
Slalom is an alpine skiing and alpine snowboarding discipline, involving skiing between poles or gates. These are spaced more closely than those in giant slalom, super giant slalom and downhill, necessitating quicker and shorter turns. Internationally, the sport is contested at the FIS Alpine World Ski Championships, and at the Olympic Winter Games.

The long jump is a track and field event in which athletes combine speed, strength and agility in an attempt to leap as far as possible from a takeoff point. Along with the triple jump, the two events that measure jumping for distance as a group are referred to as the "horizontal jumps". This event has a history in the ancient Olympic Games and has been a modern Olympic event for men since the first Olympics in 1896 and for women since 1948.

Alpine skiing, or downhill skiing, is the pastime of sliding down snow-covered slopes on skis with fixed-heel bindings, unlike other types of skiing, which use skis with free-heel bindings. Whether for recreation or for sport, it is typically practiced at ski resorts, which provide such services as ski lifts, artificial snow making, snow grooming, restaurants, and ski patrol.
Nordic combined is a winter sport in which athletes compete in cross-country skiing and ski jumping. The Nordic combined at the Winter Olympics has been held since the first Winter Olympics in 1924, while the FIS Nordic Combined World Cup has been held since 1983. Many Nordic combined competitions use the Gundersen method, where placement in the ski jumping segment results in time (dis)advantages added to the contestant's total in the cross-country skiing segment.

Ski jumping is a winter sport in which competitors aim to achieve the farthest jump after sliding down on their skis from a specially designed curved ramp. Along with jump length, competitor's aerial style and other factors also affect the final score. Ski jumping was first contested in Norway in the late 19th century, and later spread through Europe and North America in the early 20th century. Along with cross-country skiing, it constitutes the traditional group of Nordic skiing disciplines.
Freestyle skiing is a skiing discipline comprising aerials, moguls, cross, half-pipe, slopestyle and big air as part of the Winter Olympics. It can consist of a skier performing aerial flips and spins and can include skiers sliding rails and boxes on their skis. Known as "hot-dogging" in the early 1970s, it is also commonly referred to as freeskiing, jibbing, as well as many other names, around the world.

Trampolining or trampoline gymnastics is a competitive Olympic sport in which athletes perform acrobatics while bouncing on a trampoline. In competition, these can include simple jumps in the straight, pike, tuck, or straddle position to more complex combinations of forward and/or backward somersaults and twists. Scoring is based on the difficulty and on the total seconds spent in the air. Points are deducted for bad form and horizontal displacement from the center of the bed.
Trampolining terms are used to describe various positions and types of skill performed in the sport of trampolining.

Ski flying is a winter sport discipline derived from ski jumping, in which much greater distances can be achieved. It is a form of competitive individual Nordic skiing where athletes descend at high speed along a specially designed takeoff ramp using skis only; jump from the end of it with as much power as they can generate; then glide – or 'fly' – as far as possible down a steeply sloped hill; and ultimately land within a target zone in a stable manner. Points are awarded for distance and stylistic merit by five judges. Events are governed by the International Ski Federation.

The telemark landing or just "Telemark" as it is referred to by experts, is a landing technique in ski jumping. It was first tested by Torju Torjussen in 1883 and is still considered a safe landing technique today. To perform this landing, the athlete pushes one ski a little more to the front and the other ski a little further back during the landing process. The landing point is not the ski binding but the point in the middle between the heel of the front foot and the toes of the back foot. The upper body should be erect while the knees are slightly bent to absorb the impact of the jump.

Andreas Kofler is an Austrian former ski jumper.

Single skating is a discipline of figure skating in which male and female skaters compete individually. Men's singles and women's singles are governed by the International Skating Union (ISU). Figure skating is the oldest winter sport contested at the Olympics, with men's and women's single skating appearing as two of the four figure skating events at the London Games in 1908.

Gregor Schlierenzauer is an Austrian former ski jumper who competed from 2006 to 2021. He is one of the most successful ski jumpers of all time, having won the Ski Jumping World Cup overall title, the Four Hills Tournament, and Nordic Tournament twice each; the Ski Flying World Cup overall title three times; as well as four medals at the Winter Olympics, twelve at the Ski Jumping World Championships, and five at the Ski Flying World Championships.
The 2006–07 Four Hills Tournament was a series of ski jumping competitions held in the traditional venues of Oberstdorf, Garmisch-Partenkirchen, Innsbruck and Bischofshofen, located in Germany and Austria. The tournament was part of the 2006–07 Ski Jumping World Cup and points scored in each of the four competitions also counted towards the World Cup rankings. Before the tournament started on 28 December 2006 the World Cup leader was Simon Ammann.
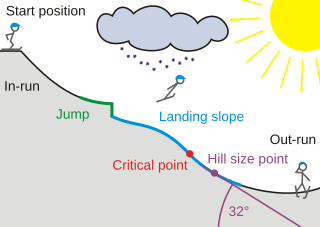
A ski jumping hill is a sports venue used for ski jumping. They vary in size from temporary handmade snow structures to permanent competition venues. At the top is an in-run where the jumper runs down to generate sufficient speed, before reaching the jump. The skier is then airborne until landing on the landing slope. The last part of the hill is the out-run, which may be either flat or even uphill, allowing the jumper to stop. The steepest point of the hill is the construction point, which is used to determine the score of a particular length. The size of a hill is measured in the hill size. Hills with a hill size exceeding HS185 are designated ski flying hills; there are five such hills in the world.
This is a general glossary of the terms used in the sport of gymnastics.

Aerial skiing or aerials is a freestyle skiing discipline where athletes ski down a slope to launch themselves off a kicker and perform multiple twists and flips before landing on an inclined landing hill. Aerialists are scored on their jumps based on air, form and landing with their score multiplied by the degree of difficulty of the jump they performed.

Vladimir Zografski, born 14 July 1993 in Samokov, Bulgaria, is a Bulgarian ski jumper. He took 14th place at the normal hill individual event at the 2018 Winter Olympics, which was the best result for a Bulgarian ski jumper in Olympic history, beating Vladimir Breitchev's 19th place at the 1984 Winter Olympics. Zografski is the son of former Olympic ski jumper Emil Zografski.
The men's normal hill individual ski jumping competition for the 2010 Winter Olympics in Vancouver, Canada was held on 12 and 13 February 2010 at Whistler Olympic Park in Whistler, British Columbia. It was the first medal event of the 2010 Games.

Julian Schmid is a German nordic combined skier.















