36-gun Perseverance-class fifth-rate frigate of the Royal Navy. The shipbuilder George Parsons built her at Bursledon and launched her on 15 July 1783. She served in the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars and was instrumental in the events leading up to the battle of Trafalgar. Phoenix was involved in several single-ship actions, the most notable occurring on 10 August 1805 when she captured the French frigate Didon, which was more heavily armed than her. She was wrecked, without loss of life, off Smyrna in 1816.

Uranie was a frigate of the French Navy launched in 1788. She took part in a frigate action in 1793, capturing HMS Thames, and was renamed Tartu in honour of her captain, Jean-François Tartu, who was killed in the action. The Royal Navy captured her in 1797. She served as HMS Uranie until the Royal Navy sold her in 1807.

HMS Lark was a 16-gun ship sloop of the Cormorant class, launched in 1794 at Northfleet. She served primarily in the Caribbean, where she took a number of prizes, some after quite intensive action. Lark foundered off San Domingo in August 1809, with the loss of her captain and almost all her crew.

HMS Entreprenante, was a 10-gun cutter that the Royal Navy captured from the French in 1798. The British commissioned her in 1799 and she served during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars, participating in the Battle of Trafalgar. She has been the only ship of the Royal Navy to bear the name. She took part in several small engagements, capturing Spanish and French ships before she was sold in 1812 for breaking up.
HMS Nemesis was a 28-gun Enterprise-class sixth-rate frigate of the Royal Navy. The French captured her in 1795 at Smyrna, but in 1796 a squadron led by Barfleur brought her out of the neutral port of Tunis. Throughout her career she served under a number of commanders who would go on to have distinguished careers. She was converted to a troopship in 1812 and was sold in 1814.
During the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars, British vessels captured at least 12 French warships and privateers named Espoir, which means “Hope” in French. In only one case was there mention of an exchange of fire or casualties. In general, the privateers tried to escape, and failing that surrendered.

HMS Circe was a 28-gun Enterprise-class sixth-rate frigate of the Royal Navy. She was launched in 1785 but not completed or commissioned until 1790. She then served in the English Channel on the blockade of French ports before she was wrecked in 1803.
HMS Netley was launched in 1798 with an experimental design. During the French Revolutionary Wars she spent some years on the Oporto station, where she captured many small privateers. The French captured her in 1806, early in the Napoleonic Wars. They lengthened her and she became the 17-gun privateer Duquesne. In 1807 the British recaptured her and the Royal Navy returned her to service as the 12-gun gun-brig HMS Unique. She was expended in an unsuccessful fire ship attack at Guadeloupe in 1809.
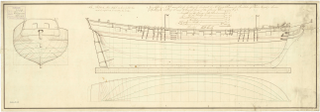
HMS Diligence was the name ship of her class of brig-sloops of the Royal Navy. She was launched in 1795 and lost in 1800. She spent her brief career on the Jamaica station where she captured four armed vessels, one of them after a short engagement, and many small Spanish and French merchant vessels in the Caribbean inter-island and coastal trade.

HMS Seagull, was a Royal Navy Diligence-class brig-sloop, launched in 1795. During the French Revolutionary Wars she shared in the capture of a number of small French and Dutch privateers. Then early in the Napoleonic Wars she participated in a notable single-ship action before she disappeared without a trace in 1805.

HMS Harpy was a Royal Navy Diligence-class brig-sloop, launched in 1796 and sold in 1817. She was the longest lived vessel of her class, and the most widely travelled. She served in both the battle of Copenhagen and the British invasion of Java, took part in several actions, one of which won for her crew a clasp to the Naval General Service Medal, and captured numerous privateers. The Navy sold her in 1817.

HMS Swallow was an 18-gun Albatross-class brig-sloop of the British Royal Navy, launched in 1795 and sold in 1802. During her naval career she captured a number of French privateers while on the Jamaica station. After her sale she became an armed whaler sailing under a letter of marque. As a privateer she captured two French whaling vessels but then is no longer listed after 1810.
Numerous French privateers have borne the name Vengeur ("Avenger"):

HMS Snake was a British Royal Navy ship launched in 1797 as the only member of her class of brig-sloops. She captured or destroyed two French privateers and one Danish privateer. She also captured numerous small merchantmen, but spent time escorting convoys to and from the West Indies. She was sold in 1816.
HMS Sparrow was launched in 1780, almost surely under another name. She first appears in 1793 in readily accessible records as the privateer cutter Rattler. The British Admiralty hired her and employed her as HM Hired armed cutter Rattler. During this time she was present at the largest naval battle of the French Revolutionary Wars. The Navy purchased her in 1796 for the Royal Navy and renamed her HMS Sparrow. She was sold for breaking up in 1805.

HMS Bonetta was the French privateer Huit Amis, launched at Bordeaux in 1798 that the British Royal Navy captured in May. In her brief naval career she captured a number of small prizes, one of them a 2-gun privateer. Bonetta was wrecked in 1801.

HMS Albacore was launched in 1793 at Rotherhithe. She captured several privateers and a French Navy corvette before she was sold in 1802.
Lord Hawke was launched at Ostend in 1793, almost certainly under a different name. In 1798 she became a British privateer. The French captured her in 1799 and she became the French privateer Revanche. The British Royal Navy recaptured her in 1800. New owners returned her to her original British name. She disappeared in early 1801, presumed to have foundered with all hands.
References
- Hepper, David J. (1994). British Warship Losses in the Age of Sail, 1650-1859. Rotherfield: Jean Boudriot. ISBN 0-948864-30-3.
- Winfield, Rif (2008). British Warships in the Age of Sail 1793–1817: Design, Construction, Careers and Fates. Seaforth Publishing. ISBN 978-1-86176-246-7.